As data centers continue to migrate from 10G to 25 Gigabit Ethernet, SFP28 25G SR has become a foundational optical transceiver for high-speed, short-distance connectivity. Built on the SFP28 form factor, this module enables single-lane 25Gbps transmission over multimode fiber, making it ideal for dense switch ports and modern leaf-spine architectures. Thanks to its balance of performance, cost efficiency, and power consumption, SFP28 25G SR is now widely deployed in enterprise networks, cloud data centers, and high-performance computing environments.
For many network engineers and IT buyers, a common question is “what is SFP28 25G SR and how is it used?” This guide provides a clear and practical explanation of the SFP28 25G SR transceiver, covering its definition, technical specifications, IEEE standards compliance, and real-world use cases. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how SFP28 25G SR works, where it fits in a 25G Ethernet network, and how to determine whether it is the right optical solution for your infrastructure.
✅ What Is SFP28 25G SR?
SFP28 25G SR is a short-range 25 Gigabit Ethernet (25GbE) optical transceiver that delivers 25Gbps per lane over multimode fiber using an 850nm wavelength. It is designed for high-density data center networks where short-distance, high-bandwidth connectivity is required.

Definition of the SFP28 25G SR Module
An SFP28 25G SR module is a hot-pluggable optical transceiver built in the SFP28 form factor. It converts electrical signals from switches or network interface cards into optical signals for transmission over multimode fiber (MMF), and then converts them back to electrical signals at the receiving end. The module is optimized for short-reach links commonly found inside data centers.
Data Rate: 25Gbps per Lane
SFP28 25G SR supports a single-lane data rate of 25 gigabits per second, which is the defining characteristic of SFP28 technology. This single-lane architecture allows higher bandwidth compared to 10G SFP+ modules while maintaining the same physical size and port density.
Transmission Type: Short Range (SR)
The SR (Short Range) designation indicates that the module is intended for short-distance transmission. SFP28 25G SR operates at an 850nm wavelength and is specifically designed for multimode fiber, making it ideal for distances typically under 100 meters within data center environments.
Standard Compliance (IEEE 802.3by / IEEE 802.3cc)
SFP28 25G SR is compliant with IEEE 802.3by and IEEE 802.3cc standards, which define the physical layer specifications for 25GbE over multimode fiber. Standards compliance ensures predictable performance, interoperability across vendors, and reliable operation in multi-vendor network deployments.
Typical Use Scenarios
SFP28 25G SR is most commonly used in:
-
Server-to-switch (Top-of-Rack) connections
-
Short-reach switch-to-switch links
-
Leaf-spine data center architectures
-
High-density 25G Ethernet deployments
These use cases highlight why SFP28 25G SR has become a default optical choice for modern data centers.
✅ Key Specifications of SFP28 25G SR
The SFP28 25G SR transceiver is defined by a set of standardized technical specifications that ensure consistent performance and broad interoperability across networking platforms. Understanding these key parameters helps network designers quickly evaluate whether SFP28 25G SR meets the requirements of their 25G Ethernet deployment.
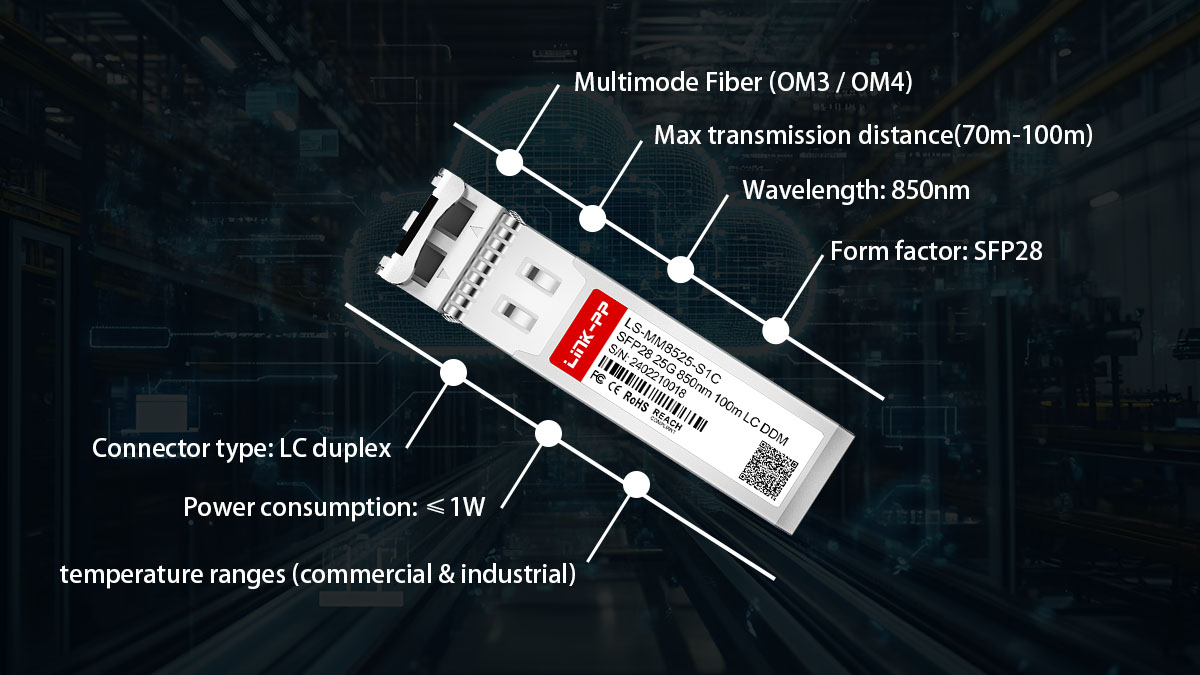
SFP28 25G SR Specifications (Quick Overview)
-
Form factor: SFP28
-
Data rate: 25Gbps (single lane)
-
Wavelength: 850nm
-
Fiber type: Multimode Fiber (OM3 / OM4)
-
Maximum distance:
-
OM3: up to 70 meters
-
OM4: up to 100 meters
-
Connector: LC duplex
-
Power consumption: Typically ≤ 1W
-
Operating temperature:
Form Factor: SFP28
SFP28 25G SR uses the SFP28 (Small Form-Factor Pluggable 28) form factor, which is physically identical in size to SFP and SFP+ modules. This compact, hot-pluggable design allows for high port density on switches and network interface cards (NICs), enabling easy upgrades from 10G to 25G without changes to chassis design.
Wavelength: 850nm
Operating at an 850nm wavelength, SFP28 25G SR relies on short-wavelength optics optimized for multimode fiber transmission. This wavelength is well suited for short-reach links, offering stable performance and lower optical component costs compared to long-wavelength (1310nm or 1550nm) solutions.
Fiber Type: Multimode Fiber (OM3 / OM4)
SFP28 25G SR is designed for multimode fiber (MMF), specifically OM3 and OM4 fiber types. These fibers are commonly deployed inside data centers and enterprise buildings, making SFP28 25G SR an ideal option for environments with existing MMF infrastructure.
Maximum Transmission Distance
The maximum supported distance depends on the multimode fiber type used:
These distances cover most in-rack, adjacent-rack, and row-level connections typically found in modern data centers.
Connector Type: LC Duplex
SFP28 25G SR modules use a standard LC duplex connector, providing a compact and reliable optical interface. LC connectors are widely adopted in data centers due to their small size, secure connection, and compatibility with high-density patch panels and cabling systems.
Power Consumption
Power efficiency is another key advantage of SFP28 25G SR. Most modules have a typical power consumption of less than 1 watt, which helps reduce overall energy usage and heat generation in high-density switch deployments.
Operating Temperature Ranges
Standard SFP28 25G SR modules are rated for a commercial temperature range of 0°C to 70°C, suitable for controlled data center environments. For harsher conditions, some vendors also offer industrial-grade versions supporting temperatures from –40°C to 85°C, ensuring reliable operation in edge or specialized installations.
By clearly defining these specifications, SFP28 25G SR makes it easy for network engineers and IT professionals to assess compatibility, performance, and deployment feasibility. In the next section, we’ll explore how SFP28 25G SR works and how these specifications translate into real-world network performance.
✅ How Does SFP28 25G SR Work?
SFP28 25G SR works by converting high-speed electrical signals from network equipment into optical signals for short-range transmission over multimode fiber, and then converting them back into electrical signals at the receiving end. This process enables reliable 25Gbps data transfer within data centers while maintaining low latency and high signal integrity.
How SFP28 25G SR Works (Quick Explanation)
-
An electrical 25Gbps signal is generated by the switch ASIC or NIC.
-
The SFP28 25G SR module converts the electrical signal into an optical signal.
-
The optical signal is transmitted over multimode fiber using an 850nm light source.
-
At the destination, the optical signal is converted back into an electrical signal.
Electrical to Optical Signal Conversion
Inside an SFP28 25G SR module, a high-speed electrical-to-optical (E/O) conversion takes place. The electrical data stream from the host device is processed by internal circuitry, including a laser driver and modulation components, before being converted into optical pulses. On the receiving side, a photodiode performs the reverse optical-to-electrical (O/E) conversion, ensuring accurate data recovery at 25Gbps.
Role of VCSEL Lasers
SFP28 25G SR modules typically use VCSEL (Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser) technology as the light source. VCSEL lasers are well suited for short-range, high-speed transmission over multimode fiber because they offer:
-
Stable performance at 850nm
-
Lower power consumption
-
Cost-effective manufacturing
-
Efficient coupling with multimode fiber
These characteristics make VCSEL-based optics ideal for dense data center environments where scalability and energy efficiency are critical.
Single-Lane 25Gbps Architecture
Unlike higher-speed modules that rely on multiple parallel lanes, SFP28 25G SR uses a single-lane 25Gbps architecture. This means all data is transmitted over one electrical lane and one optical channel. The single-lane design simplifies cabling, reduces complexity, and allows SFP28 to deliver higher bandwidth without increasing the physical size of the module.
Differences Between SFP+ and SFP28 Signaling
Although SFP+ and SFP28 modules share the same physical form factor, their signaling capabilities are fundamentally different:
SFP28 achieves higher speeds through improved signal integrity, tighter electrical specifications, and enhanced forward error correction (FEC) at the system level. As a result, SFP28 25G SR enables significantly higher performance while remaining backward-compatible in terms of physical port design.
By combining efficient electrical-to-optical conversion, VCSEL laser technology, and single-lane 25Gbps signaling, SFP28 25G SR delivers a reliable and scalable short-range optical solution for 25G Ethernet networks. In the next section, we’ll explore the most common use cases where these technical advantages provide real-world value.
✅ Common Use Cases for SFP28 25G SR
SFP28 25G SR is primarily used for short-reach, high-bandwidth connections inside data centers where 25GbE links are required over multimode fiber. Its performance, cost efficiency, and compact form factor make it a standard optical choice for a wide range of modern network architectures.
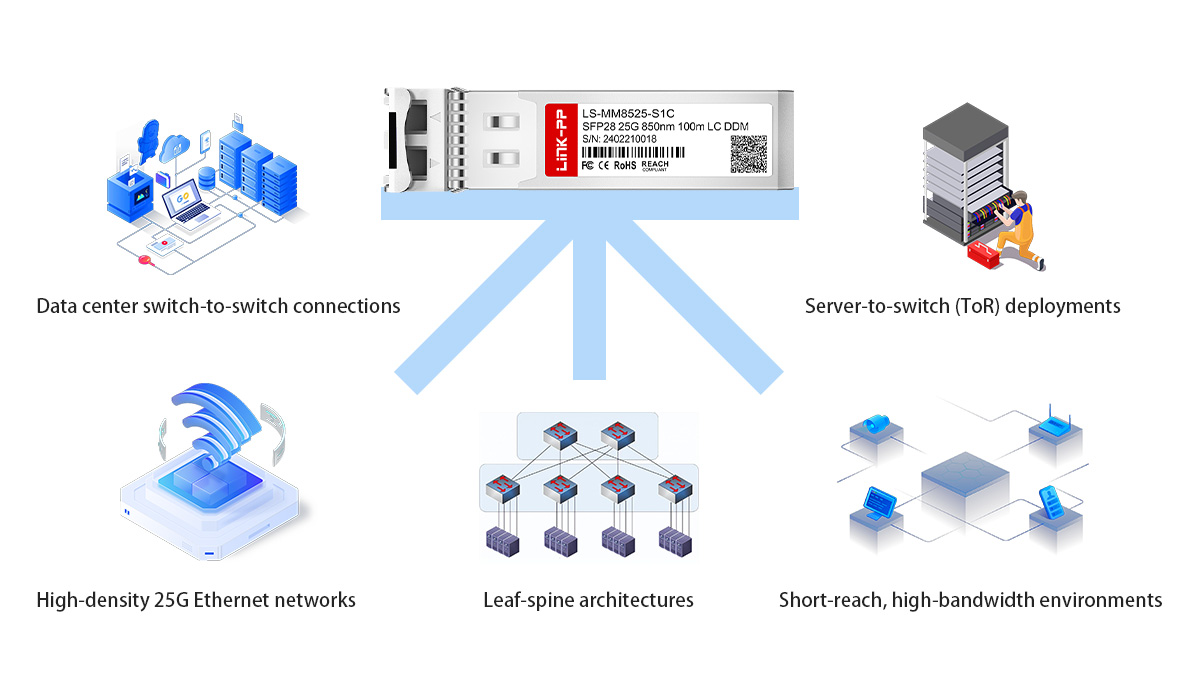
Typical Use Cases of SFP28 25G SR (Quick List)
-
Data center switch-to-switch connections
-
Server-to-switch (Top-of-Rack) deployments
-
High-density 25G Ethernet networks
-
Leaf-spine architectures
-
Short-reach, high-bandwidth environments
Data Center Switch-to-Switch Connections
One of the most common applications for SFP28 25G SR is switch-to-switch connectivity within data centers. These links often span short distances between top-of-rack, aggregation, or leaf switches. Using multimode fiber and 850nm optics, SFP28 25G SR provides reliable, low-latency performance while keeping optical costs under control.
Server-to-Switch (ToR) Deployments
SFP28 25G SR is widely used for server-to-switch connections, particularly in Top-of-Rack (ToR) architectures. Many modern servers and network interface cards support 25GbE, making SFP28 25G SR an ideal choice for connecting servers to ToR switches within the same rack or adjacent racks.
High-Density 25G Ethernet Networks
Thanks to the compact SFP28 form factor and low power consumption, SFP28 25G SR enables high port density on switches. This is especially important in environments where hundreds or thousands of 25G ports are deployed in a limited space. The ability to reuse existing multimode fiber infrastructure further enhances scalability and reduces deployment costs.
Leaf-Spine Architectures
In leaf-spine network architectures, SFP28 25G SR is commonly used for short-distance links between leaf switches and servers, as well as certain leaf-to-spine connections when distances permit. Its consistent performance and IEEE standards compliance make it suitable for building predictable, high-throughput fabrics in modern data centers.
Short-Reach, High-Bandwidth Environments
Overall, SFP28 25G SR is best suited for short-reach, high-bandwidth environments where distances are typically under 100 meters and performance requirements are high. Examples include cloud data centers, enterprise data halls, colocation facilities, and high-performance computing (HPC) clusters that demand fast, reliable interconnects over short distances.
By covering these common use cases, it becomes clear why SFP28 25G SR has become a default optical solution for 25G Ethernet inside data centers. In the next section, we’ll compare SFP28 25G SR with other 25G optical and cabling options to help you choose the right solution for your network.
✅ SFP28 25G SR vs Other 25G Optical Modules
When designing a 25G Ethernet network, choosing the right transceiver depends on distance, fiber type, cost, and deployment flexibility. SFP28 25G SR is often compared with SFP28 25G LR and non-optical alternatives such as 25G DAC and AOC. The comparisons below highlight the key differences to help you make an informed decision.
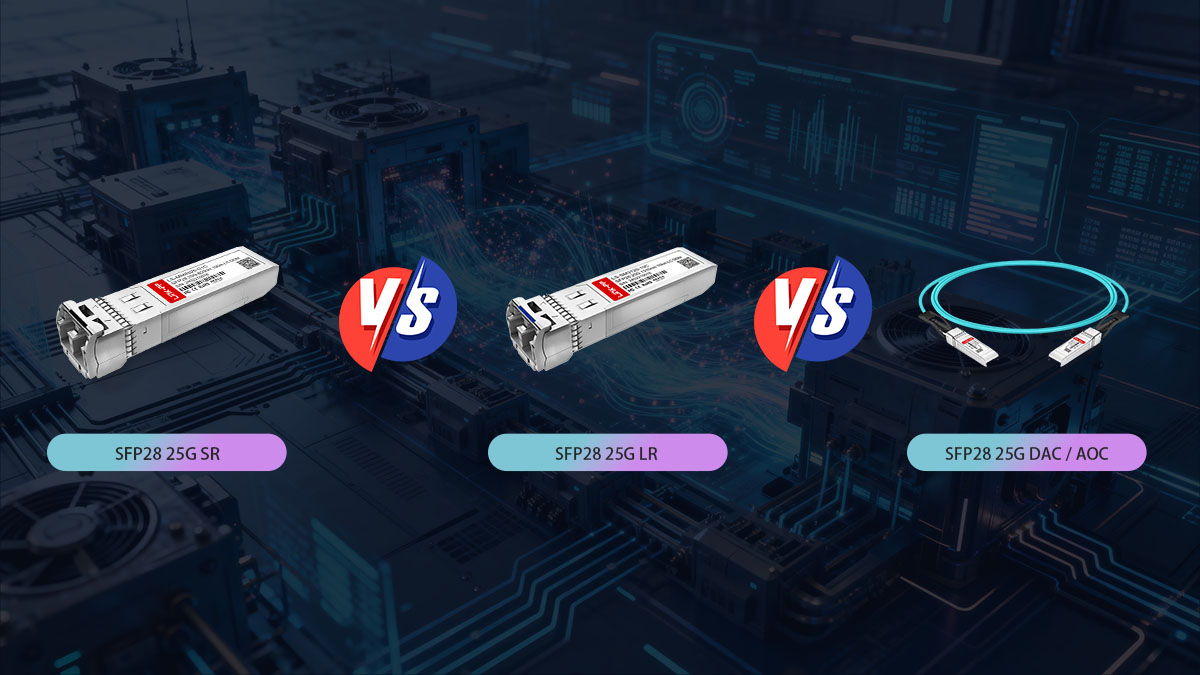
SFP28 25G SR vs SFP28 25G LR
The main difference between SFP28 25G SR and SFP28 25G LR is transmission distance and fiber type. While both support 25Gbps over a single lane, they are optimized for very different network scenarios.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature |
SFP28 25G SR |
SFP28 25G LR |
| Wavelength |
850nm |
1310nm |
| Fiber type |
Multimode (OM3 / OM4) |
Single-mode (OS2) |
| Maximum distance |
70m (OM3) / 100m (OM4) |
Up to 10km |
| Typical cost |
Lower |
Higher |
| Best use case |
Data center short links |
Long-reach links |
Distance Comparison
SFP28 25G SR is designed for short-range transmission, typically within data center halls. In contrast, SFP28 25G LR supports distances of up to 10 kilometers, making it suitable for campus networks, metro links, or inter-building connections.
Fiber Type: MMF vs SMF
-
SFP28 25G SR uses multimode fiber (MMF), which is commonly installed inside data centers and offers lower transceiver costs.
-
SFP28 25G LR uses single-mode fiber (SMF), which supports longer distances but requires more expensive optical components.
Cost Considerations
From a cost perspective, SFP28 25G SR is significantly more economical than LR modules. Both the transceiver itself and multimode fiber cabling are generally less expensive, making SR the preferred option when distance requirements allow.
Typical Deployment Scenarios
-
Choose SFP28 25G SR for in-rack, adjacent-rack, or row-level connections inside data centers.
-
Choose SFP28 25G LR for building-to-building links or long-distance enterprise networks.
SFP28 25G SR vs SFP28 25G DAC / AOC
Another common comparison is between optical transceivers and direct-attach alternatives such as DAC and AOC cables.
Optical vs Copper Solutions
-
SFP28 25G SR is an optical solution using multimode fiber.
-
25G DAC (Direct Attach Copper) uses passive or active copper cables.
-
25G AOC (Active Optical Cable) uses optical fiber with integrated transceivers.
Reach and Flexibility Comparison
| Solution |
Typical Reach |
Flexibility |
Use Case |
| SFP28 25G SR |
Up to 100m |
High |
Structured cabling |
| 25G DAC |
Up to 3–5m |
Low |
In-rack connections |
| 25G AOC |
Up to 30m |
Medium |
Short inter-rack links |
This comparison table helps users quickly identify the right solution based on reach and deployment needs.
Power Consumption and Cost
-
25G DAC has the lowest power consumption and cost, but very limited reach.
-
25G AOC consumes more power than DAC but offers longer reach and better signal integrity.
-
SFP28 25G SR consumes slightly more power than DAC but provides superior flexibility, scalability, and compatibility with structured fiber cabling.
In summary, SFP28 25G SR is the best choice for short-range, high-density 25G Ethernet deployments where flexibility and scalability are required. DAC is ideal for ultra-short connections, while LR modules are better suited for long-distance applications. In the next section, we’ll explore the advantages and limitations of SFP28 25G SR to further refine your selection.
✅ Advantages and Limitations of SFP28 25G SR
SFP28 25G SR offers an excellent balance of performance and cost for short-range 25G Ethernet links, but it is not designed for every networking scenario. Understanding both its advantages and limitations helps ensure the right transceiver is selected for each deployment.
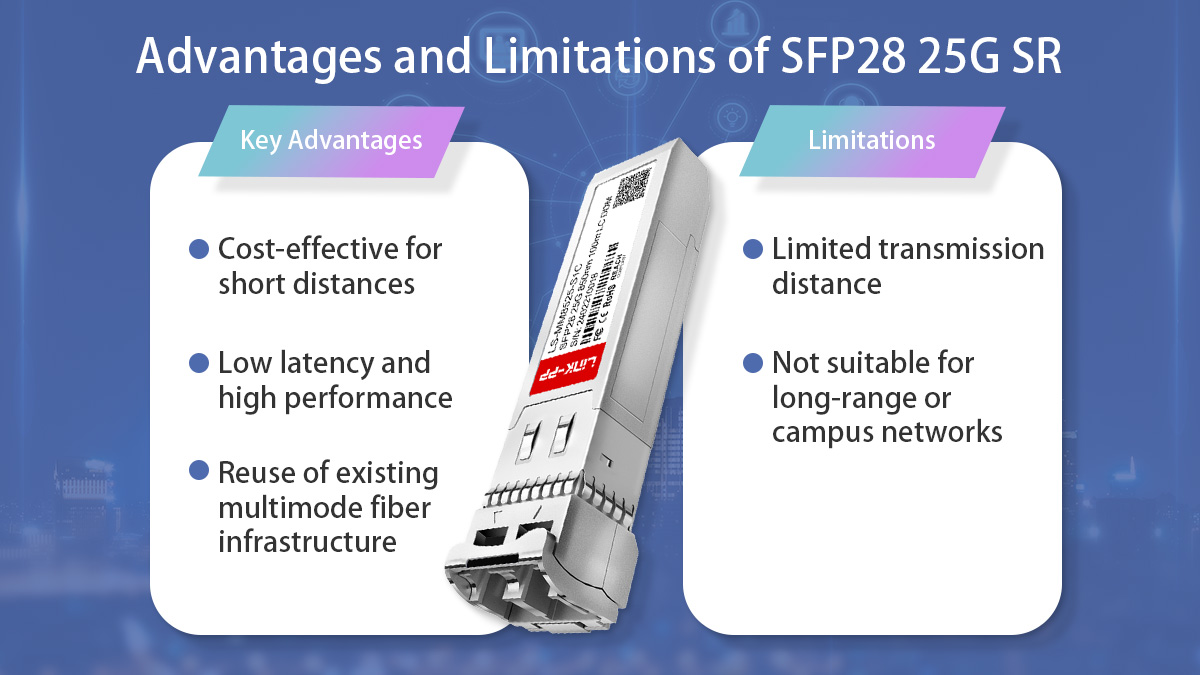
SFP28 25G SR Pros and Cons (Quick Summary)
Advantages
-
Cost-effective for short-distance links
-
Low latency and high performance
-
Reuses existing multimode fiber infrastructure
Limitations
Key Advantages
Cost-Effective for Short Distances
One of the biggest advantages of SFP28 25G SR is its cost efficiency. Compared to long-range optics, SR modules use simpler optical components and multimode fiber, which significantly reduces overall deployment costs. For data center links under 100 meters, SFP28 25G SR provides the most economical way to achieve 25Gbps bandwidth.
Low Latency and High Performance
SFP28 25G SR delivers low-latency, high-throughput performance thanks to its single-lane 25Gbps architecture and short optical reach. The use of VCSEL-based 850nm optics minimizes signal processing overhead, making SR modules well suited for latency-sensitive environments such as cloud computing and high-performance workloads.
Reuse of Existing Multimode Fiber Infrastructure
Many data centers already have OM3 or OM4 multimode fiber installed. SFP28 25G SR allows operators to reuse this existing cabling when upgrading from 10G to 25G Ethernet, avoiding costly re-cabling projects and accelerating deployment timelines.
Limitations
Limited Transmission Distance
The primary limitation of SFP28 25G SR is its restricted transmission range. With a maximum distance of 70 meters on OM3 fiber and 100 meters on OM4 fiber, it is not suitable for applications that require longer reach.
Not Suitable for Long-Range or Campus Networks
Because it relies on multimode fiber and short-wavelength optics, SFP28 25G SR is not designed for campus, metro, or inter-building networks. For these scenarios, long-range options such as SFP28 25G LR over single-mode fiber are a better choice.
Overall, SFP28 25G SR is an ideal solution for short-reach, high-density data center deployments, as long as its distance limitations are clearly understood. In the next section, we’ll look at compatibility and interoperability considerations to ensure smooth integration with network equipment.
✅ Compatibility and Interoperability
When deploying SFP28 25G SR, compatibility and interoperability are critical to ensure stable performance and avoid unnecessary troubleshooting. Although SFP28 transceivers follow industry standards, factors such as switch platforms, firmware, and vendor coding can directly impact successful deployment.

Supported Switches and NICs
SFP28 25G SR modules are widely supported by mainstream networking vendors and platforms. They are commonly used with 25G-capable switches and network interface cards (NICs) from manufacturers such as:
As long as the switch or NIC includes SFP28 ports and supports 25GbE, SFP28 25G SR modules can typically be used without issue. However, it is always recommended to verify the device hardware compatibility list (HCL) or datasheet before deployment.
Backward Compatibility Considerations
Physically, SFP28 shares the same form factor as SFP and SFP+, but electrical signaling is different. Key compatibility points include:
-
An SFP28 port can usually accept an SFP+ module, allowing 10GbE operation on a 25G-capable port (depending on switch support).
-
An SFP+ port cannot support SFP28 25G SR, as it lacks the required electrical bandwidth.
Understanding this distinction is important when planning phased upgrades from 10G to 25G Ethernet.
MSA Compliance and Third-Party Optics
Most SFP28 25G SR modules are designed in accordance with MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) and IEEE standards, ensuring interoperability across vendors. MSA-compliant optics allow network operators to choose third-party transceivers that offer the same performance as OEM modules at a lower cost.
High-quality third-party SFP28 25G SR modules are typically:
This makes them a popular choice in cost-sensitive or large-scale deployments.
Importance of Vendor Coding
Despite MSA compliance, many network vendors implement vendor-specific EEPROM coding to identify and validate transceivers. If a module is not correctly coded, the switch may:
For this reason, it is essential to ensure that SFP28 25G SR modules are properly coded for the target switch brand (for example, Cisco-compatible or Arista-compatible). Reputable third-party suppliers offer vendor-coded optics that ensure seamless recognition and full functionality.
In summary, SFP28 25G SR offers broad compatibility across modern 25G switches and NICs, but careful attention must be paid to backward compatibility, MSA compliance, and vendor coding. In the next section, we’ll discuss how to choose the right SFP28 25G SR module for your specific network environment and requirements.
✅ How to Choose the Right SFP28 25G SR Module
Selecting the right SFP28 25G SR module involves more than just matching speed and form factor. By evaluating hardware compatibility, cabling, operating conditions, and long-term network plans, you can ensure reliable performance and cost-effective scalability.
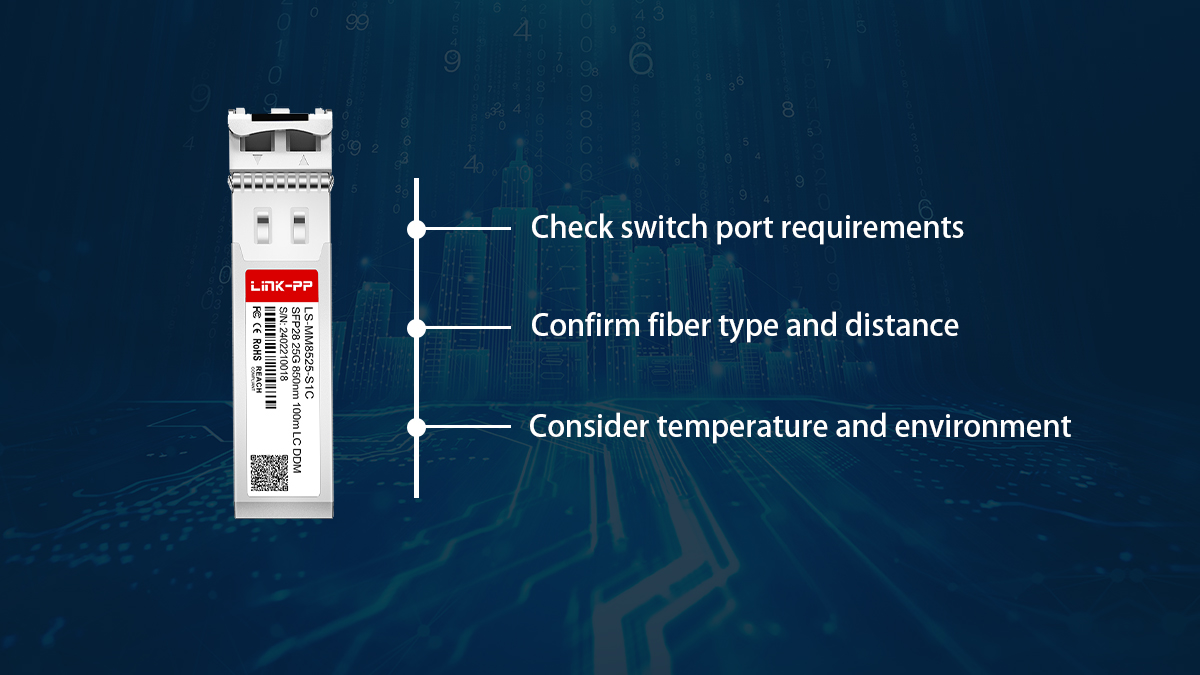
Check Switch Port Requirements
The first step is to verify that your switch or NIC supports SFP28 and 25GbE. Key points to confirm include:
-
The port type is SFP28, not SFP+
-
The device supports 25GbE operation on that port
-
Firmware and OS versions allow third-party optics (if applicable)
Always consult the switch datasheet or hardware compatibility list to avoid mismatches.
Confirm Fiber Type and Distance
SFP28 25G SR is designed specifically for multimode fiber. Before deployment, confirm:
If your network requires longer reach or uses single-mode fiber, a different transceiver (such as 25G LR) may be more appropriate.
Consider Temperature and Environment
Most SFP28 25G SR modules are rated for commercial temperature ranges (0°C to 70°C), which is sufficient for standard data center environments. For edge deployments or harsher conditions, consider modules that support:
Choosing the right environmental rating helps ensure long-term reliability.
OEM vs Third-Party Optics
When choosing between OEM and third-party SFP28 25G SR modules, consider the following:
High-quality third-party modules, when properly vendor-coded and tested, can deliver equivalent performance at a significantly lower price—making them ideal for large-scale deployments.
Budget and Scalability Planning
Finally, consider both current needs and future growth. SFP28 25G SR is widely used in scalable data center architectures, so planning ahead can help you:
-
Standardize on 25G ports and cabling
-
Reduce future upgrade costs
-
Maintain consistent performance as the network expands
Balancing upfront cost with long-term scalability ensures that your SFP28 25G SR deployment delivers lasting value.
By following these selection guidelines, you can confidently choose the right SFP28 25G SR module for your network. In the next section, we’ll address frequently asked questions about SFP28 25G SR to clarify common concerns and deployment scenarios.
✅ Frequently Asked Questions About SFP28 25G SR
Below are answers to some of the most common questions about SFP28 25G SR. These concise, direct explanations are designed to address real-world deployment concerns.
What does “SR” stand for in SFP28?
“SR” stands for Short Range.
In SFP28 25G SR modules, SR indicates that the transceiver is designed for short-distance transmission over multimode fiber, typically using an 850nm wavelength. SR modules are optimized for data center links rather than long-distance networks.
How far can SFP28 25G SR transmit?
The maximum transmission distance depends on the fiber type:
These distances cover most in-rack, adjacent-rack, and row-level connections inside data centers.
Can SFP28 25G SR work with OM2 fiber?
SFP28 25G SR is not recommended for OM2 fiber.
OM2 does not provide sufficient bandwidth to reliably support 25Gbps transmission. While short links may occasionally work in controlled environments, OM3 or OM4 fiber is strongly recommended to ensure stable and standards-compliant performance.
Is SFP28 backward compatible with SFP+?
Physically, SFP28 and SFP+ share the same form factor, but electrical compatibility depends on the port:
-
An SFP28 port can often support SFP+ modules, allowing 10GbE operation
-
An SFP+ port cannot support SFP28 25G SR, as it lacks the required signaling capability
Always verify switch support before mixing module types.
Is SFP28 25G SR suitable for 100G breakout?
Yes, SFP28 25G SR is commonly used in 100G breakout scenarios.
In a typical 100G to 4×25G breakout, a 100G QSFP28 port is split into four 25G links, each using an SFP28 module such as 25G SR. This approach is widely used to connect 100G spine or aggregation switches to multiple 25G leaf switches or servers.
These FAQs address the most frequent questions engineers and buyers ask when evaluating SFP28 25G SR. In the final section, we’ll summarize the key points and help you decide whether SFP28 25G SR is the right choice for your network.
✅ Summary: Is SFP28 25G SR Right for Your Network?
SFP28 25G SR is a short-range 25GbE optical transceiver designed for high-density, cost-effective data center connectivity over multimode fiber. It delivers reliable 25Gbps performance while keeping power consumption and deployment costs low.
Key Takeaways
-
Supports 25Gbps per lane in a compact SFP28 form factor
-
Optimized for short-range transmission over OM3/OM4 multimode fiber
-
Cost-effective, low latency, and widely compatible with 25G switches and NICs
When SFP28 25G SR Is the Best Choice
Choose SFP28 25G SR if your network:
-
Requires links under 100 meters
-
Uses existing multimode fiber infrastructure
-
Focuses on data center, ToR, or leaf-spine deployments
-
Prioritizes high port density and scalability
When to Consider Alternative 25G Optics
Consider other 25G options if:
-
You need longer reach (use 25G LR over single-mode fiber)
-
Connections are very short and cost-sensitive (DAC cables)
-
You need simplified cabling for short inter-rack links (AOC solutions)
Final Recommendation
For most data center and enterprise network deployments, SFP28 25G SR remains the most practical and widely adopted choice for deploying 25G Ethernet. When properly matched with fiber type and distance requirements, it delivers consistent performance and long-term scalability.
If you’re looking for reliable, standards-compliant SFP28 25G SR transceivers, explore available options at the LINK-PP Official Store to support your 25G network deployment with confidence.