A QSFP+ LC transceiver is a 40Gbps optical module that uses LC duplex connectors and is primarily designed for single-mode fiber transmission. It is most commonly deployed in 40G networks that require longer reach, simpler fiber management, or direct compatibility with LC-based infrastructure, making it a practical alternative to MPO/MTP-based QSFP+ module.
In real-world deployments, QSFP+ LC transceivers are typically selected for 2km, 10km, 40km, and even ultra-long 80km links, depending on the optical standard used (FR4, LR4, ER4, or ZR4). These modules are widely used in data center interconnection (DCI), enterprise core networks, campus backbones, and metro or telecom environments, where link distance, fiber availability, and operational simplicity are key decision factors.
Compared with QSFP+ transceivers using MPO connectors, QSFP+ LC transceivers require fewer fiber strands, avoid polarity and breakout complexity, and integrate seamlessly with existing LC patch panels and single-mode cabling. For many network engineers and procurement teams, this translates into lower deployment risk, easier maintenance, and more predictable scalability.
This guide focuses on the practical buying and selection considerations for QSFP+ LC transceivers. It explains the different module types, supported distances, compatibility considerations, and real deployment scenarios, helping you determine which QSFP+ LC transceiver is the right choice for your 40G network.
🔰 What Is a QSFP+ LC Transceiver?
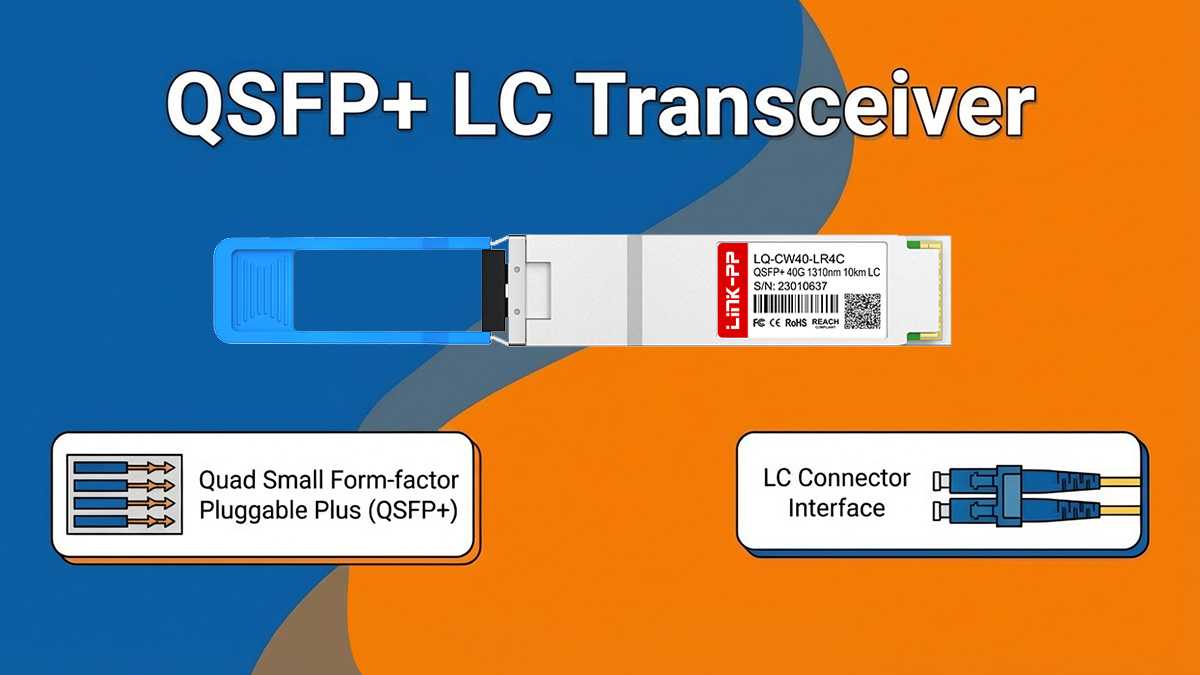
A QSFP+ LC transceiver is a 40Gbps optical transceiver module that combines the QSFP+ form factor with a duplex LC optical interface, specifically designed for single-mode fiber (SMF) transmission. It enables high-speed 40G links over longer distances while using the same LC connector type commonly found in enterprise and data center fiber infrastructure.
From a functional perspective, QSFP+ LC transceivers transmit and receive data using four parallel 10Gbps optical lanes, which are typically multiplexed onto a single pair of fibers through CWDM or DWDM technology. This design allows a single QSFP+ LC module to deliver full 40Gbps bandwidth over two fibers only, instead of the multiple fiber pairs required by MPO-based solutions.
Key Characteristics of a QSFP+ LC Transceiver
A QSFP+ LC transceiver is defined by several core technical attributes that directly affect deployment and compatibility.
| Parameter |
Description |
| Form Factor |
QSFP+ |
| Connector Type |
LC duplex |
| Fiber Type |
Single-mode fiber |
| Typical Data Rate |
40Gbps |
| Optical Technology |
CWDM or DWDM |
These characteristics make QSFP+ LC transceivers particularly suitable for longer-reach 40G links, where fiber efficiency and operational simplicity are more important than ultra-high port density.
How a QSFP+ LC Transceiver Works
At the optical layer, a QSFP+ LC transceiver splits the 40Gbps electrical signal into four 10Gbps channels. Each channel is transmitted on a different wavelength around 1310nm, and all wavelengths are combined onto a single fiber using wavelength multiplexing. On the receiving side, the process is reversed, ensuring synchronized delivery of the original 40Gbps data stream.
This wavelength-based approach explains why QSFP+ LC transceivers:
-
Support longer transmission distances than multimode QSFP+ modules
-
Require only two fibers instead of parallel fiber ribbons
-
Are commonly specified as FR4, LR4, ER4, or ZR4 modules
When a QSFP+ LC Transceiver Is Typically Used
QSFP+ LC transceivers are chosen when network design priorities extend beyond short-reach data center switching.
-
When single-mode fiber is already deployed or preferred
-
When link distances exceed the practical limits of multimode optics
-
When LC-based patching and cross-connects are required
-
When simplified fiber management is a priority in core or backbone networks
In these scenarios, a QSFP+ LC transceiver provides a balanced combination of reach, compatibility, and operational efficiency, making it a standard choice for many 40G network architectures.
🔰 Common Types of QSFP+ LC Transceivers
QSFP+ LC transceivers are primarily differentiated by optical standard and supported transmission distance, not by form factor or connector type. In practice, most deployments fall into four categories—FR4, LR4, ER4, and ZR4—each targeting a specific distance range and network scenario. Choosing the correct type is mainly a matter of link length, optical budget, and application environment.
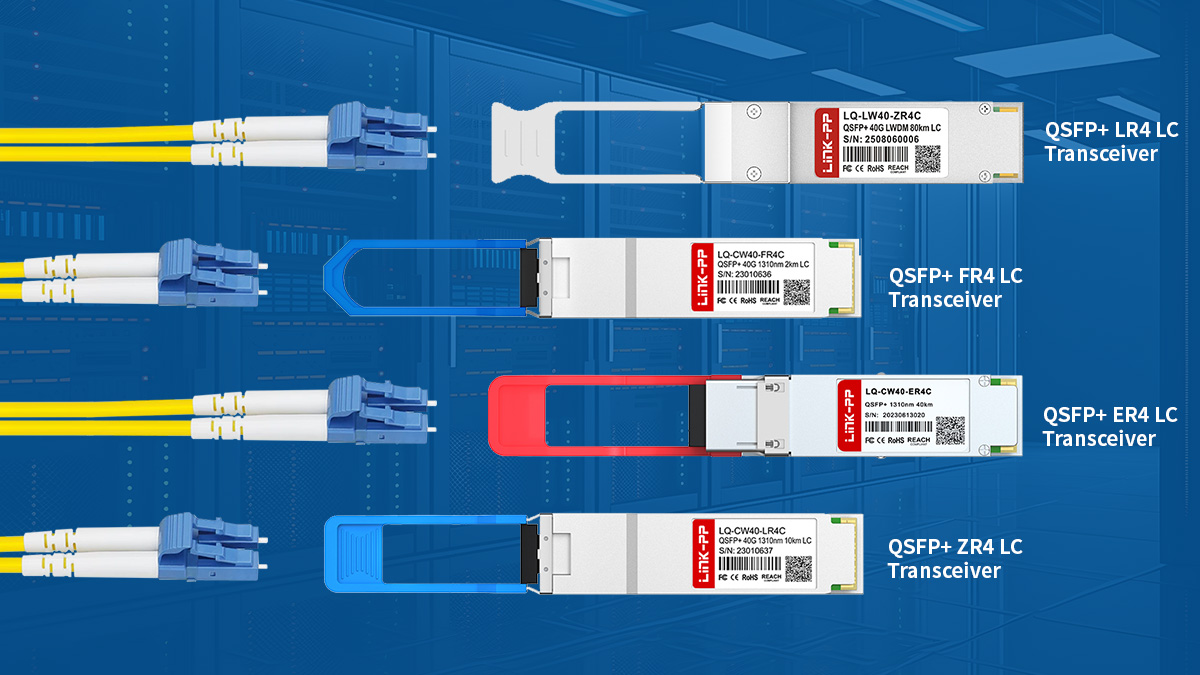
QSFP+ FR4 LC Transceiver
A QSFP+ LC FR4 transceiver is designed for short-reach single-mode 40G links, typically up to 2km. It is often selected when multimode fiber is not available, but the required distance does not justify higher-cost long-reach optics.
| Parameter |
QSFP+ FR4 LC |
| Standard |
40G FR4 |
| Reach |
Up to 2km |
| Fiber Type |
Single-mode fiber |
| Connector |
LC duplex |
| Wavelength |
~1310nm (4×10G CWDM) |
FR4 modules provide a cost-efficient way to deploy 40G over SMF while maintaining LC-based connectivity. They are commonly used in intra-campus links, data center edge connections, and short DCI scenarios where fiber management simplicity is a priority.
QSFP+ LR4 LC Transceiver
A QSFP+ LC LR4 transceiver supports medium-reach 40G transmission up to 10km and represents the most widely deployed QSFP+ LC type in enterprise and data center backbone networks.
| Parameter |
QSFP+ LR4 LC |
| Standard |
40GBASE-LR4 |
| Reach |
Up to 10km |
| Fiber Type |
Single-mode fiber |
| Connector |
LC duplex |
| Wavelength |
~1310nm (CWDM) |
LR4 is often considered the default choice when building 40G single-mode links, offering a strong balance between reach, cost, and interoperability across network equipment vendors.
QSFP+ ER4 LC Transceiver
A QSFP+ ER4 LC transceiver is engineered for longer-reach 40G links up to 40km, making it suitable for metro networks and inter-data center connectivity.
| Parameter |
QSFP+ ER4 LC |
| Standard |
40GBASE-ER4 |
| Reach |
Up to 40km |
| Fiber Type |
Single-mode fiber |
| Connector |
LC duplex |
| Wavelength |
~1310nm (CWDM) |
ER4 modules feature a higher optical power budget than LR4, but they also require closer attention to link loss and receiver saturation, especially on shorter fiber runs.
QSFP+ ZR4 LC Transceiver
A QSFP+ ZR4 LC transceiver is designed for ultra-long 40G transmission, typically supporting distances of 80km over single-mode fiber.
| Parameter |
QSFP+ ZR4 LC |
| Standard |
40GBASE-ZR4 |
| Reach |
Up to 80km |
| Fiber Type |
Single-mode fiber |
| Connector |
LC duplex |
| Wavelength |
~1310nm (LAN-WDM) |
ZR4 modules are primarily deployed in telecom, metro backbone, and long-haul DCI environments, where extended reach and high optical budgets are mandatory. Due to their power characteristics, careful optical link planning is essential.
Each QSFP+ LC transceiver type serves a clearly defined distance segment. Understanding these distinctions allows network designers and buyers to avoid over-specifying optics, control costs, and ensure stable long-term operation.
🔰 QSFP+ LC vs QSFP+ MPO Transceivers
The difference between QSFP+ LC and QSFP+ MPO transceivers is not the data rate—both support 40Gbps—but how the optical signals are transmitted and how fiber infrastructure is managed. In practice, the choice between LC and MPO directly affects fiber count, cabling complexity, deployment flexibility, and long-term operational cost.

Core Differences at a Glance
For most networks, the decision comes down to connector type, fiber usage, and typical transmission distance.
| Aspect |
QSFP+ LC Transceiver |
QSFP+ MPO Transceiver |
| Connector Type |
LC duplex |
MPO/MTP |
| Fiber Count |
2 fibers (SMF) |
8 or 12 fibers (MMF) |
| Transmission Method |
Wavelength multiplexing |
Parallel optics |
| Typical Reach |
2km–80km |
Up to 100m |
| Common Fiber Type |
Single-mode fiber |
Multimode fiber |
QSFP+ LC transceivers prioritize fiber efficiency and reach, while QSFP+ MPO transceivers focus on short-reach, high-density parallel connections inside the data center.
Fiber and Cabling Implications
QSFP+ LC transceivers use wavelength-division multiplexing, allowing four 10Gbps lanes to share a single fiber pair. This simplifies cabling and aligns well with existing LC-based patch panels.
QSFP+ MPO transceivers, by contrast, rely on parallel fibers, which increases fiber consumption and introduces additional considerations such as:
These factors become more significant as network scale increases.
Deployment Scenarios and Practical Selection
The optimal choice depends on where and how the 40G link is deployed.
Cost and Operational Considerations
While QSFP+ MPO modules often have a lower unit price, the overall cost picture includes fiber infrastructure, installation complexity, and ongoing maintenance. QSFP+ LC solutions may reduce these hidden costs by minimizing fiber usage and simplifying cross-connects, especially in backbone or inter-building links.
In summary, QSFP+ LC transceivers are optimized for reach and fiber efficiency, whereas QSFP+ MPO transceivers are optimized for short-reach, high-density switching environments. The right choice depends less on speed and more on distance, infrastructure, and operational priorities.
🔰 Fiber Type and Distance Considerations
For QSFP+ LC transceivers, fiber selection and link distance are not optional details—they directly determine which optical standard is usable, whether the link will operate reliably, and how much margin exists for future changes. In most cases, the decision is governed by single-mode fiber characteristics and required reach, rather than by the transceiver form factor itself.
Supported Fiber Type
QSFP+ LC transceivers are designed exclusively for single-mode fiber (SMF). Unlike MPO-based QSFP+ modules that commonly operate over multimode fiber, LC-based QSFP+ optics rely on wavelength multiplexing and therefore require the optical properties of SMF.
| Parameter |
QSFP+ LC Requirement |
| Fiber Type |
Single-mode fiber |
| Core Size |
9/125µm |
| Connector Interface |
LC duplex |
| Typical Wavelength |
~1310nm |
Because of this, QSFP+ LC transceivers integrate seamlessly with existing SMF backbones, LC patch panels, and cross-connect systems, reducing the need for additional cabling infrastructure.
Distance Ranges by Optical Standard
The achievable transmission distance of a QSFP+ LC transceiver depends on the optical standard used. Each standard is engineered for a specific reach range with a corresponding optical power budget.
| Optical Standard |
Typical Reach |
Common Use Case |
| FR4 |
Up to 2km |
Short SMF links, campus connections |
| LR4 |
Up to 10km |
Enterprise and data center backbones |
| ER4 |
Up to 40km |
Metro networks, DCI |
| ZR4 |
Up to 80km |
Long-haul and telecom links |
Selecting a transceiver with excessive reach can introduce unnecessary cost and power considerations, while under-specifying reach can result in unstable links.
Link Budget and Insertion Loss Planning
Beyond nominal distance, total link loss plays a critical role in determining whether a QSFP+ LC transceiver will perform as expected. Key contributors include:
-
Fiber attenuation over distance
-
Connector and splice losses
-
Patch panel and cross-connect insertion loss
Higher-reach modules such as ER4 and ZR4 offer larger optical budgets, but they may also require attenuation management on shorter links to avoid receiver overload.
Practical Distance Selection Guidelines
When planning a QSFP+ LC link, distance should be evaluated alongside fiber quality and network design constraints.
-
Use FR4 or LR4 for most enterprise and data center applications
-
Choose ER4 when link distances approach or exceed campus-scale limits
-
Reserve ZR4 for true long-haul or metro backbone scenarios
-
Always validate link loss against the transceiver’s optical budget
By aligning fiber type and distance requirements with the appropriate QSFP+ LC standard, network designers can ensure stable performance, cost efficiency, and long-term scalability.
🔰 Compatibility with Network Equipment
For a QSFP+ LC transceiver, compatibility is determined less by the connector type and more by how the module is recognized, initialized, and supported by the host switch or router. In practice, ensuring compatibility is critical to avoid link failures, warning messages, or disabled ports in production networks.

Vendor Platform Compatibility
QSFP+ LC transceivers are widely deployed across mainstream networking platforms, provided that the module follows the correct electrical, optical, and management specifications.
| Equipment Vendor |
Typical Compatibility |
| Cisco |
Supported with compliant or coded QSFP+ LC modules |
| Juniper |
Supported on most 40G-capable QSFP+ ports |
| Arista |
Broad interoperability with standards-based optics |
| HPE |
Supported with approved or compatible modules |
Most modern platforms can operate with standards-compliant third-party QSFP+ LC transceivers, but behavior may vary depending on firmware policies.
OEM vs Third-Party QSFP+ LC Transceivers
The main difference between OEM-branded and third-party QSFP+ LC transceivers lies in EEPROM coding and vendor enforcement, not in optical performance.
| Aspect |
OEM Modules |
Third-Party Compatible Modules |
| Coding |
Vendor-specific |
Vendor-matched or programmable |
| Interoperability |
Guaranteed on same brand |
Broad cross-vendor support |
| Cost |
Higher |
More cost-efficient |
| Availability |
Limited to vendor supply |
Widely available |
In environments with strict vendor locking, properly coded third-party modules are often required to ensure plug-and-play operation without system warnings.
EEPROM Coding and Recognition Behavior
QSFP+ LC transceivers communicate with host devices through EEPROM data, which defines parameters such as:
If the EEPROM does not match the host’s expectations, the device may:
Correct coding is therefore essential, especially in multi-vendor network environments.
Practical Compatibility Validation
Before large-scale deployment, compatibility should be validated under real operating conditions.
-
Confirm switch firmware supports the target QSFP+ standard (FR4, LR4, ER4, ZR4)
-
Verify vendor-specific compatibility requirements
-
Test link stability, DOM reporting, and error rates
-
Ensure hot-swap behavior functions as expected
By addressing compatibility at both the platform and firmware level, QSFP+ LC transceivers can be deployed reliably across diverse network infrastructures without operational surprises.
🔰 Typical Use Cases for QSFP+ LC Transceivers
QSFP+ LC transceivers are primarily deployed in scenarios where 40G bandwidth, single-mode fiber, and LC-based connectivity are required at the same time. Their value becomes most evident in medium- to long-distance links, where fiber efficiency, operational simplicity, and compatibility outweigh the benefits of short-reach parallel optics.
Data Center Interconnection (DCI)
QSFP+ LC transceivers are a common choice for interconnecting separate data centers or data halls over single-mode fiber.
| Requirement |
QSFP+ LC Fit |
| Distance |
2km–40km typical |
| Fiber Type |
Single-mode fiber |
| Connector Preference |
LC duplex |
| Deployment Goal |
Stable, scalable DCI links |
In DCI scenarios, LR4 and ER4 modules are frequently selected to balance reach and cost, while ZR4 is reserved for extended metro connections.
Enterprise Core and Backbone Networks
In enterprise environments, QSFP+ LC transceivers are often used to aggregate access and distribution layers or to connect core switches across buildings.
-
Suitable for campus-scale distances
-
Compatible with existing LC patch panels
-
Simplifies fiber management in backbone links
-
Reduces dependence on parallel fiber infrastructure
These characteristics make QSFP+ LC modules easier to integrate into legacy SMF networks.
Campus and Metro Backbone Links
QSFP+ LC transceivers are well-suited for inter-building and metro backbone connections, where link distances exceed the limits of multimode optics.
| Scenario |
Recommended Type |
| Campus backbone |
LR4 |
| City-wide metro link |
ER4 |
| Long metro span |
ZR4 |
Their extended reach and high optical budgets allow stable operation even across multiple patch points and cross-connects.
Telecom and Service Provider Environments
Service providers deploy QSFP+ LC transceivers in aggregation and transport layers, where consistent performance over long distances is critical.
-
Support for long-haul single-mode transmission
-
Compatibility with LC-based optical distribution frames
-
Suitable for backbone and access aggregation roles
In these environments, ER4 and ZR4 modules are often preferred due to their optical margin and reliability.
Across all these use cases, QSFP+ LC transceivers provide a practical and scalable solution for 40G links that demand reach, compatibility, and efficient fiber utilization.
🔰 How to Choose the Right QSFP+ LC Transceiver
Choosing the right QSFP+ LC transceiver is primarily a process of matching link requirements to the appropriate optical standard, rather than selecting by form factor alone. A correct choice ensures stable operation, avoids unnecessary cost, and simplifies long-term maintenance.
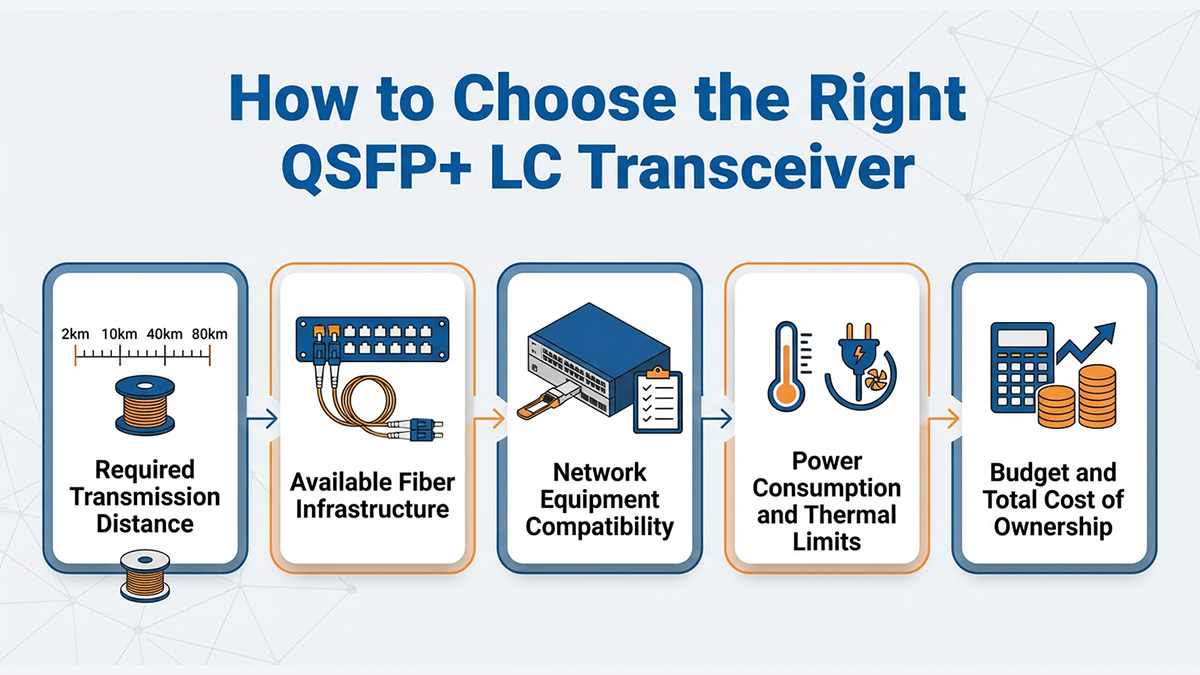
Step 1: Determine the Required Link Distance
Transmission distance is the first and most critical decision point. QSFP+ LC transceivers are available in multiple reach classes, each optimized for a specific distance range.
| Required Distance |
Recommended Type |
| Up to 2km |
QSFP+ FR4 |
| Up to 10km |
QSFP+ LR4 |
| Up to 40km |
QSFP+ ER4 |
| Up to 80km |
QSFP+ ZR4 |
Selecting a module with significantly more reach than required can increase cost and may introduce optical power management challenges.
Step 2: Verify Fiber Infrastructure
QSFP+ LC transceivers rely on single-mode fiber with LC duplex connectors, so existing cabling should be evaluated before deployment.
-
Confirm SMF availability end-to-end
-
Check connector quality and cleanliness
-
Identify patch panels and cross-connect points
-
Estimate total link loss across the path
This step helps ensure that the selected module’s optical budget aligns with real-world conditions.
Step 3: Confirm Network Equipment Compatibility
Not all switches enforce optics compatibility in the same way. Before finalizing a QSFP+ LC transceiver choice:
-
Verify supported QSFP+ standards on the target switch or router
-
Check firmware or operating system restrictions
-
Confirm whether vendor-specific EEPROM coding is required
Compatibility validation is especially important in multi-vendor networks or when using third-party transceivers.
Step 4: Evaluate Power and Environmental Constraints
Higher-reach QSFP+ LC transceivers generally consume more power and generate more heat.
-
Review transceiver power consumption limits
-
Ensure adequate airflow and cooling
-
Consider operating temperature ranges
These factors become more critical in dense chassis or edge deployments.
Step 5: Balance Cost and Long-Term Value
Cost should be evaluated in the context of total cost of ownership, not just unit price.
-
Avoid over-specifying reach
-
Consider availability and lead times
-
Factor in testing, warranty, and support
By systematically assessing distance, fiber infrastructure, compatibility, and operational constraints, network designers can confidently select a QSFP+ LC transceiver that meets both technical and business requirements.
🔰 QSFP+ LC Transceiver Pricing Factors
The price of a QSFP+ LC transceiver is influenced by more than just the form factor or data rate. In practice, pricing is driven by optical reach, component complexity, compatibility requirements, and supply conditions. Understanding these factors helps buyers avoid unnecessary costs while still meeting technical requirements.
Optical Standard and Transmission Distance
Transmission distance is the most direct pricing driver. Longer-reach QSFP+ LC transceivers require higher-grade optical components and tighter manufacturing tolerances.
| Optical Type |
Typical Reach |
Relative Price Level |
| FR4 |
Up to 2km |
Low |
| LR4 |
Up to 10km |
Medium |
| ER4 |
Up to 40km |
High |
| ZR4 |
Up to 80km |
Very High |
For most enterprise and data center applications, FR4 or LR4 provides the best balance between cost and performance.
OEM-Branded vs Compatible Modules
Branding and vendor policies have a significant impact on pricing, even when optical performance is equivalent.
| Factor |
OEM Modules |
Compatible Modules |
| Unit Cost |
Higher |
Lower |
| Coding |
Fixed, vendor-specific |
Vendor-matched or programmable |
| Availability |
Limited to brand supply |
More flexible |
| Lead Time |
Often longer |
Typically shorter |
Compatible QSFP+ LC transceivers are widely used to reduce capital expenditure without compromising functionality, provided compatibility is properly validated.
Component Quality and Testing Level
Pricing also reflects the quality control and testing processes applied during manufacturing.
-
Higher-grade lasers and optical components increase cost
-
Extended temperature support adds complexity
-
Per-port testing and compatibility validation add value
Modules that undergo full functional and interoperability testing generally command a modest premium but reduce deployment risk.
Market and Supply Considerations
External factors can also affect QSFP+ LC transceiver pricing.
-
Global component availability
-
Volume purchasing and project-based pricing
-
Custom coding or labeling requirements
For large deployments, aligning module specifications closely with real network needs can significantly optimize overall procurement cost while maintaining reliable performance.
🔰 LINK-PP QSFP+ LC Transceiver Solutions
LINK-PP QSFP+ LC transceivers are designed to meet real-world deployment requirements across enterprise, data center, and service provider networks, with a focus on standards compliance, interoperability, and procurement efficiency. The product lineup covers the full range of QSFP+ LC optical standards, enabling precise matching to link distance and application needs.
Available QSFP+ LC Transceiver Types
LINK-PP provides QSFP+ LC transceivers across all commonly deployed 40G single-mode distance classes.
| Optical Standard |
Supported Reach |
Typical Application |
| FR4 |
Up to 2km |
Short SMF and campus links |
| LR4 |
Up to 10km |
Enterprise and DC backbones |
| ER4 |
Up to 40km |
Metro and DCI networks |
| ZR4 |
Up to 80km |
Long-haul and telecom links |
This coverage allows network designers to avoid over-specification while maintaining flexibility across different network segments.
Compatibility and Interoperability Assurance
LINK-PP QSFP+ LC transceivers are built with standards-based hardware and vendor-matched EEPROM coding, ensuring reliable operation across mainstream platforms.
-
Compatibility with Cisco, Juniper, Arista, HPE, and other vendors
-
Support for custom coding to match specific switch requirements
-
Plug-and-play operation without compatibility warnings
-
Verified DOM reporting and stable link behavior
Each module is tested to ensure consistent recognition and performance in heterogeneous network environments.
Quality Control and Deployment Reliability
To minimize deployment risk, LINK-PP applies structured testing and validation processes.
-
Electrical and optical performance verification
-
Interoperability testing on real network equipment
-
Environmental and stability checks before shipment
These measures help ensure that QSFP+ LC transceivers perform predictably in production networks, even in large-scale or long-term deployments.
Procurement and Project Support
LINK-PP solutions are tailored for B2B purchasing and project-based deployments.
-
Flexible supply for volume orders
-
Short lead times for standard configurations
-
Support for labeling, coding, and documentation requirements
By combining broad product coverage, proven compatibility, and controlled cost, LINK-PP QSFP+ LC transceiver solutions provide a practical option for organizations building or expanding 40G single-mode networks.
🔰 FAQs About QSFP+ LC Transceivers

Is a QSFP+ LC transceiver the same as a QSFP+ LR4 transceiver?
Not exactly. QSFP+ LC describes the connector type, while QSFP+ LR4 refers to a specific optical standard. Most QSFP+ LR4 modules do use LC duplex connectors, but QSFP+ LC transceivers also include other standards such as FR4, ER4, and ZR4, each supporting different transmission distances.
Can a QSFP+ LC transceiver be used with MPO fiber?
No. QSFP+ LC transceivers are designed for LC duplex single-mode fiber, not MPO/MTP cabling. MPO-based QSFP+ modules rely on parallel optics and require multiple fiber strands, whereas QSFP+ LC transceivers use wavelength multiplexing over two fibers.
Are QSFP+ LC transceivers hot-swappable?
Yes. QSFP+ LC transceivers are hot-swappable, meaning they can be inserted or removed while the host device is powered on. However, standard operational practices should still be followed, such as verifying compatibility and avoiding unnecessary insertions during active traffic.
How do I check if a QSFP+ LC transceiver is compatible with my switch?
Compatibility can be verified by:
-
Checking the switch vendor’s supported optics list
-
Confirming the required QSFP+ standard (FR4, LR4, ER4, or ZR4)
-
Ensuring correct EEPROM coding for the target platform
-
Testing the module on the switch with the intended firmware version
Proper validation helps prevent port errors or compatibility warnings.
Can QSFP+ LC transceivers be used for short links?
Yes, but with consideration. FR4 or LR4 modules are suitable for shorter single-mode links. Using ER4 or ZR4 on very short distances may require optical attenuation to avoid receiver saturation.
Do QSFP+ LC transceivers support DOM monitoring?
Most modern QSFP+ LC transceivers support Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM), providing real-time data such as temperature, voltage, and optical power levels. Actual DOM support depends on both the transceiver design and the host platform’s capabilities.
🔰 Conclusion: When to Choose a QSFP+ LC Transceiver
A QSFP+ LC transceiver is the right choice when a 40G network requires single-mode fiber connectivity, extended transmission distance, and LC-based cabling simplicity. With support for reach options ranging from 2km to 80km through FR4, LR4, ER4, and ZR4 standards, QSFP+ LC transceivers provide the flexibility to address enterprise, data center, metro, and telecom deployment scenarios without changing form factor or infrastructure approach.
By selecting the appropriate optical standard based on actual link distance, fiber conditions, and equipment compatibility, organizations can avoid over-specification, control costs, and ensure stable long-term operation. Compared with MPO-based QSFP+ solutions, LC transceivers offer clear advantages in fiber efficiency, scalability, and operational manageability, especially outside short-reach, high-density switching environments.
For teams looking to deploy or upgrade 40G single-mode links, LINK-PP QSFP+ LC transceiver solutions deliver a complete range of distance options, proven multi-vendor compatibility, and consistent quality control. Explore available models and specifications at the LINK-PP Official Store to find the right QSFP+ LC transceiver for your network requirements.