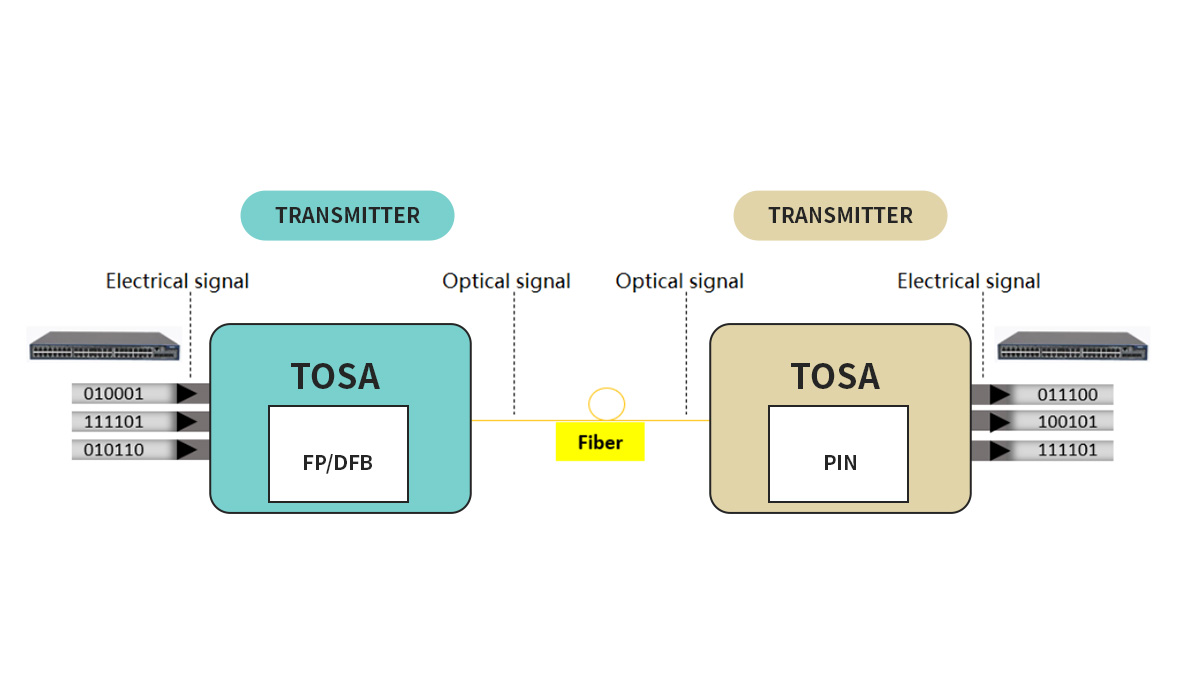
🔷 1310nm vs 850nm vs 1550nm Optical Modules
Choosing the right optical wavelength is a key design decision in fiber-optic networks. 850nm, 1310nm, and 1550nm optical modules are each optimized for different fiber types, distances, and deployment goals. Understanding their differences helps avoid overdesign, compatibility issues, and unnecessary cost.

The table below provides a high-level comparison from a practical networking perspective.
Wavelength Comparison Overview
| Parameter | 850nm Optical Module | 1310nm Optical Module | 1550nm Optical Module |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Multimode fiber (OM3/OM4) | Single-mode fiber (OS2) | Single-mode fiber (OS2) |
| Typical Distance | Short reach (hundreds of meters) | Up to 10km | 40km and beyond |
| Dispersion | Higher modal dispersion | Low chromatic dispersion | Very low dispersion |
| Cost Level | Lower (short reach) | Moderate | Higher |
| Common Use Cases | Data center short links | Campus, enterprise, metro edge | Long-haul, metro core |
This comparison highlights how wavelength choice directly impacts network architecture.
850nm vs 1310nm: Multimode vs Single-Mode
The most fundamental difference between 850nm and 1310nm optical modules lies in fiber type:
-
850nm modules are designed for multimode fiber and excel at short distances inside data centers
-
1310nm modules operate over single-mode fiber, enabling longer links and better scalability
When link distance exceeds the practical limits of multimode fiber, 1310nm becomes the more reliable and future-proof option.
1310nm vs 1550nm: Balanced Reach vs Long-Haul Performance
Both 1310nm and 1550nm modules use single-mode fiber, but they serve different purposes:
-
1310nm optical modules are optimized for short-to-medium distances with lower system complexity
-
1550nm optical modules support much longer distances but typically require higher optical budgets and stricter design considerations
For many enterprise and access networks, 1310nm provides sufficient reach without the added cost and complexity of long-haul solutions.
How to Choose the Right Wavelength
In practical terms, wavelength selection should be based on:
-
Required transmission distance
-
Existing fiber infrastructure
-
Network scalability and budget constraints
For most short-to-medium range single-mode deployments, 1310nm optical modules represent the most balanced choice, offering reliable performance without overengineering the link.
🔷 Advantages and Limitations of 1310nm Single Mode Modules
1310nm single mode optical transceivers are widely adopted because they deliver a practical balance between performance, distance, and cost. However, like any optical solution, they are designed for specific scenarios and come with both strengths and constraints. Understanding these factors helps ensure the module is used where it performs best.
Advantages of 1310nm Single Mode Optical Modules
From a network design perspective, 1310nm modules offer several clear advantages.
-
Balanced transmission distance
Supporting link lengths up to 10km, 1310nm modules cover most campus, enterprise, and access network requirements without additional complexity. -
Low dispersion over single-mode fiber
Operating at 1310nm minimizes chromatic dispersion, helping maintain signal integrity and low bit error rates across typical deployment distances. -
Broad standards and device compatibility
1310nm is a widely standardized wavelength across Ethernet and telecom protocols, making these modules compatible with a broad range of switches, routers, and network equipment. -
Cost-effective for single-mode deployments
Compared with long-reach 1550nm solutions, 1310nm modules generally offer lower system cost while still delivering reliable performance.
Limitations of 1310nm Single Mode Optical Modules
Despite their versatility, 1310nm modules are not ideal for every use case.
-
Limited reach compared to 1550nm
For long-haul or metro-core links exceeding typical campus distances, 1310nm modules may not provide sufficient reach without amplification. -
Not suitable for multimode fiber
1310nm single mode optical modules are designed specifically for single-mode fiber and cannot operate correctly over multimode infrastructure. -
Less optimal for ultra-short links
In very short-distance, high-density environments, such as within a single data hall, multimode 850nm solutions may offer lower overall cost and simpler cabling.
When 1310nm Is the Right Choice
In practice, 1310nm single mode modules are best suited for networks that require:
-
Stable performance over short-to-medium distances
-
Scalability beyond multimode fiber limits
-
A standardized, widely supported optical solution
By recognizing both the advantages and limitations, network planners can confidently determine when 1310nm single mode optical modules are the most appropriate option.
🔷 How to Choose the Right 1310nm Optical Module
Choosing the right 1310nm optical transceiver is less about finding the “highest specification” and more about matching the module’s capabilities to real network requirements. A well-matched module improves link stability, simplifies deployment, and avoids unnecessary cost or overdesign.

From a practical perspective, selection can be broken down into a few key decision factors.
Match the Required Data Rate
The first step is to confirm the data rate supported by your network equipment and application.
-
1G (Gigabit Ethernet): Access and aggregation layers
-
10G: Enterprise backbones and data center interconnections
-
Higher-speed variants: Upgrade paths in modern networks
The optical module must support the same data rate on both ends of the link to ensure proper operation.
Confirm Transmission Distance Requirements
1310nm single mode optical modules are commonly designed for link distances up to 10km, which covers most campus and enterprise scenarios.
When evaluating distance, consider:
-
Actual fiber length, not just straight-line distance
-
Connector and splice loss along the link
-
Required optical power margin for long-term stability
Selecting a module that comfortably meets, rather than barely reaches, the distance requirement improves reliability.
Verify Fiber Type and Connector Compatibility
A 1310nm optical module is intended for single-mode fiber, typically OS2. In addition, physical compatibility must be checked:
-
Fiber type matches module design (single-mode only)
-
Connector type (commonly LC duplex) matches existing cabling
-
Polarity and cabling standards are consistent across the link
These details help prevent installation issues and troubleshooting later.
Ensure Device and Vendor Compatibility
Although optical standards are widely adopted, compatibility can still vary across network platforms.
-
Check whether the module supports the target switch or router
-
Verify firmware or coding requirements if applicable
-
Consider interoperability in multi-vendor environments
Reliable compatibility reduces deployment risk and simplifies future expansion.
Balance Performance, Scalability, and Cost
Finally, consider how the optical module fits into long-term network planning.
-
Avoid over-specifying reach beyond actual needs
-
Choose standardized solutions for easier replacement
-
Plan for future bandwidth upgrades when possible
A properly selected 1310nm optical module delivers predictable performance today while supporting scalable network growth, making it a practical choice for many single-mode fiber deployments.
🔷 LINK-PP 1310nm Single Mode Fiber Optical Module Overview
LINK-PP 1310nm single mode fiber optical modules are designed to support stable and standards-compliant optical transmission across common enterprise, data center, and access network environments. Rather than focusing on a single niche application, these modules are positioned as general-purpose single-mode solutions that align with widely adopted Ethernet and optical communication standards.
Design Focus and Technical Positioning
LINK-PP’s 1310nm optical modules are engineered around practical deployment requirements:
-
Operation at the standard 1310nm wavelength for single-mode fiber
-
Support for commonly used form factors such as SFP and SFP+
-
Transmission distances suitable for typical campus and enterprise links (up to 10km)
This positioning allows the modules to integrate smoothly into existing single-mode fiber infrastructures without requiring special design considerations.
Compatibility and Interoperability
A key consideration in real-world deployments is cross-platform compatibility. LINK-PP 1310nm single mode fiber optical modules are developed with interoperability in mind:
-
Compliance with mainstream optical and Ethernet standards
-
Designed for use in multi-vendor network environments
-
Suitable for switches, routers, and network devices across common platforms
This helps reduce integration risk and simplifies both initial deployment and future network expansion.
Quality Control and Reliability Considerations
Consistent optical performance depends heavily on manufacturing and testing processes. LINK-PP emphasizes:
-
Module-level functional and optical performance testing
-
Verification of transmitter and receiver stability
-
Consistency across production batches
These practices help ensure predictable behavior in long-term network operation, particularly in environments where reliability is a priority.
Typical Deployment Scenarios
LINK-PP 1310nm single mode fiber optical modules are commonly applied in:
-
Enterprise and campus network backbones
-
Inter-building single-mode fiber links
-
Data center connectivity requiring short-to-medium reach
By aligning standard specifications with practical deployment needs, LINK-PP’s 1310nm optical modules serve as a reference solution within modern single-mode optical networks.
🔷 FAQs About 1310nm Single Mode Fiber Optical Transceivers
Do 1310nm optical modules require single-mode fiber?
Yes. 1310nm optical modules are designed specifically for single-mode fiber (typically OS2) and are not suitable for multimode fiber deployments.
Is a 1310nm optical module suitable for distances up to 10km?
Yes. Standard 1310nm single mode fiber optical modules are commonly specified for transmission distances up to 10km under normal link conditions.
Can I use a 1310nm optical module in any SFP or SFP+ port?
Only if the port supports the same data rate and standard. Physical fit alone is not sufficient; electrical and protocol compatibility must match.
Should I choose 1310nm instead of 850nm for inter-building links?
Yes. For inter-building or campus links that exceed multimode distance limits, 1310nm single mode optical modules are the more appropriate choice.
Is 1310nm a better choice than 1550nm for enterprise networks?
In most cases, yes. If long-haul transmission is not required, 1310nm provides sufficient reach without the added complexity of 1550nm solutions.
Are 1310nm single mode optical modules still widely used today?
Yes. 1310nm remains a standardized and commonly deployed wavelength in enterprise, data center, and access networks.
🔷 Summary: Is a 1310nm Single Mode Fiber Optical Module Right for You?
A 1310nm single mode fiber optical transceiver is the right choice when your network requires stable, standards-based optical transmission over short-to-medium distances without the complexity of long-haul solutions. It remains a practical default for enterprise networks, campus backbones, data center interconnections, and access-layer deployments where single-mode fiber is already in place.
From a technical and operational perspective, 1310nm modules stand out because they offer:
-
Sufficient reach for most real-world single-mode links
-
Broad compatibility across common Ethernet standards and devices
-
Predictable performance that simplifies network design and scaling
Rather than chasing maximum distance or niche specifications, choosing a 1310nm single mode optical module is often about matching proven technology to actual deployment needs—a balance that continues to make this wavelength relevant in modern optical networks.
If you’re evaluating reliable, standards-compliant 1310nm single mode fiber optical modules for your network, you can explore practical solution options at the LINK-PP Official Store, where these modules are positioned to support real-world enterprise and infrastructure deployments.