40G QSFP+ modules are hot-swappable, quad-lane transceivers that deliver 40 Gbps by combining four 10.3125 Gbps electrical/optical lanes — the form factor and lane mapping are defined in the QSFP+/SFF specifications.
They come in several flavors (SR4, LR4, CSR4, PSM4, BiDi) that trade off fiber type, connector (MPO/MTP vs LC) and reach — for example, SR4 typically serves short multimode links (≈100 m on OM3, 150 m on OM4) while LR4 supports single-mode links up to ~10 km.
In this guide you will learn:
-
The real differences between the main 40G QSFP+ types and when to use each.
-
How breakout cables, DAC/AOC and 4×10G split modes work and when to choose them.
-
Standards and interoperability pitfalls (SFF-8436, IEEE compliance), plus a compatibility checklist to avoid vendor lock-in.
-
Deployment best practices (power, thermal, MPO cable management), troubleshooting steps, and quick reference tables you can copy into specs or procurement sheets.
Who this is for: data-center/network engineers, architects, and procurement teams who need a compact, authoritative reference to choose, deploy, and validate 40G QSFP+ Transceivers with confidence.
✳️ 40G QSFP+ Modules Overview: What It Is, Speed & Use Cases
A 40G QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) module is a compact, hot-pluggable optical/electrical transceiver that delivers 40 Gbps by aggregating four independent full-duplex lanes (4 Tx + 4 Rx). Each lane operates at ~10.3125 Gbps (64b/66b encoded in 40G Ethernet), so the QSFP+ achieves 40 Gbps by combining 4 × 10.3125 Gbps channels in a single, hot-swappable package.

How 40G QSFP+ Achieves 40 Gbps Through Lane Aggregation
-
Four lanes, one module. The QSFP+ form factor exposes four separate transmit and four receive channels. Electrically and optically these are treated as four parallel 10-plus Gbps links that the host ASIC or MAC aggregates into a 40G logical interface. This lane architecture is defined by the QSFP+ / SFF specifications.
-
Encoding & protocol support. For Ethernet, those lanes typically carry 10.3125 Gbps each using 64b/66b encoding as specified in 40G Ethernet standards (IEEE 802.3ba family). QSFP+ is also used for other protocols (InfiniBand QDR, Fibre Channel variants) because the lanes are general purpose high-speed links.
Hot-Swappable Design and Operational Advantages
QSFP+ modules are designed to be hot-pluggable (hot-swappable): you can insert or remove a module from a powered host slot without powering down the system. The QSFP/SFF specs include mechanical and low-speed bus behaviors that protect the host during insertion/removal and support safe hot-plug operations. This characteristic makes maintenance, upgrades and staged rollouts much easier in live environments.
Typical Applications in Data Centers and HPC Networks
-
Data-center spine & leaf interconnects. 40G QSFP+ is commonly used for high-capacity links between leaf switches and spine switches (or between spine switches) where port density and uplink capacity matter. It provides a compact way to aggregate multiple 10G server links or to carry higher east-west traffic inside the fabric.
-
Server aggregation and top-of-rack uplinks. When moving from 10G to higher aggregation rates, QSFP+ lets you use breakout cables (4×10G) or native 40G uplinks to reduce port count and simplify cabling.
-
High-Performance Computing (HPC) and storage fabrics. QSFP+ is used in latency-sensitive, high-bandwidth clusters where dense, low-latency interconnects are required.
-
Campus core and data-center interconnect (DCI). Single-mode LR4/ER4 variants of QSFP+ support longer distances (e.g., LR4 ≈10 km), making QSFP+ suitable for campus backbone links or metro DCI when single-mode optics are used.
Quick technical snapshot
-
Aggregate data rate: ≈40 Gbps (4 × 10.3125 Gbps).
-
Typical form factor spec: SFF-8436 / QSFP MSA family (mechanical, electrical, and management interfaces).
-
Common optical types: SR4 (MPO/MTP, multimode), LR4 (duplex LC, single-mode), CSR4/PSM4/BiDi (variants for extended reach or duplex reuse).
-
Hot-plug: supported by QSFP+ mechanical/management design; safe insertion/removal procedures are in the SFF specs.
✳️ 40G QSFP+ Types & How They Differ (SR4, LR4, ER4, ZR4, CSR4, PSM4, BiDi)
Below is a vendor-neutral, engineering-grade breakdown of the common QSFP+ Modules optical types. Each sub-type includes the technical approach, typical wavelengths, connector style, and representative reach. Distances and optics behavior are typical values taken from MSA / vendor datasheets — always confirm with the specific module datasheet and your fiber plant power budget before procurement.

40GBASE-SR4 (Short-Range, Parallel MMF)
- Tech: Parallel multimode optics that use four separate transmit and four separate receive fibers (one per 10G lane). The module uses 4× 10G lasers/receivers and an internal MPO/MTP interface.
- Wavelength: ~850 nm (multimode).
- Connector: MPO/MTP (parallel ribbon).
- Typical Distance: ~100 m on OM3, ~150 m on OM4 (vendor variance applies).
- Use Case: Short-reach leaf-to-leaf or top-of-rack to aggregation links in dense data centers where MPO trunking and high port density are favored.
40GBASE-LR4 (Long-Range, CWDM over SMF)
- Tech: WDM approach that multiplexes four 10G channels onto four CWDM wavelengths, then combines them into duplex LC single-mode fiber with an internal mux/demux. LR4 is designed for single-mode fiber runs.
- Wavelengths: CWDM wavelengths centered at 1271 / 1291 / 1311 / 1331 nm (per IEEE 802.3ba) (depends on vendor / CWDM plan).
- Connector: Duplex LC (single-mode).
- Typical Distance: ~10 km on standard single-mode fiber (SMF), subject to power budget and link margin.
- Use Case: Campus backbone, data-center interconnect (DCI) and metro links where single-mode optics and longer reach are required.
40GBASE-ER4 (Extended Reach, CWDM over SMF)
- Tech: High-power CWDM optics using four 10G lanes multiplexed into duplex SMF, with extended optical budget.
- Wavelength: CWDM set around 1270–1330 nm (1310 nm class).
- Connector: Duplex LC (single-mode).
- Typical Distance: Up to ~40 km on standard SMF.
- Use Case: Metro networks, long-distance DCI, carrier backbone links.
40GBASE-ZR4 (Vendor-Specific Ultra-Long Reach)
- Tech: High-power CWDM or DWDM optics, multiplexing four 10G lanes into duplex SMF for ultra-long distances.
- Wavelength: Vendor-dependent CWDM / DWDM grid.
- Connector: Duplex LC (single-mode).
- Typical Distance: Up to ~80 km (vendor dependent).
- Use Case: Metro DCI, long-haul backbone, legacy 40G transport.
- Note: Not an IEEE standardized specification; vendor-defined.
40GBASE-CSR4 (Extended-Reach SR Variant)
- Tech: An extended-reach multimode variant of SR4 with higher modal bandwidth/laser power for longer multimode runs. Uses the same parallel MPO/MTP approach as SR4 but with improved reach.
- Wavelength: ~850 nm (multimode).
- Connector: MPO/MTP (parallel).
- Typical Distance: Vendor-specified: up to ~300 m on OM3 and ~400 m on OM4 (not IEEE standardized).
- Use Case: Longer multimode links inside large campus or data-center buildings where single-mode is not deployed but extended reach over OM3/OM4 is needed.
40GBASE-PSM4 (Parallel Single-Mode)
- Tech: Parallel single-mode optics — like SR4 but on single-mode fiber: uses 4 spatial single-mode fibers per direction (typically in an MPO/MTP-style housing) with four 1310 nm channels. PSM4 provides a cost-effective single-mode option without wavelength multiplexing.
- Wavelength: ~1310 nm per lane (single-mode).
- Connector: MPO/MTP (parallel single-mode fiber ribbon) or vendor variations.
- Typical Distance: Typically 500 m – 2 km; some vendor-enhanced variants support up to ~10 km for PSM4 parts from multiple vendors (power budget and module variant dependent). Confirm the datasheet for exact reach.
- Use Case: Cost-sensitive single-mode deployments where parallel fiber is available (e.g., some DCI and campus links), avoiding the cost and complexity of LR4 wavelength muxing.
40G BiDi (Bidirectional over Duplex MMF/LC)
- Tech: BiDirectional BiDi QSFP modules use bidirectional optics that carry two 20G signals (or two aggregated 20G channels) over a duplex fiber pair — typically implemented by using two different wavelengths traveling in opposite directions on the same fiber pair. The module internally multiplexes/demultiplexes as needed to present a 40G logical interface.
- Wavelengths: Vendor dependent — Cisco and others describe BiDi 40G implementations using wavelength pairs in the ~832–918 nm range for certain multimode BiDi parts; other BiDi designs use different wavelength pairs for duplex MMF operation. Always check the vendor spec.
- Connector: Duplex LC (typical for BiDi) — enables reuse of existing duplex fiber runs.
- Typical Distance: Varies by BiDi implementation — commonly short to medium reach on multimode duplex fiber (check vendor datasheet for exact reach and link budget).
- Use Case: Migrating to 40G while reusing existing duplex MMF infrastructure (minimizes fiber re-cabling) — helpful for brownfield upgrades.
Comparison Table
| Type |
Connector |
Typical Wavelength(s) |
Typical Max Distance |
Typical Use Case |
| 40GBASE-SR4 |
MPO / MTP (MMF) |
850 nm |
OM3: ~100 m; OM4: ~150 m |
Short-reach data-center leaf/spine, high-density MMF fabrics |
| 40GBASE-LR4 |
Duplex LC (SMF) |
CWDM 1270–1330 nm (1310 nm class) |
≈ 10 km |
Campus backbone, DCI, metro single-mode links |
| 40GBASE-ER4 |
Duplex LC (SMF) |
CWDM 1270–1330 nm (1310 nm class) |
≈ 40 km |
Metro networks, long-distance DCI, carrier backbone links |
| 40GBASE-ZR4* |
Duplex LC (SMF) |
CWDM / DWDM (vendor dependent) |
Up to ≈ 80 km |
Metro DCI, long-haul backbone, legacy 40G transport |
| 40GBASE-CSR4 |
MPO / MTP (MMF) |
850 nm |
OM3: ~300 m; OM4: ~400 m |
Extended MMF reach in large data halls |
| 40GBASE-PSM4 |
MPO / MTP (SMF) |
~1310 nm × 4 lanes |
Up to ~10 km |
Parallel SMF deployments, cost-sensitive links |
| 40G BiDi |
Duplex LC |
Vendor dependent (e.g., ~832–918 nm pairs) |
Vendor dependent |
Duplex fiber reuse, brownfield upgrades |
Notes & Procurement Tips (practical)
-
Vendor Datasheets Matter: The distances above are typical reference points — final link reach depends on module power budget, fiber type and loss, connector/patching loss, and safety margins. Always validate with the specific part TDP/optical budget.
-
Connector Strategy: MPO/MTP is standard for parallel optics (SR4, CSR4, PSM4); LC duplex is standard for LR4 and many BiDi parts. Ensure your patching/trunk panels and MPO polarity plan match the module type.
-
Breakout & Migration: SR4/PSM4 can be broken out to 4×10G using MPO-to-4×LC fanouts or breakout cables; LR4 cannot be passively broken out without protocol/gear support because it uses WDM onto duplex LC.
-
Check Interoperability / MSA: QSFP+ adheres to QSFP MSA/SFF specs (mechanical/electrical/management), but vendor firmware or switch compatibility lists still matter — test before wide deployment.
✳️ 40G QSFP+ Breakout, AOC & DAC Options (4×10G Connectivity)
QSFP+ ports support multiple cabling and breakout options, allowing one QSFP+ interface to operate as either a native 40G link or four independent 10G connections. The most common solutions include passive DAC, active optical cables (AOC), and QSFP+ breakout cables.

QSFP+ to 4×SFP+ Breakout Overview
A QSFP+ breakout cable splits a single 40G port into 4 × 10G SFP+ links by mapping each internal 10G lane to a separate SFP+ interface.
Typical use cases:
-
Gradual migration from 10G → 40G
-
High-density server aggregation
-
Legacy 10G switch interconnection
Note: The switch must support port breakout configuration at both hardware and firmware levels.
Advantages: Lowest cost, zero power, simple deployment
Limitations: Very short reach, thicker cabling
Active Optical Cable (AOC)
-
Technology: Embedded optics + multimode fiber
-
Typical length: 3–100 m
-
Power consumption: ~1.5–3 W
-
Best for: Cross-rack and medium-distance connections
Advantages: Lightweight, flexible routing, longer reach than DAC
Limitations: Higher cost than passive DAC
QSFP+ Breakout DAC & AOC (4×10G Fan-out)
-
Breakout DAC:
-
Breakout AOC:
Cable Selection Quick Guide
| Distance |
Recommended Solution |
| ≤ 5 m |
Passive DAC |
| 5–30 m |
AOC |
| 30–100 m |
AOC or Fiber Modules |
| 10G fan-out |
QSFP+ → 4×SFP+ Breakout |
Vendor & Deployment Notes
-
Confirm switch breakout support before deployment.
-
Some OEM switches require vendor-coded DAC/AOC cables.
-
High-quality third-party optics can significantly reduce cost while maintaining full MSA compliance.
Why It Matters
Breakout, DAC, and AOC options give QSFP+ exceptional deployment flexibility, enabling efficient bandwidth scaling, cabling optimization, and cost control in modern data centers.
✳️ QSFP+ Modules Standards, DOM, and Interoperability
Standards: SFF-8436 & IEEE 802.3ba
QSFP+ modules primarily follow the SFF-8436 Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) and IEEE 802.3ba Ethernet standards.
-
SFF-8436 defines:
-
Electrical interface and pinout
-
Optical interface requirements
-
Mechanical dimensions
-
Management interface and diagnostics framework
-
IEEE 802.3ba defines:
-
40G Ethernet physical layer specifications
-
Optical reach models (e.g., 40GBASE-SR4, LR4)
-
Signal encoding and lane architecture
Together, these standards ensure multi-vendor interoperability, electrical compatibility, and network stability across compliant switches, routers, and transceivers.
DOM (DDM): Real-Time Optical Monitoring
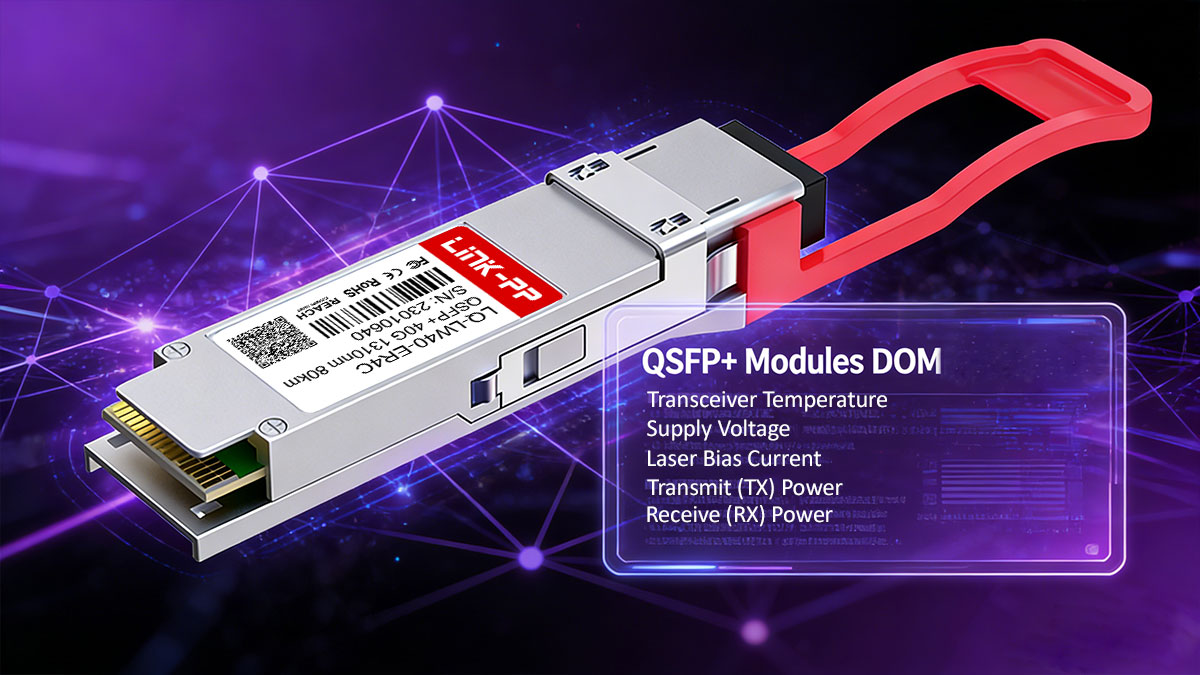
Most QSFP+ 40G transceivers support Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM), also known as Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM), as defined in SFF-8436.
DOM provides real-time access to key operating parameters:
These diagnostics enable proactive fault detection, predictive maintenance, and network health monitoring, which are essential for data center and carrier-grade deployments.
Interoperability & Vendor Lock-In Considerations
Although QSFP+ follows open standards, many switch vendors implement firmware-based compatibility enforcement, commonly referred to as vendor lock-in.
To avoid interoperability issues:
-
Verify transceiver compatibility with official vendor hardware compatibility lists (HCL)
-
Choose MSA-compliant third-party optics with proven cross-vendor support
-
Confirm DOM visibility and alarm reporting across target platforms
Proper compatibility validation ensures plug-and-play deployment, firmware stability, and long-term scalability.
QSFP+ Transceivers Compatibility
QSFP+ modules follow the SFF-8436 MSA standard and IEEE 802.3ba family for 40G Ethernet, ensuring mechanical, electrical, and management consistency. Most modules support DOM/DDM, providing real-time feedback on temperature, voltage, and optical power.
Compatibility can vary by vendor—some modules are platform-locked, while standard SR4/LR4/CSR4 modules are generally interoperable across compliant switches. Always verify module vendor compatibility lists before deployment to avoid insertion errors or degraded performance.
✳️ How to Choose the Right 40G QSFP+ Modules (Distance, Fiber, Cost, Compatibility)
Choosing the right 40G QSFP+ module requires evaluating four main factors: distance requirements, fiber type, cost considerations, and vendor compatibility. Making informed decisions ensures reliable performance, optimal network design, and long-term scalability.

1. Distance and Reach
-
Short-reach links (≤150 m): QSFP-SR4 over OM3/OM4 multimode fiber is most cost-effective for leaf-spine interconnects in data centers.
-
Medium-reach links (~10 km): QSFP-LR4 over single-mode fiber supports campus backbone or DCI applications.
-
Long-reach links (~40 km): QSFP-ER4 extends the optical budget for metro networks or longer DCI links.
-
Ultra-long reach (~80 km): QSFP-ZR4 (vendor-specific) provides extended single-mode transport; verify link budget and vendor specifications.
Tip: Always check optical loss, connector loss, and fiber type against module specifications to ensure target distance is achievable.
2. Fiber Type
-
Multimode fiber (MMF): SR4 and CSR4 modules use MPO/MTP parallel multimode fiber; cost-effective for short to medium distances.
-
Single-mode fiber (SMF): LR4, ER4, ZR4, PSM4 use duplex or parallel single-mode fiber; required for longer distances or metro links.
-
Bidirectional deployment: BiDi modules can reuse existing duplex fiber, ideal for brownfield upgrades.
Tip: Confirm fiber core, type (OM3/OM4 or OS2), and connector compatibility before module selection.
3. Cost Considerations
-
SR4 / CSR4: Lower cost per module, lower power, suitable for high-density, short-distance deployments.
-
LR4 / ER4: Moderate to high cost; power consumption increases with reach.
-
ZR4 / PSM4: Highest cost due to optical budget, power, and vendor-specific design.
Tip: Evaluate TCO: module cost, breakout cable needs, power consumption, and maintenance overhead.
4. Vendor Compatibility and Interoperability
-
Standards compliance: Verify modules meet SFF-8436 QSFP+ MSA, IEEE 802.3ba, or vendor-specific extended specifications.
-
Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM/DDM): Check if the module supports real-time monitoring for temperature, voltage, and optical power.
-
Vendor lock-in: Some modules are only fully supported on certain platforms; always review vendor compatibility lists.
-
Cross-vendor use: SR4/LR4/CSR4 modules are generally interoperable, but ER4/ZR4 may require exact vendor validation.
Summary / Key Takeaways
-
Distance first: Match module type (SR4/LR4/ER4/ZR4) to link distance.
-
Fiber type: MMF for short reach, SMF for long reach, BiDi for fiber reuse.
-
Cost vs. performance: Balance initial module cost, power, and breakout requirements.
-
Compatibility check: Confirm QSFP+ MSA compliance, DOM support, and vendor platform validation.
Following these guidelines ensures reliable, scalable 40G deployments, whether in data centers, campus networks, or metro DCIs.
✳️ 40G QSFP+ Deployment Best Practices
Deploying QSFP+ 40G modules requires careful planning across optical design, cabling, installation, and ongoing operations. Following best practices ensures maximum performance, long-term stability, and simplified troubleshooting.

Link Budget Planning and Optical Design
Before deployment, calculate the optical link budget, including:
-
Fiber attenuation
-
Connector and splice loss
-
Patch panel insertion loss
-
Module transmit power and receiver sensitivity
Ensure sufficient system margin (typically ≥2–3 dB) to accommodate aging, temperature variation, and fiber degradation.
Best practice: Validate link budgets using QSFP datasheet and IEEE specifications before large-scale rollout.
Fiber Infrastructure and Cabling Management
-
Use OM3/OM4 multimode fiber for SR4/CSR4 deployments and OS2 single-mode fiber for LR4/ER4/ZR4 links.
-
Maintain proper polarity and fiber mapping for MPO/MTP parallel optics.
-
Implement structured cabling and labeling to reduce troubleshooting time and minimize human error.
Best practice: Use low-loss connectors and minimize intermediate connections to preserve optical margin.
Installation, Handling, and Cleanliness
-
Always inspect and clean LC and MPO/MTP connectors before insertion.
-
Avoid tight fiber bends; respect minimum bend radius specifications.
-
Insert and remove 40G QSFP+ modules using proper handling procedures to prevent electrical or mechanical damage.
Best practice: Adopt fiber inspection and cleaning protocols as part of standard operational procedures.
Monitoring, Testing, and Troubleshooting
-
Leverage DOM/DDM monitoring to track temperature, voltage, Tx/Rx optical power, and laser bias.
-
Perform optical power measurements and BER testing during commissioning.
-
Set threshold alarms for early detection of fiber degradation or connector contamination.
Best practice: Integrate QSFP+ monitoring into centralized NMS or DCIM platforms.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
-
Reserve fiber count and rack space for future speed upgrades.
-
Design cabling paths to support 100G/400G migration using existing infrastructure where possible.
-
Consider parallel fiber topology compatibility when planning MPO/MTP trunk systems.
Best practice: Choose QSFP+ optics and cabling architectures that align with long-term network evolution plans.
✳️ Troubleshooting Common 40G QSFP+ Issues
Effective troubleshooting of 40G QSFP+ links requires systematic analysis of optical power, fiber quality, cabling topology, and module compatibility. The following covers the most common failure scenarios and proven resolution steps.

❗ Link Down or No Light Detected
Possible causes:
-
Fiber polarity mismatch (especially with MPO/MTP cables)
-
Dirty or damaged connectors
-
Incorrect module type or wavelength mismatch
-
Incompatible transceiver coding
Resolution steps:
-
Verify Tx/Rx polarity mapping and MPO key orientation
-
Inspect and clean connectors using fiber cleaning tools
-
Confirm module type (SR4/LR4/ER4/BiDi) matches fiber infrastructure
-
Check switch compatibility list and firmware support
❗ High Bit Error Rate (BER) or Packet Loss
Possible causes:
Resolution steps:
-
Measure Tx/Rx optical power via DOM/DDM
-
Perform OTDR testing to locate excessive loss points
-
Reduce connector count and replace degraded patch cords
❗ Intermittent Link Flapping
Possible causes:
Resolution steps:
-
Check DOM temperature and voltage stability
-
Improve airflow and thermal management
-
Replace marginal optics or suspect cabling
❗ Module Not Recognized by Switch
Possible causes:
Resolution steps:
❗ Breakout Link Not Working (4×10G)
Possible causes:
Resolution steps:
-
Confirm breakout cable specification
-
Configure port mode to 40G → 4×10G
-
Validate lane assignments on both ends
Quick Troubleshooting Checklist
-
✔ Module type matches fiber and distance
-
✔ Fiber connectors inspected and cleaned
-
✔ DOM power levels within vendor range
-
✔ Switch compatibility validated
-
✔ Proper port breakout configuration
✳️ 40G QSFP+ FAQs

Q1: What Is a 40G QSFP+ Module?
A 40G QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) module is a hot-pluggable optical or electrical transceiver that delivers 40 Gbps aggregate bandwidth using four parallel 10.3125 Gbps lanes. It is widely used in data centers, campus backbones, and metro networks for high-density, high-speed interconnects.
Q2: What Fiber Types Are Used for 40G QSFP+?
-
Multimode fiber (MMF): SR4 and CSR4 modules using MPO/MTP connectors.
-
Single-mode fiber (SMF): LR4, ER4, ZR4, and PSM4 modules using LC or MPO/MTP connectors.
-
Duplex MMF / SMF reuse: BiDi modules for brownfield upgrades.
Q3: What Is the Difference Between SR4, LR4, ER4, and ZR4?
-
40G-SR4: Short reach over MMF, up to ~150 m.
-
40G-LR4: Long reach over SMF, up to ~10 km.
-
40G-ER4: Extended reach over SMF, up to ~40 km.
-
40G-ZR4: Vendor-specific ultra-long reach, typically up to ~80 km.
Q4: Can a 40G QSFP+ Port Be Broken Out Into 4×10G?
Yes. Most QSFP+ ports support breakout mode, allowing one 40G port to split into four independent 10G SFP+ links using appropriate breakout DAC, AOC, or fiber cables. Switch configuration must explicitly enable breakout mode.
Q5: Are 40G QSFP+ Modules Hot-Swappable?
Yes. QSFP+ modules are fully hot-swappable, allowing insertion and removal without powering down the host device, provided standard handling and safety procedures are followed.
Q6: How Much Power Does a Typical 40G QSFP+ Module Consume?
Actual values vary by vendor, temperature, and optical architecture.
Q7: Are Third-Party 40G QSFP+ Modules Compatible With Major Switch Brands?
In most cases, yes—if properly coded and MSA-compliant. However, many switch vendors enforce firmware-based compatibility controls. Always verify platform compatibility and DOM functionality before large-scale deployment.
Q8: When Should You Choose 40G Instead of 100G?
40G remains suitable for existing 40G infrastructure, cost-sensitive upgrades, and legacy platforms. However, for new data center builds, 100G QSFP28 typically offers better long-term scalability and cost efficiency per bit.
✳️ Conclusion
40G QSFP+ modules remain a proven, reliable, and widely deployed solution for high-density networking across data centers, campus backbones, and metro networks. With multiple optical variants—SR4, LR4, ER4, ZR4, CSR4, PSM4, and BiDi—QSFP+ offers flexible deployment options that balance distance, cost, fiber infrastructure, and performance requirements.
By understanding optical reach, fiber type, breakout capabilities, standards compliance, and interoperability, network engineers and system architects can design scalable, stable, and cost-efficient 40G infrastructures while maintaining a smooth upgrade path toward 100G and beyond.
Key Takeaways
-
Choose SR4 / CSR4 for short-reach, high-density data center environments.
-
Use LR4 / ER4 / ZR4 for campus, metro, and long-distance single-mode links.
-
Leverage breakout cables (4×10G) to maximize port utilization and flexibility.
-
Always verify QSFP+ standards compliance, DOM support, and platform compatibility before deployment.

Looking for high-performance, fully compatible 40G QSFP+ modules for your next deployment?
Visit the LINK-PP Official Store to explore our complete range of 40G QSFP+ transceivers, breakout cables, and optical connectivity solutions. All products are MSA-compliant, rigorously tested for multi-vendor interoperability, and engineered for carrier-grade reliability.
👉 Contact LINK-PP’s technical team today for expert consultation, compatibility verification, and customized optical connectivity solutions tailored to your network architecture.