In today’s high-speed networking environment, selecting the right QSFP module is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. From data centers and cloud infrastructure to AI training clusters and telecom networks, QSFP transceivers have become the backbone of modern fiber-optic connectivity. Whether you are considering 40G QSFP+, 100G QSFP28, or the latest 400G QSFP-DD modules, understanding the technical specifications, compatibility requirements, and deployment scenarios is essential to make informed decisions.
LINK-PP QSFP modules offer a wide range of options that are MSA-compliant and tested for interoperability with leading switch and router brands such as Cisco, Juniper, Huawei, and Arista.
By reading this guide, you will learn how to:
-
Distinguish between QSFP+, QSFP28, QSFP56, and QSFP-DD modules and understand their respective speeds and use cases.
-
Match modules to your network speed, protocol, and fiber type for maximum efficiency.
-
Evaluate key factors such as transmission distance, connector types, vendor compatibility, and power consumption.
-
Compare OEM vs third-party QSFP modules and make cost-effective purchasing decisions.
-
Identify suitable LINK-PP QSFP products for your specific application scenarios.
-
Quickly answer common questions about QSFP modules through our FAQ section, improving your technical decision-making confidence.
This article will provide a complete, practical guide to help network engineers, IT managers, and procurement teams confidently choose the right QSFP module for their high-performance network deployments.
For readers seeking deeper insights into high-speed transceiver deployment strategies, you can also explore our related guides on fiber optic module selection and network infrastructure optimization.
1. What Is a QSFP Module and How Does It Work?
A QSFP module (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable) is a high-density, hot-pluggable optical transceiver designed to support high-speed data transmission in modern Ethernet and fiber-optic networks. Compared with earlier form factors, QSFP transceivers integrate multiple high-speed lanes into a compact module, enabling higher bandwidth while saving switch port space.
Today, QSFP optical modules are widely deployed in 40G, 100G, 200G, and 400G Ethernet networks, making them a critical component in data centers, cloud infrastructure, telecom systems, and AI computing clusters.
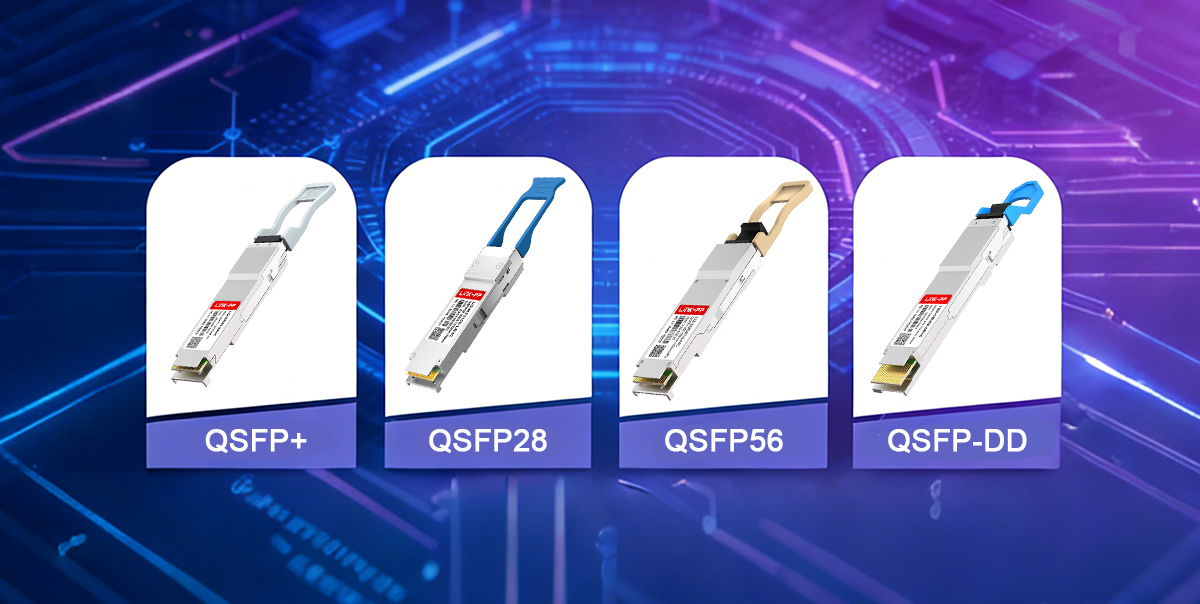

1.1 QSFP Family Overview — QSFP, QSFP+, QSFP28, QSFP-DD
The term QSFP refers to an entire transceiver family rather than a single product type. Each generation is designed to support higher data rates while maintaining backward compatibility where possible.
| QSFP Type |
Typical Speed |
Electrical Lanes |
Modulation |
Common Use Cases |
| QSFP |
Up to 40G |
4 × 10G |
NRZ |
Legacy 40G Ethernet |
| QSFP+ |
40G |
4 × 10G |
NRZ |
Data center aggregation |
| QSFP28 |
100G |
4 × 25G |
NRZ |
100G Ethernet uplinks |
| QSFP56 |
200G |
4 × 50G |
PAM4 |
AI / HPC networks |
| QSFP-DD |
400G |
8 × 50G |
PAM4 |
Hyperscale & DCI |
1.2 How Does a QSFP Transceiver Work?
A QSFP transceiver module converts electrical signals from network equipment (such as switches or routers) into optical signals for transmission over fiber, and vice versa. This process enables high-speed, long-distance data communication with minimal signal loss.
1.2.1 Multi-Lane Architecture
One of the defining features of QSFP modules is their multi-lane design:
-
QSFP+ / QSFP28 use 4 parallel lanes
-
QSFP-DD doubles this to 8 lanes, significantly increasing bandwidth
-
Each lane operates independently, allowing parallel data transmission
This architecture allows a single QSFP module to deliver much higher throughput than traditional SFP-based solutions.
1.3 High-Speed Optical-Electrical Signal Conversion
Inside a QSFP optical module, several key components work together:
-
Laser diodes generate optical signals
-
Photodiodes receive incoming light signals
-
DSP (Digital Signal Processor) manages signal encoding, decoding, and error correction
-
Driver and TIA circuits handle signal amplification
For newer generations such as QSFP56 and QSFP-DD, PAM4 modulation is used instead of NRZ, effectively doubling the data rate per lane without increasing the baud rate.
1.4 Supported Data Rates and Ethernet Standards
QSFP modules support a wide range of Ethernet standards, making them flexible for different network architectures.
| Data Rate |
Typical Module |
Ethernet Standard |
| 40G |
QSFP+ |
40GBASE-SR4 / LR4 |
| 100G |
QSFP28 |
100GBASE-SR4 / LR4 |
| 200G |
QSFP56 |
200GBASE-SR4 / FR4 |
| 400G |
QSFP-DD |
400GBASE-SR8 / DR4 / FR4 / LR4 |
These standards define not only speed, but also transmission distance, fiber type, and connector interface, which are critical factors discussed later in this guide.
1.5 Why QSFP Modules Are Preferred in High-Speed Networks
QSFP modules have become the industry standard for high-bandwidth applications because they offer:
-
High port density on switches and routers
-
Scalable upgrade paths from 40G to 400G
-
Support for breakout configurations (e.g., 100G to 4 × 25G)
-
Lower cost per bit compared with legacy solutions
As a result, QSFP transceivers are widely used in data centers, cloud computing platforms, telecom networks, and AI training clusters.
1.6 Built-in Monitoring — DDM / DOM Functionality
Most modern QSFP modules support DDM (Digital Diagnostic Monitoring) or DOM, allowing real-time monitoring of:
This functionality helps network operators proactively identify issues, optimize performance, and ensure long-term reliability.
2. Types of QSFP Transceivers: 40G, 100G, QSFP-DD & Beyond
QSFP transceivers are available in multiple generations and optical variants, each designed to support different data rates, transmission distances, and network architectures. Understanding the differences between 40G QSFP+, 100G QSFP28, QSFP56, and QSFP-DD modules is essential for selecting the right solution for your network upgrade or deployment.

2.1 QSFP+ Transceiver (40G QSFP+)
The QSFP+ transceiver is the first widely adopted member of the QSFP family and is designed specifically for 40G Ethernet networks.
2.1.1 Key characteristics of 40G QSFP+ modules:
-
Data rate: 40 Gbps (4 × 10G lanes)
-
Modulation: NRZ
-
Common standards: 40GBASE-SR4, 40GBASE-LR4
-
Typical applications: Data center aggregation, legacy core networks
| 40G QSFP+ Type |
Fiber Type |
Connector |
Typical Distance |
| QSFP 40G SR4 |
Multi-mode (OM3/OM4) |
MPO |
100 m (OM3) / 150 m (OM4) |
| QSFP 40G LR4 |
Single-mode (OS2) |
LC |
Up to 10 km |
Despite being gradually replaced by 100G solutions, 40G QSFP+ transceivers are still widely used in existing infrastructures where cost efficiency and backward compatibility are priorities.
2.2 100G QSFP28 Modules
QSFP28 modules represent the most popular choice for modern 100G Ethernet deployments, offering higher bandwidth while maintaining the same physical form factor as QSFP+.
2.2.1 Key characteristics of 100G QSFP28 modules:
-
Data rate: 100 Gbps (4 × 25G lanes)
-
Modulation: NRZ
-
Higher port density compared to 40G solutions
-
Lower cost per bit, making them ideal for large-scale data centers
| 100G QSFP28 Type |
Fiber Type |
Connector |
Typical Distance |
| 100GBASE SR4 |
Multi-mode (OM3/OM4) |
MPO |
70 m (OM3) / 100 m (OM4) |
| 100GBASE LR4 |
Single-mode (OS2) |
LC |
Up to 10 km |
| 100GBASE ER4 |
Single-mode (OS2) |
LC |
Up to 40 km |
| 100GBASE ZR4 |
Single-mode (OS2) |
LC |
80 km or more |
100G QSFP28 transceivers are widely deployed for data center interconnects (DCI), spine-leaf architectures, and high-speed uplinks, making them one of the highest-search-volume QSFP products on the market.
2.3 QSFP56 and 200G QSFP56 Modules
As bandwidth demands continue to rise, QSFP56 modules were introduced to support 200G Ethernet while keeping a compact footprint.
2.3.1 Key characteristics of QSFP56 modules:
-
Data rate: 200 Gbps (4 × 50G lanes)
-
Modulation: PAM4
-
Optimized for AI, HPC, and cloud computing
-
Lower latency and higher throughput than QSFP28
| QSFP56 Type |
Fiber Type |
Connector |
Typical Distance |
| SR4 |
Multi-mode (OM4) |
MPO |
Up to 100 m |
| FR4 / DR4 |
Single-mode (OS2) |
LC / MPO |
2 km – 10 km |
QSFP56 transceivers are commonly used in AI training clusters and high-performance computing (HPC) environments, where high bandwidth and efficient power usage are critical.
2.4 QSFP-DD and 400G QSFP-DD Modules
QSFP-DD (Double Density) is the latest evolution of the QSFP form factor, designed to meet the requirements of 400G Ethernet and beyond.
2.4.1 Key characteristics of QSFP-DD modules:
-
Data rate: 400 Gbps (8 × 50G lanes)
-
Modulation: PAM4
-
Double-density electrical interface
-
Backward compatibility with QSFP+/QSFP28 ports (host-dependent)
| 400G QSFP-DD Type |
Fiber Type |
Connector |
Typical Distance |
| 40G SR8 |
Multi-mode (OM4) |
MPO-16 |
Up to 100 m |
| 400G DR4 |
Single-mode (OS2) |
MPO-12 |
Up to 500 m |
| 400G FR4 |
Single-mode (OS2) |
LC |
Up to 2 km |
| 400G LR4 |
Single-mode (OS2) |
LC |
Up to 10 km |
400G QSFP-DD transceivers are now widely adopted in hyperscale data centers, cloud service providers, and DCI environments, serving as the foundation for next-generation network architectures.
2.5 SR4, LR4, ER4, ZR4 — Optical Types and Transmission Distances
QSFP modules are further classified by their optical reach, which determines the appropriate deployment scenario.
2.5.1 Short-Reach (SR4) QSFP Modules
-
Designed for short-distance transmission
-
Typically use multi-mode fiber (OM3/OM4)
-
Cost-effective for intra-data-center connections
2.5.2 Long-Reach (LR4) QSFP Modules
-
Designed for longer distances up to 10 km
-
Use single-mode fiber (OS2)
-
Common for campus and metro networks
2.5.3 Extended & Ultra-Long Reach (ER4 / ZR4)
| Optical Type |
Typical Distance |
Fiber Type |
Common Use Case |
| SR4 |
≤100 m |
OM3 / OM4 |
Intra-DC |
| LR4 |
≤10 km |
OS2 |
Campus / Metro |
| ER4 |
≤40 km |
OS2 |
DCI |
| ZR4 |
≥80 km |
OS2 |
Long-haul |
3. Key Factors When Choosing a QSFP Module
Choosing the right QSFP module involves more than matching port speed. Network engineers and procurement teams must consider protocol compatibility, transmission distance, fiber type, connector interface, vendor interoperability, and power consumption to ensure long-term reliability and scalability.

3.1 Speed and Protocol Compatibility
Before selecting a QSFP transceiver, confirm that the module matches the port speed and Ethernet protocol supported by your switch or router.
3.1.1 Key considerations include:
-
Supported port speed (40G / 100G / 200G / 400G)
-
Required Ethernet standard
-
Support for breakout or backward compatibility
Best practice: Always check the switch vendor’s compatibility matrix to confirm supported protocols and firmware requirements.
3.2 Transmission Distance and Fiber Type
Transmission distance directly determines both the optical type and the fiber cabling required for a QSFP module.
3.2.1 Multi-Mode Fiber (OM3 / OM4)
Multi-mode fiber is designed for short-reach connections within data centers.
| Fiber Type |
Typical Distance |
Application |
| OM3 |
70–100 m |
Intra-rack / row |
| OM4 |
100–150 m |
Intra-DC |
3.2.2 Single-Mode Fiber (OS1 / OS2)
Single-mode fiber supports long-distance transmission and is required for LR4, ER4, and ZR4 modules.
| Optical Type |
Distance |
Fiber |
| LR4 |
≤10 km |
OS2 |
| ER4 |
≤40 km |
OS2 |
| ZR4 |
≥80 km |
OS2 |
Single-mode QSFP modules are commonly used in campus networks, metro networks, and data center interconnects (DCI).
3.3 Connector and Interface Types
QSFP modules use different connector interfaces depending on optical type and lane architecture.
3.3.1 LC Duplex Connector
-
Used in LR4 / ER4 / ZR4 QSFP modules
-
Supports duplex single-mode fiber
-
Common in long-reach applications
3.3.2 MPO / MTP Connector
-
Used in SR4, DR4, SR8 modules
-
Supports parallel fiber transmission
-
Required for high-density data center deployments
| Connector |
Typical Module |
Fiber |
| LC |
LR4 / ER4 / ZR4 |
Single-mode |
| MPO-12 |
SR4 / DR4 |
MMF / SMF |
| MPO-16 |
SR8 (400G) |
MMF |
3.3.3 Breakout Cable Support
Many QSFP modules support breakout configurations to improve port utilization:
Breakout compatibility must be supported by both the module and host device.
3.4 Vendor Compatibility (OEM vs MSA-Compliant QSFP Modules)
Vendor compatibility is a major concern during QSFP procurement.
3.4.1 OEM QSFP Modules
3.4.2 MSA-Compliant / Third-Party QSFP Modules
-
Fully compliant with industry MSA standards
-
Tested across multi-vendor platforms
-
Lower cost and shorter lead time
| Factor |
OEM |
MSA-Compliant |
| Cost |
High |
Lower |
| Flexibility |
Limited |
High |
| Compatibility |
Vendor-locked |
Multi-vendor |
LINK-PP QSFP modules are MSA-compliant and validated for compatibility with leading network equipment.
3.5 Power Consumption and Cooling Considerations
As QSFP speeds increase, power consumption and thermal design become critical.
| QSFP Type |
Typical Power |
| 40G QSFP+ |
~3.5 W |
| 100G QSFP28 |
~4.5 W |
| 200G QSFP56 |
6–8 W |
| 400G QSFP-DD |
10–14 W |
Higher-power QSFP-DD modules require:
3.6 Selection Checklist
When choosing a QSFP module, always confirm:
-
✔ Speed and Ethernet protocol
-
✔ Transmission distance and fiber type
-
✔ Connector and breakout requirements
-
✔ Vendor compatibility (OEM vs MSA)
-
✔ Power consumption and cooling capacity
4. QSFP Module Comparison & Buying Guide
Choosing the right QSFP module requires balancing performance, compatibility, and cost.
This section provides a structured comparison of OEM vs third-party QSFP modules, evaluates 40G, 100G, and QSFP-DD generations, and highlights pricing strategies for enterprise and data center buyers.

4.1 How to Compare QSFP Modules: Brands, Price & Compatibility
When comparing QSFP transceivers, decision-makers should avoid focusing solely on speed.
A complete evaluation must include brand strategy, interoperability, lifecycle cost, and upgrade flexibility.
4.1.1 OEM vs Third-Party QSFP Modules
OEM QSFP modules are typically branded by switch vendors such as Cisco, Juniper, or Huawei, while third-party QSFP modules are MSA-compliant optics supplied by independent manufacturers.
| Aspect |
OEM QSFP Modules |
Third-Party QSFP Modules |
| Price |
High |
30–70% lower |
| Compatibility |
Vendor-locked |
Multi-vendor |
| MSA Compliance |
Yes |
Yes |
| Lead Time |
Often long |
Shorter |
| Flexibility |
Limited |
High |
Buying insight:
For large-scale deployments, MSA-compliant third-party QSFP transceivers offer significant cost advantages without sacrificing performance—provided compatibility testing is ensured.
4.1.2 100G QSFP28 vs. 40G QSFP+ Performance Comparison
Although 40G QSFP+ modules remain in use, 100G QSFP28 has become the industry standard for modern networks.
| Feature |
40G QSFP+ |
100G QSFP28 |
| Bandwidth |
40 Gbps |
100 Gbps |
| Lane Speed |
4 × 10G |
4 × 25G |
| Power Efficiency |
Lower |
Higher |
| Port Density |
Limited |
Optimized |
| Long-term Scalability |
Low |
High |
Recommendation:
4.1.3 QSFP-DD / QSFP56 vs Older QSFP Modules
Next-generation QSFP modules introduce higher speeds through increased lane counts and higher modulation rates.
| QSFP Type |
Max Speed |
Lane Architecture |
Typical Power |
| QSFP+ |
40G |
4 × 10G |
~3.5 W |
| QSFP28 |
100G |
4 × 25G |
~4.5 W |
| QSFP56 |
200G |
4 × 50G |
~7 W |
| QSFP-DD |
400G |
8 × 50G |
10–14 W |
Key insight:
QSFP-DD modules are not direct replacements for QSFP28—they require new switch platforms and enhanced cooling, but they offer unmatched scalability for AI and hyperscale networks.
4.2 Pricing Considerations and Bulk Purchasing Strategy
4.2.1 Cost per Gbps: A Better Pricing Metric
Instead of evaluating unit price alone, enterprises should calculate cost per Gbps:
-
40G QSFP+: higher cost per bandwidth unit
-
QSFP28 100G: optimal cost-performance balance
-
QSFP-DD: higher upfront cost, lower long-term TCO
4.2.2 Bulk Purchasing for Data Centers and Integrators
Bulk purchasing QSFP modules can significantly reduce procurement costs.
Best practices include:
-
Requesting multi-vendor compatibility reports
-
Locking in long-term pricing contracts
-
Ensuring consistent BOM and firmware stability
For system integrators and hyperscale deployments, this approach minimizes downtime risk and operational expense.
4.2.3 Choosing a Reliable QSFP Supplier
When selecting a QSFP transceiver supplier, evaluate:
-
MSA compliance and testing coverage
-
Support for Cisco, Juniper, Huawei compatibility
-
Stable manufacturing and supply chain
-
Clear warranty and RMA policy
Reputable suppliers like LINK-PP provide fully tested QSFP+, QSFP28, QSFP56, and QSFP-DD modules designed for enterprise and data center environments.
5. QSFP Module Applications
QSFP modules are widely deployed across modern network architectures due to their high bandwidth density, scalability, and multi-vendor compatibility. From traditional data centers to AI-driven infrastructures, different QSFP transceivers serve distinct application requirements based on speed, distance, and network topology.
This section outlines the most common QSFP module application scenarios and explains which QSFP types are best suited for each environment.

5.1 Data Center Interconnects (DCI)
Data Center Interconnects require high-speed, low-latency, and long-distance optical links to connect geographically distributed facilities.
Key requirements:
-
High bandwidth (100G / 400G)
-
Low signal loss over long distances
-
High reliability and redundancy
Recommended QSFP modules:
| Application |
Typical Distance |
Recommended Module |
| Campus DCI |
2–10 km |
100G QSFP28 LR4 |
| Metro DCI |
10–40 km |
100G QSFP28 ER4 |
| Long-haul DCI |
40 km+ |
400G QSFP-DD LR4 |
5.2 Cloud & High-Performance Computing (HPC)
Cloud computing platforms and HPC clusters demand ultra-high throughput, low latency, and dense port configurations.
Typical characteristics:
-
East–west traffic dominates
-
Short-reach, high-density fiber links
-
High port utilization on leaf–spine architectures
Recommended QSFP transceivers:
| Environment |
Architecture |
Preferred QSFP Type |
| Cloud DC |
Leaf–Spine |
100G QSFP28 SR4 |
| HPC Cluster |
Fat Tree |
200G QSFP56 |
| Hyperscale Cloud |
Spine Core |
400G QSFP-DD |
Why QSFP excels here:
QSFP modules support parallel optics via MPO connectors, enabling efficient scaling without increasing fiber complexity.
5.3 Telecommunication & Metro Networks
Telecom and metro networks prioritize stability, standard compliance, and long-term availability.
Network characteristics:
-
Carrier-grade reliability
-
Strict power and temperature requirements
-
Compatibility with multiple generations of equipment
Common QSFP deployments:
| Use Case |
Distance |
QSFP Module Type |
| Aggregation |
<10 km |
100G QSFP28 LR4 |
| Metro Core |
10–40 km |
100G QSFP28 ER4 |
| Network Upgrade |
Variable |
QSFP-DD |
Procurement insight:
Telecom operators increasingly adopt MSA-compliant third-party QSFP modules to reduce CAPEX while maintaining interoperability.
5.4 AI Training Clusters
AI and machine learning workloads generate massive east–west data flows, making network performance a critical bottleneck.
AI cluster requirements:
Preferred QSFP solutions:
| AI Infrastructure |
Network Speed |
QSFP Module |
| GPU Pods |
200G |
QSFP56 |
| Large AI Clusters |
400G |
QSFP-DD |
Key takeaway:
QSFP-DD has become the default optical interface for next-generation AI fabrics due to its 8-lane electrical design and future scalability.
5.5 Application-to-Module Selection Summary
| Application Scenario |
Recommended QSFP Type |
| Data Center Interconnect |
100G QSFP28 / 400G QSFP-DD |
| Cloud Computing |
100G QSFP28 |
| HPC Clusters |
200G QSFP56 |
| Telecom Networks |
100G QSFP28 |
| AI Training |
400G QSFP-DD |
6. LINK-PP QSFP Modules Recommendations
After comparing different QSFP modules and understanding their applications, network engineers and procurement teams often seek reliable, cost-effective, and compatible QSFP transceivers.
LINK-PP offers a broad range of QSFP modules suitable for data centers, AI clusters, cloud networks, and telecom infrastructures, all designed to meet MSA compliance standards and multi-vendor compatibility.

6.1 Recommended QSFP Modules by Speed and Application
| Module Model |
Speed |
Fiber Type |
Distance |
Key Features |
Ideal Application |
| LQ-SW40-SR4C |
40G |
Multi-mode OM4 |
≤100 m |
Low power, compact, high reliability |
Legacy DC, short-reach connections |
| LQ-SM3150-LRC |
50G |
Single-mode OS2 |
≤10km |
MSA compliant, low insertion loss |
Campus networks, mid-range DC links |
| LQ-LW100-L24C |
100G |
Single-mode OS2 |
≤10km (LR4) |
High density, low power, DDM/DOM supported |
Modern data centers, DCI |
| LQ-M85200-SR4C |
200G |
Multi-mode OM4 |
≤150m |
Parallel optics, high port density |
HPC clusters, cloud DC |
| LQD-CW400-LR4C |
400G |
Single-mode OS2 |
≤10km (LR4) |
8-lane design, advanced cooling, MSA compliant |
AI training clusters, hyperscale DC, DCI |
Tip: Each module comes with DOM/DDM monitoring, ensuring real-time diagnostics for temperature, voltage, and optical power, which is critical for large-scale deployments.
6.2 Feature Highlights of LINK-PP QSFP Modules
-
Multi-Vendor Compatibility
-
Fully tested with Cisco, Juniper, Huawei, Arista, and other major switch/router brands
-
Supports both OEM and MSA-compliant deployments
-
MSA Compliance & Reliability
-
Adheres to industry standards (QSFP+, QSFP28, QSFP56, QSFP-DD)
-
Provides consistent optical performance across multiple deployments
-
Flexible Transmission Distance
-
SR4 for short-reach intra-rack links
-
LR4 / ER4 for campus/metro networks
-
ZR4 and QSFP-DD for long-haul DCI and AI fabrics
-
Low Power & Efficient Cooling
-
Breakout & Upgrade Support
6.3 Recommended Module by Scenario
| Scenario |
Recommended LINK-PP Module |
| Legacy Data Center |
LQ-SW40-SR4C 40G QSFP+ |
| Campus / Metro |
LQ-SM3150-LRC 50G QSFP28, LQ-LW100-L24C 100G QSFP28 |
| High-Density HPC / Cloud |
LQ-M85200-SR4C 200G QSFP56 |
| AI Training / Hyperscale DC |
LQD-CW400-LR4C 400G QSFP-DD |
6.4 Buying Recommendations
-
For short-reach data center links, prioritize SR4 modules for cost efficiency.
-
For medium- to long-distance campus or metro deployments, select LR4 or ER4 modules.
-
For AI, HPC, and hyperscale environments, invest in QSFP-DD or QSFP56 modules to maximize bandwidth and future-proof your infrastructure.
-
Always check switch/vendor compatibility, firmware requirements, and DOM/DDM support.
7. FAQs about QSFP Modules
7.1 What is the difference between QSFP+, QSFP28, and QSFP-DD?
-
QSFP+: Supports 40G Ethernet (4 × 10G lanes), commonly used in legacy data centers.
-
QSFP28: Supports 100G Ethernet (4 × 25G lanes), offering higher bandwidth, better port density, and future scalability.
-
QSFP-DD: Supports 400G Ethernet (8 × 50G lanes) with double-density design, suitable for AI, HPC, and hyperscale deployments.
7.2 How far can a 100G QSFP28 LR4 transceiver transmit?
-
100G QSFP28 LR4 is designed for single-mode fiber (OS1/OS2) and supports transmission distances up to 10 km.
-
For longer distances, ER4 (up to 40 km) or ZR4 (80 km+) modules are recommended.
7.3 Can I use a third-party QSFP module on Cisco or Juniper switches?
Yes, as long as the module is MSA-compliant and tested for interoperability.
-
LINK-PP third-party modules are fully compatible with major OEMs like Cisco, Juniper, and Huawei.
-
Ensure firmware compatibility and check vendor validation reports to avoid errors or limited functionality.
7.4 What is the difference between SR4, LR4, and ER4 QSFP modules?
| Module Type |
Fiber Type |
Max Distance |
Use Case |
| SR4 |
Multi-mode (OM3/OM4) |
≤150 m |
Short-reach, intra-rack or intra-DC |
| LR4 |
Single-mode (OS1/OS2) |
≤10 km |
Campus links, medium-reach DCI |
| ER4 |
Single-mode (OS1/OS2) |
≤40 km |
Metro networks, extended-reach connections |
Tip: Choose based on distance, fiber availability, and network topology.
7.5 How to choose between multi-mode and single-mode QSFP modules?
-
Multi-mode (OM3/OM4): Best for short-distance, high-density deployments within data centers. Cost-effective and easier to terminate.
-
Single-mode (OS1/OS2): Needed for longer distances, campus, metro, and DCI networks. Offers better signal integrity over extended links.
Buying tip: Always match fiber type with module optics to avoid signal loss or compatibility issues.
7.6 Does QSFP-DD consume more power than QSFP28?
Yes, QSFP-DD modules have higher power consumption due to more lanes and higher data rates.
-
Typical power:
-
QSFP28 (100G) ~ 4.5 W
-
QSFP-DD (400G) 10–14 W
Design consideration: Ensure adequate cooling and thermal management in racks and switches for QSFP-DD deployments.
8. Conclusion
Choosing the right QSFP module is critical for network performance, cost-efficiency, and future scalability. Whether deploying 40G QSFP+, 100G QSFP28, 200G QSFP56, or 400G QSFP-DD, consider speed, fiber type, distance, compatibility, and power requirements.
LINK-PP QSFP modules offer:
-
Multi-vendor compatibility (Cisco, Juniper, Huawei)
-
MSA compliance and reliability
-
Full range: 40G, 50G, 100G, 200G, 400G
-
Flexible transmission distances and breakout options
Ready to upgrade your network?
👉 Explore LINK-PP QSFP modules here: LINK-PP QSFP Transceivers
Optimize your network with LINK-PP — reliable, cost-effective, and fully tested QSFP solutions for modern data centers and high-performance networks.