➡️ How Does QSFP-40G-SR-BD Work?
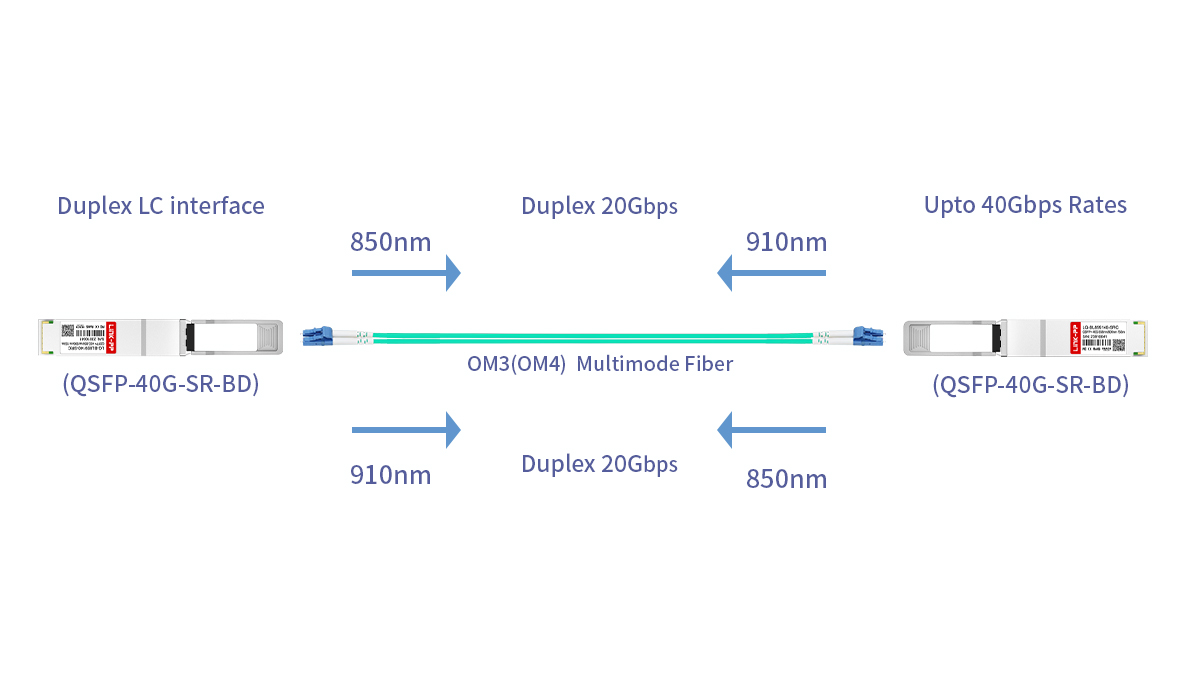
QSFP-40G-SR-BD achieves 40GbE full-duplex transmission over a single pair of multimode fibers by using bidirectional (BiDi) optical signaling, where two separate wavelengths carry transmit and receive data simultaneously. This allows it to deliver high-speed 40GbE links while reducing fiber usage and cabling complexity compared to parallel SR4 modules.
Bidirectional Transmission Principle
The module uses two distinct wavelengths (850nm and 910nm) on a single fiber pair:
-
Transmit (Tx): One wavelength (e.g., 850nm) sends data from the local module to the remote module
-
Receive (Rx): A second wavelength (e.g., 910nm) carries incoming data from the remote module in the opposite direction
-
Full-duplex operation: Both directions operate simultaneously on the same fiber, with no interference due to wavelength separation
Key Advantages:
-
Only one fiber pair needed instead of four
-
Compatible with LC duplex cabling
-
Maintains 40Gbps link speed without lane splitting
Optical Signal Architecture
| Component | Function | Technical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Transmitter (Tx) | Sends 20Gbps per wavelength | 850nm assigned for one direction |
| Receiver (Rx) | Receives 20Gbps per wavelength | 910nm assigned for opposite direction |
| Wavelength Multiplexer/Demultiplexer | Combines/separates 850nm & 910nm on the same fiber | Ensures signals do not interfere |
| Duplex LC Interface | Connects to multimode fiber | OM3/OM4 compatible |
| Multimode Fiber | Carries bidirectional signals | OM3 up to 100m, OM4 up to 150m |
Explanation: The transmitter converts the 40Gbps data stream into two 20Gbps optical signals, each assigned a specific wavelength. The MUX/DEMUX components ensure bidirectional signals coexist on the same fiber pair without interference, while the receiver converts the optical signals back into electrical 40Gbps data.
Deployment and Performance Considerations
When deploying QSFP-40G-SR-BD, the following factors are critical:
-
Module Pairing: Each link requires a matched pair of BiDi modules with complementary wavelengths
-
Fiber Type: OM3 for up to 100m, OM4 for up to 150m; fiber quality affects signal integrity
-
Insertion Loss: Proper LC connections are essential to maintain optical power budgets
-
Temperature and Environmental Limits: QSFP+ modules typically operate within 0–70°C ambient; exceeding limits may reduce performance
-
Compatibility Check: Not interchangeable with SR4 or LR4 modules on the same link
Summary: 40G SR BiDi works by splitting 40GbE into two bidirectional wavelength channels, transmitting over a single duplex fiber pair. Its architecture reduces fiber usage, simplifies cabling, and maintains full 40GbE throughput, making it ideal for short-reach, high-density data center interconnects.
➡️ Key Specifications of QSFP-40G-SR-BD
QSFP-40G-SR-BD’s specifications are optimized for short-reach 40GbE links over duplex multimode fiber, balancing high bandwidth with fiber efficiency and low deployment complexity. Understanding these parameters helps engineers choose the right module for data center upgrades, high-density racks, or constrained fiber environments.
Core Specifications
| Specification | Value | Technical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Data Rate | 40Gbps full-duplex | Supports 40GbE without lane splitting; ensures high-throughput interconnects |
| Form Factor | QSFP+ | Standard 40G interface for easy compatibility with most switches |
| Fiber Type | OM3 / OM4 multimode | OM3: up to 100m, OM4: up to 150m; OM4 has higher modal bandwidth |
| Connector Type | LC duplex | Compatible with existing duplex MMF cabling; avoids MPO adapters |
| Wavelength | BiDi dual-wavelength | Each fiber carries Tx and Rx in opposite directions, reducing fiber count by 75% |
| Maximum Distance | OM3: 100 m, OM4: 150 m | Short-reach design optimized for data center interconnects |
| Optical Power | Tx: -4.0 to 2 dBm, Rx sensitivity: ≤ -8.4 dBm | Maintains signal integrity within standard multimode fiber losses |
| Compliance | IEEE 802.3ba, QSFP+ MSA | Ensures interoperability and vendor neutrality |
Detailed Analysis of Key Parameters
-
Fiber Type and Maximum Distance
-
OM3 supports up to 100 meters; OM4 supports longer distances up to 150 meters due to higher effective modal bandwidth.
-
Designers must consider patch panels, splices, and connector loss when planning reach.
-
-
Wavelength and BiDi Operation
-
Each module uses a unique Tx/Rx wavelength pair, requiring proper pairing at each end of the link.
-
Wavelength separation avoids interference, allowing full-duplex operation on a single fiber pair.
-
-
Optical Power and Link Budget
-
Tx power and Rx sensitivity define the optical power budget, critical for ensuring reliable links in dense rack deployments.
-
Factors such as fiber attenuation (0.5 dB/km for OM3/OM4), connector loss (~0.3 dB per LC), and patch panel loss must be considered.
-
-
Form Factor and Connector Type
-
QSFP+ ensures hot-swappable installation in high-density switches.
-
LC duplex connectors preserve existing 10G duplex infrastructure, enabling cost-effective 10G → 40G upgrades.
-
-
Compliance and Interoperability
-
IEEE 802.3ba compliance guarantees compatibility with other 40GbE network equipment.
-
QSFP+ MSA standard ensures cross-vendor deployment with proper module pairing.
-
Comparison With Other 40G Modules
| Parameter | QSFP-40G-SR-BD | QSFP-40G-SR4 | QSFP-40G-LR4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Count | 2 fibers | 8 fibers | 2 single-mode fiber |
| Connector Type | LC duplex | MPO | LC duplex |
| Reach | 100–150m | 100–150m | 10km+ |
| Deployment Complexity | Low | Medium | Medium |
| Application | Short-reach, fiber-limited | New parallel-fiber installs | Long-reach interconnects |
Implications: Engineers choosing QSFP-40G-SR-BD gain reduced fiber usage, simplified cabling, and lower operational cost for short-reach links, while SR4 is suited for greenfield deployments with MPO infrastructure and LR4 for long-reach single-mode applications.
➡️ QSFP-40G-SR-BD vs QSFP-40G-SR4
The main difference between QSFP-40G-SR-BD and QSFP-40G-SR4 lies in fiber usage, connector type, and deployment complexity. QSFP-40G-SR-BD uses bidirectional signaling over two fibers, whereas QSFP-40G-SR4 uses parallel optics across four fiber pairs (eight fibers). Choosing the right module depends on existing cabling, fiber availability, and deployment goals.
Key Technical Differences
| Feature | QSFP-40G-SR-BD | QSFP-40G-SR4 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Requirement | 2 fibers (duplex) | 8 fibers (4 pairs) | BD reduces fiber usage by 75% |
| Connector Type | LC duplex | MPO/MTP | SR-BD works with existing LC cabling |
| Transmission Method | BiDi (dual wavelength) | Parallel (4×10Gbps lanes) | SR4 splits 40GbE into four separate lanes |
| Maximum Distance | OM3: 100 m, OM4: 150 m | OM3: 100 m, OM4: 150 m | Both short-reach; SR-BD limited by duplex fiber constraints |
| Deployment Complexity | Low | Medium | SR4 requires MPO patching and higher cable management |
| Upgrade Compatibility | Ideal for 10G duplex → 40G | Best for greenfield parallel-fiber installations | SR-BD preserves existing infrastructure |
Decision Points for Choosing Between SR-BD and SR4
-
Existing LC Cabling:
-
Use SR-BD to upgrade from 10G duplex links without re-cabling.
-
-
Fiber Availability:
-
SR-BD is preferred if fiber is limited or high-density racks make MPO management difficult.
-
-
Future Scalability:
-
SR4 may be better for networks planning to scale to higher lane counts (e.g., 100GbE with parallel optics).
-
-
Cost Considerations:
-
SR-BD reduces fiber and cabling costs; SR4 may require MPO trunks and adapters, increasing infrastructure investment.
-
Deployment and Compatibility Notes
-
Module Pairing: SR-BD requires matched BiDi modules at each end; using mismatched wavelengths will break the link.
-
Interoperability: SR-BD cannot directly replace SR4 transceivers on the same MPO trunk; separate LC duplex paths are needed.
-
Cabling Simplicity: In high-density racks, SR-BD reduces patch panel complexity, lowers insertion loss, and simplifies management.
Summary:
QSFP-40G-SR-BD is a fiber-saving, LC-compatible alternative to SR4, ideal for upgrading short-reach data center links where fiber resources are limited or existing LC duplex cabling exists. SR4 remains suitable for greenfield deployments or parallel-optic installations where fiber count is less constrained. Selecting between the two depends on existing infrastructure, fiber availability, upgrade goals, and cost considerations.
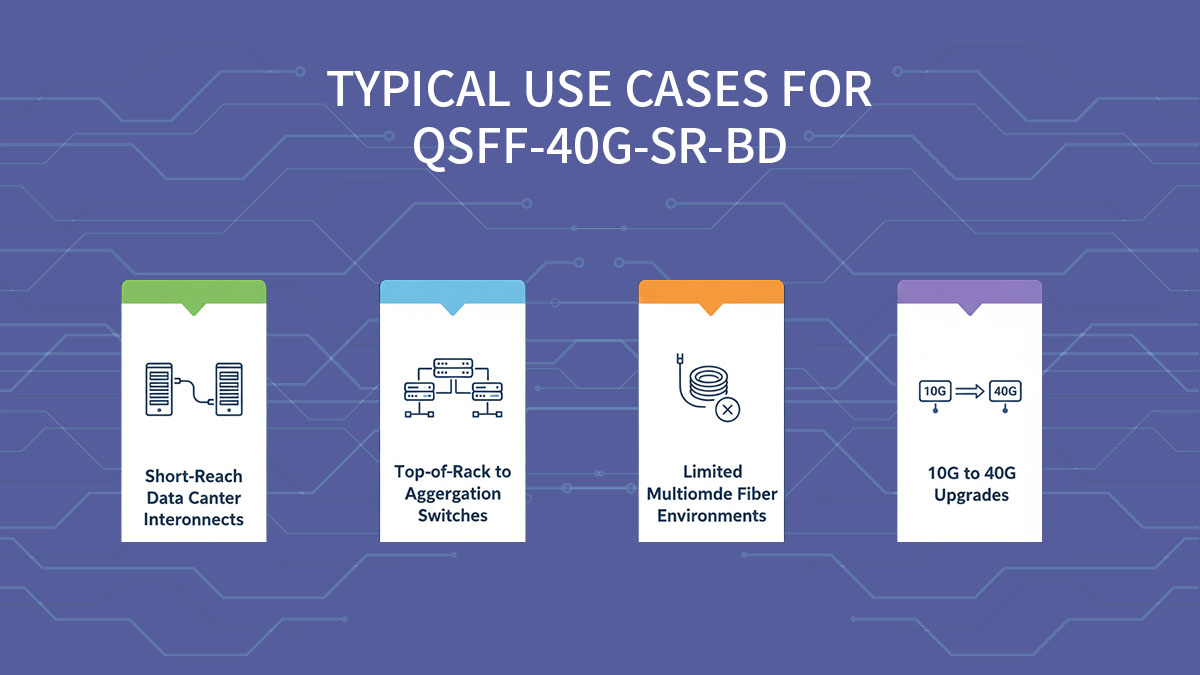
➡️ Typical Use Cases for QSFP-40G-SR-BD
QSFP-40G-SR-BD is ideal for short-reach, high-density network environments where fiber efficiency and simplified cabling are critical. Its bi-directional duplex design allows 40GbE connectivity without adding parallel fiber lanes, making it suitable for a variety of data center and enterprise network scenarios.
Key Use Cases
-
Top-of-Rack (ToR) to Aggregation Switch Links
-
Scenario: Short-reach connections between ToR switches and aggregation/distribution switches in a rack or row.
-
Why SR-BD: Reduces fiber count, allowing LC duplex cabling to connect multiple 40GbE ports without MPO trunks.
-
Deployment Tip: Ensure module pairs are matched and fiber paths are clean to maintain optical power budget.
-
-
Upgrading 10G Duplex Links to 40G
-
Scenario: Data centers with existing 10G duplex MMF infrastructure want to upgrade to 40GbE without recabling.
-
Why SR-BD: BiDi operation preserves the existing LC duplex fiber, avoiding costly MPO re-cabling.
-
Deployment Tip: Check that the existing fibers meet OM3/OM4 specifications to achieve full link distance.
-
-
Fiber-Constrained High-Density Environments
-
Scenario: Dense rack deployments where fiber availability is limited, or cable management space is restricted.
-
Why SR-BD: Uses only 2 fibers per link instead of 8, simplifying patch panel routing and reducing insertion loss.
-
Deployment Tip: Plan fiber paths to minimize bends and maintain multimode fiber bend radius guidelines.
-
-
Private Cloud or HPC Cluster Short-Reach Interconnects
-
Scenario: Short interconnects in compute clusters or private clouds where multiple 40GbE links are needed.
-
Why SR-BD: Supports multiple high-speed links over existing duplex fiber infrastructure, reducing material and labor costs.
-
Deployment Tip: Ensure consistent module pairing and wavelength alignment across all nodes for reliable cluster performance.
-
-
Temporary or Flexible Network Expansions
-
Scenario: Quick deployment of temporary racks or expansion pods in a data center.
-
Why SR-BD: Duplex LC cabling is easier to deploy and remove compared to MPO trunks, enabling rapid reconfiguration.
-
Deployment Tip: Label fibers and modules carefully to prevent wavelength mismatches during reconfiguration.
-
Summary:
QSFP-40G-SR-BD is best suited for short-reach, fiber-limited, high-density environments, and it excels in 10G-to-40G upgrades, ToR-to-aggregation connections, HPC clusters, and temporary deployments. Its duplex BiDi design simplifies cabling, reduces fiber usage, and enables cost-effective scaling of high-speed networks.
➡️ Compatibility and Interoperability Considerations
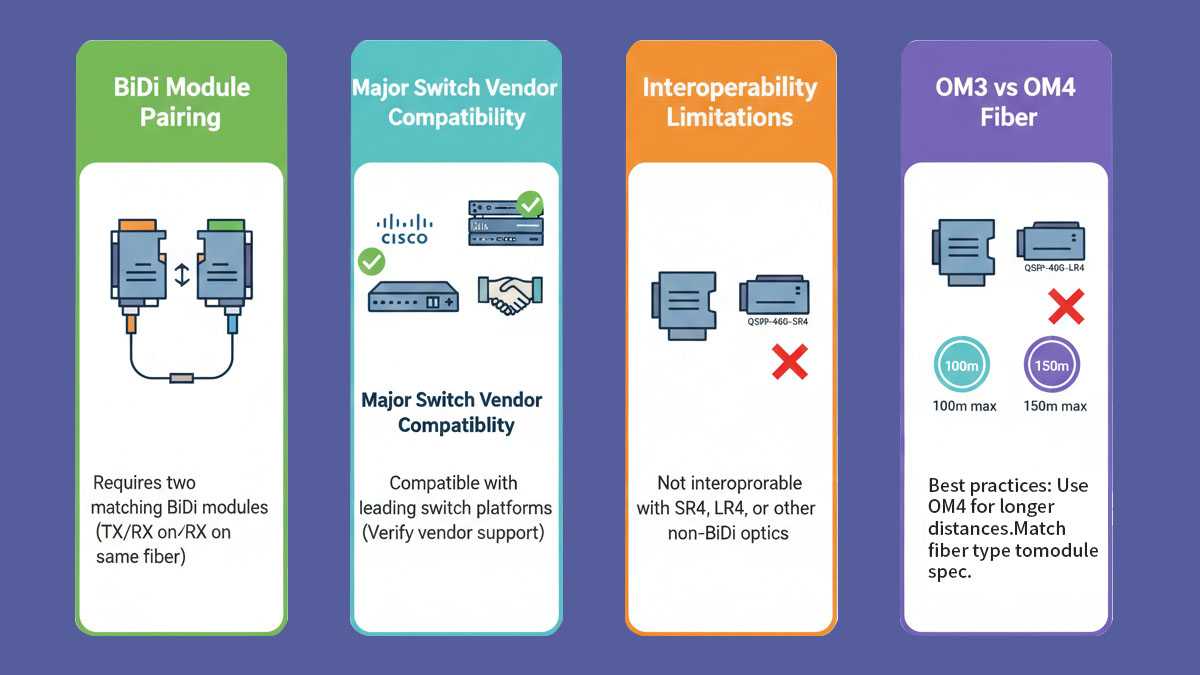
QSFP-40G-SR-BD requires careful attention to compatibility and interoperability because it relies on bidirectional signaling and specific wavelength pairing. Ensuring proper module pairing, fiber type, and switch support is critical for reliable 40GbE links.
Key Compatibility Factors
| Factor | Requirement / Recommendation | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Module Pairing | Use complementary BiDi module at each link end | Mismatched wavelengths will prevent communication |
| Fiber Type | OM3 or OM4 multimode fiber | OM4 allows slightly longer reach (up to 150m) |
| Connector Type | LC duplex | Must match existing LC duplex cabling; MPO is incompatible |
| Switch / Transceiver Support | IEEE 802.3ba 40GbE & QSFP+ MSA compliant | Some vendors require explicit support for BiDi modules |
| Distance / Optical Budget | Ensure fiber length and insertion loss ≤ optical power budget | Factor in patch panels, splices, and connectors |
Deployment Guidelines and Best Practices
-
Check Module Pairing: Always install the correct Tx/Rx wavelength pair at each end. Misalignment will cause link failure.
-
Verify Switch Compatibility: Some switches may require BiDi-aware firmware or module validation; check vendor documentation.
-
Maintain Optical Power Budget: Consider fiber loss, connector loss, and patch panel insertion loss when calculating total link budget.
-
Avoid Mixing Modules: Do not mix SR-BD with SR4 or LR4 transceiver on the same link or fiber trunk; this will break connectivity.
-
Labeling and Documentation: In high-density deployments, clearly label each module and fiber pair to prevent wavelength mismatches during maintenance or upgrades.
Practical Considerations
-
Interoperability Across Vendors:
-
QSFP-40G-SR-BD follows IEEE 802.3ba and QSFP+ MSA standards, allowing most compliant switches to work, but BiDi operation must be verified.
-
-
Patch Panel Planning:
-
Duplex LC connections reduce fiber congestion compared to MPO cabling, but careful routing and bend radius compliance are essential to maintain signal integrity.
-
-
Upgrade Scenarios:
-
When replacing 10G duplex links with SR-BD, ensure existing fibers meet OM3/OM4 specifications and that LC connections are properly aligned.
-
Summary:
QSFP-40G-SR-BD provides high-density, fiber-efficient 40GbE links, but successful deployment requires correct module pairing, LC duplex fiber usage, switch support, and careful optical power management. Following these compatibility guidelines ensures reliable, high-speed interconnects in short-reach data center environments.
➡️ Advantages and Limitations of QSFP-40G-SR-BD
QSFP-40G-SR-BD is a short-reach, fiber-efficient 40GbE transceiver that simplifies high-density deployments but comes with reach and compatibility constraints. Understanding its strengths and limitations is critical for data center planning, network upgrades, and fiber infrastructure optimization.
Advantages
| Advantage | Explanation | Deployment Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Fiber Usage | Uses only 2 fibers instead of 8 (SR4) | Ideal for fiber-limited environments or high-density racks |
| Duplex LC Compatibility | Works with existing LC duplex MMF cabling | Supports 10G → 40G upgrades without new MPO cabling |
| Simplified Cabling | Less complex patching compared to SR4 | Reduces insertion loss and lowers management overhead |
| Full 40GbE Performance | BiDi operation maintains full 40Gbps throughput | Suitable for ToR → aggregation, HPC clusters, or short-reach interconnects |
| Lower Deployment Cost | Less fiber and fewer patch panels required | Reduces material and labor expenses in upgrades or expansions |
Limitations
-
Short Reach: Limited to 100m on OM3 and 150m on OM4; not suitable for long-haul or inter-building links.
-
Module Pairing Required: Must be paired with complementary BiDi module; mispairing results in link failure.
-
Incompatibility with SR4/LR4 on Same Link: Cannot directly replace or coexist with parallel-optic modules on the same fiber trunk.
-
Fiber Quality Dependency: Signal integrity is sensitive to multimode fiber quality, connector cleanliness, and bend radius compliance.
-
Vendor-Specific Support: Some switches require explicit BiDi support or firmware validation, limiting plug-and-play flexibility in mixed-vendor environments.
Practical Deployment Implications
-
High-Density Data Centers: Advantages outweigh limitations in racks with limited fiber availability.
-
Short-Reach Upgrades: Ideal for preserving existing LC duplex cabling when upgrading 10G links to 40G.
-
Planning Considerations: Must carefully plan module pairing, optical power budget, and fiber paths to avoid performance degradation.
-
Cost-Benefit: Savings from reduced fiber count and simplified cabling often justify choosing SR-BD over SR4 in constrained environments.
Summary:
QSFP-40G-SR-BD combines fiber efficiency, duplex LC compatibility, and full 40GbE performance, making it suitable for short-reach, high-density network deployments. Its limitations—reach, module pairing, and vendor support requirements—must be considered during planning to ensure reliable performance and successful upgrades.
➡️ FAQs About QSFP-40G-SR-BD
1. What is the maximum distance of QSFP-40G-SR-BD?
Answer: Up to 100 meters on OM3 multimode fiber and 150 meters on OM4.
-
Explanation: The distance depends on fiber type, optical power budget, connector quality, and patch panel insertion loss. OM4 fiber allows longer reach due to higher modal bandwidth.
2. Can QSFP-40G-SR-BD work with QSFP-40G-SR4 modules?
Answer: No. SR-BD cannot directly interoperate with SR4 modules.
-
Explanation: SR-BD uses bidirectional signaling on two fibers, while SR4 uses parallel optics across eight fibers. Mixing them on the same link will result in link failure.
3. What type of cabling is required?
Answer: LC duplex multimode fiber (OM3 or OM4).
-
Deployment Tip: Ensure fibers are clean, maintain proper bend radius, and verify length to meet optical power budget.
4. Do both ends require BiDi modules?
Answer: Yes. A matched pair of BiDi modules is required for proper wavelength alignment.
-
Technical Note: Each module has a fixed transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) wavelength; mismatched modules will prevent communication.
5. Can QSFP-40G-SR-BD replace SR4 in existing infrastructure?
Answer: Only if LC duplex cabling exists.
-
Consideration: SR-BD is ideal for upgrading 10G duplex links to 40G. It cannot replace SR4 on MPO trunk installations without re-cabling.
6. Which switches support QSFP-40G-SR-BD?
Answer: Most IEEE 802.3ba 40GbE and QSFP+ MSA compliant switches support SR-BD, but verify vendor documentation for BiDi compatibility.
-
Tip: Some switches require explicit firmware support for BiDi modules to ensure proper recognition and link negotiation.
7. What are the advantages of using SR-BD over SR4?
Answer: Fewer fibers (2 vs 8), LC duplex compatibility, simplified cabling, and cost-efficient upgrades in high-density racks.
-
Deployment Insight: Particularly suitable for 10G → 40G upgrades and fiber-limited environments.
8. Are there any limitations to be aware of?
Answer: Yes. Limited reach, mandatory module pairing, dependency on fiber quality, and potential vendor-specific support requirements.
➡️ Conclusion
QSFP-40G-SR-BD is a short-reach, fiber-efficient 40GbE transceiver that combines high performance with simplified deployment. By using bidirectional signaling over only two LC duplex fibers, it reduces cabling complexity by 75% compared to traditional QSFP-40G-SR4 modules while maintaining full 40GbE throughput.
This module is particularly suited for:
-
Upgrading 10G duplex links to 40G without recabling
-
High-density rack deployments where fiber resources are limited
-
Short-distance interconnects such as ToR to aggregation switch links or HPC cluster nodes
Key benefits include: fiber efficiency, LC duplex compatibility, simplified patching, and lower deployment costs. Limitations such as short reach, mandatory module pairing, and switch compatibility requirements can be effectively managed through proper planning and adherence to optical power budgets.
For data centers and enterprise networks seeking reliable, high-speed 40GbE links with minimal fiber overhead, QSFP-40G-SR-BD offers a practical, cost-effective solution.
Explore QSFP-40G-SR-BD solutions at the LINK-PP Official Store to upgrade your network with fiber-efficient 40GbE transceivers that support high-density deployments and easy integration.