A 155M SFP transceiver module is a low-speed optical module designed for 155Mbps (STM-1 / OC-3) transmission in SDH and SONET networks. Despite the dominance of Gigabit and 10G optics, 155M SFP modules are still actively purchased today—not as legacy leftovers, but as deliberate, cost-efficient choices for maintaining stable and long-lifecycle networks.
For engineers and procurement teams, the real question is no longer “What is a 155M SFP?” but rather:
When does choosing a 155M SFP make more sense than upgrading to higher-speed optics?
In many telecom access networks, industrial systems, and utility infrastructures, bandwidth demand is fixed, hardware platforms are certified, and network stability outweighs raw speed. In these scenarios, a 155Mbps SFP module offers three clear advantages:
-
Exact speed matching for STM-1 / OC-3 links
-
Lower total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to unnecessary upgrades
-
Long-term availability for legacy but mission-critical systems
This article is written for readers who need to select, replace, or purchase a 155M SFP module with confidence. Rather than broad theory, it focuses on practical decision-making, including:
-
Key technical specifications that actually affect deployment
-
The main types of 155M SFP modules and how they differ
-
Compatibility risks and how to avoid them
-
Pricing logic and supplier considerations for long-term supply
By the end of this guide, you will be able to determine whether a 155M SFP is still the right choice for your network, and how to select a reliable, compatible module that meets both technical and commercial requirements.
🔰 What Is a 155M SFP Transceiver Module?
A 155M SFP is an optical SFP module designed to transmit data at a fixed rate of 155Mbps, primarily used in SDH STM-1 and SONET OC-3 networks.
In practical terms, a 155M SFP serves as the optical interface between networking equipment—such as SDH multiplexers, access switches, or industrial communication devices—and the fiber optic link. It converts electrical signals into optical signals for transmission, and converts incoming optical signals back into electrical form at the receiving end.

Why 155M SFP Is Still Used Today
A 155M SFP is not a downgraded version of modern SFP modules; it is a purpose-built transceiver for environments where:
-
The network is strictly standardized around STM-1 / OC-3
-
Hardware platforms do not support higher data rates
-
Network stability and certification matter more than bandwidth
-
Long-term maintenance and spare availability are critical
In these cases, upgrading to a 1G or 10G SFP provides no functional benefit and may even introduce compatibility risks.
Key Characteristics of a 155M SFP Module
From a deployment perspective, a standard 155M SFP module typically features:
-
Fixed data rate: 155Mbps (non-negotiable, not auto-negotiated)
-
SFP form factor: hot-pluggable and MSA-compliant
-
Multiple wavelength options: 850nm, 1310nm, or 1550nm
-
Support for both MMF and SMF, depending on model
-
Designed for point-to-point optical links in SDH/SONET systems
Unlike higher-speed SFPs, a 155M SFP does not downshift or adapt to other rates, which is precisely why it remains reliable in legacy networks.
Typical Equipment That Uses 155M SFP Modules
You will most commonly find 155M SFP modules installed in:
-
SDH multiplexers and add/drop multiplexers (ADM)
-
Telecom access and aggregation equipment
-
Industrial networking devices with optical uplinks
-
Utility and transportation communication systems
These platforms are often deployed for 10–20 years, making continued availability of 155M SFP modules a key purchasing factor.
🔰 Key Technical Specifications of 155M SFP
A 155M SFP module has a fixed and clearly defined specification set, which makes correct selection straightforward—as long as you focus on the parameters that actually affect compatibility and deployment.
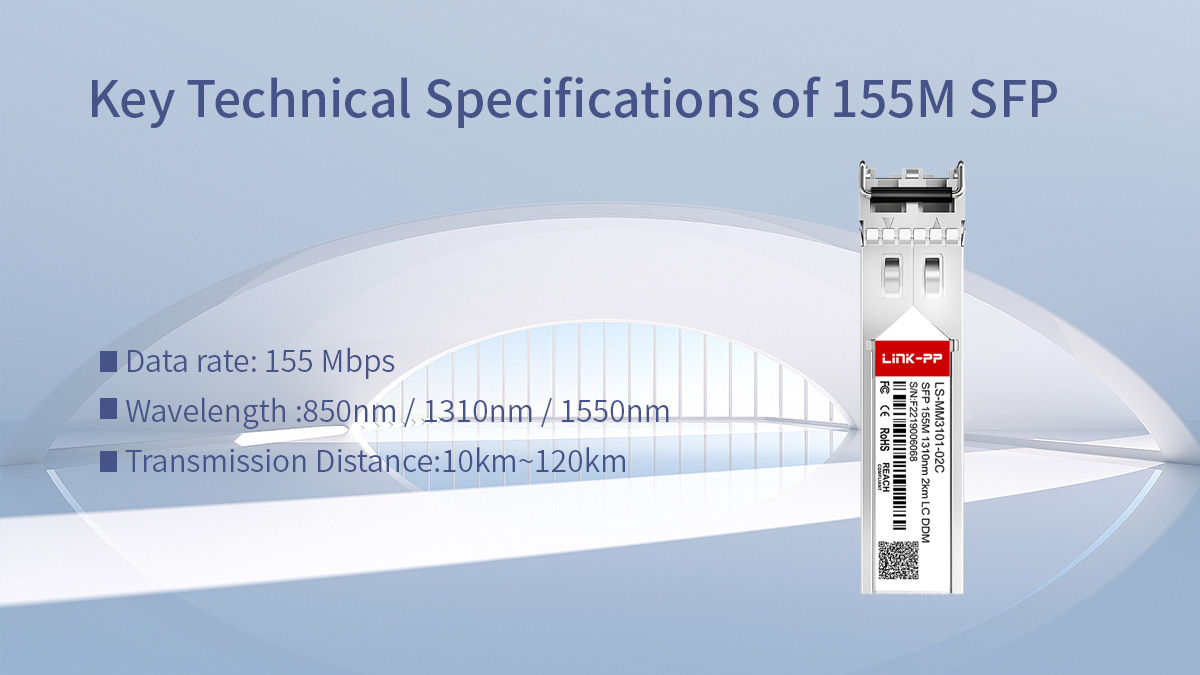
Below is a structured overview of the core technical specifications you should evaluate before purchasing a 155M SFP.
Core Technical Specifications Overview
| Specification |
Typical Values |
Why It Matters |
| Data Rate |
155Mbps (STM-1 / OC-3) |
Must exactly match SDH/SONET system requirements |
| Form Factor |
SFP (MSA-compliant) |
Ensures hot-swappability and broad hardware support |
| Wavelength |
850nm / 1310nm / 1550nm |
Determines fiber type and transmission distance |
| Fiber Type |
MMF or SMF |
Impacts link length and deployment cost |
| Transmission Distance |
2km / 15km / 40km / 80km |
Must align with actual fiber span |
| Optical Connector |
LC (standard) |
Compatibility with existing patch panels |
| Transmit Power |
Model-dependent |
Affects signal stability over distance |
| Receiver Sensitivity |
Model-dependent |
Critical for long or marginal links |
| Operating Temperature |
Commercial or Industrial |
Required for telecom or harsh environments |
Data Rate and Protocol Support
A 155M SFP operates at a fixed data rate of 155Mbps, designed specifically for:
Unlike higher-speed SFP modules, 155M SFPs do not support rate adaptation or auto-negotiation. This fixed-rate behavior is intentional and ensures:
Wavelength and Fiber Type Selection
Wavelength choice directly determines fiber type and maximum reach:
Selecting the correct wavelength avoids unnecessary signal attenuation and eliminates the need for optical amplifiers.
Transmission Distance and Optical Budget
Transmission distance is determined by the optical power budget, not just nominal distance ratings.
When choosing a 155M SFP, you should consider:
-
Actual fiber length
-
Fiber quality and splice loss
-
Connector and patch panel loss
-
Aging margin for long-term operation
For critical links, selecting a module with slightly higher optical margin improves reliability without significantly increasing cost.
Temperature Range and Environmental Requirements
155M SFP modules are typically available in:
Telecom central offices, outdoor cabinets, and industrial sites often require industrial-grade optics to ensure stable operation over long lifecycles.
Why Specifications Matter More for 155M SFP Than High-Speed Optics
Because 155M SFP modules are commonly deployed in long-lived and certified systems, incorrect specifications can result in:
For this reason, specification accuracy is more important than speed or feature flexibility when selecting a 155M SFP module.
🔰 Main Types of 155M SFP Modules
A 155M SFP module can be categorized into several main types based on fiber type, wavelength, and transmission method. Choosing the right type is less about speed—and more about matching the existing network infrastructure accurately.
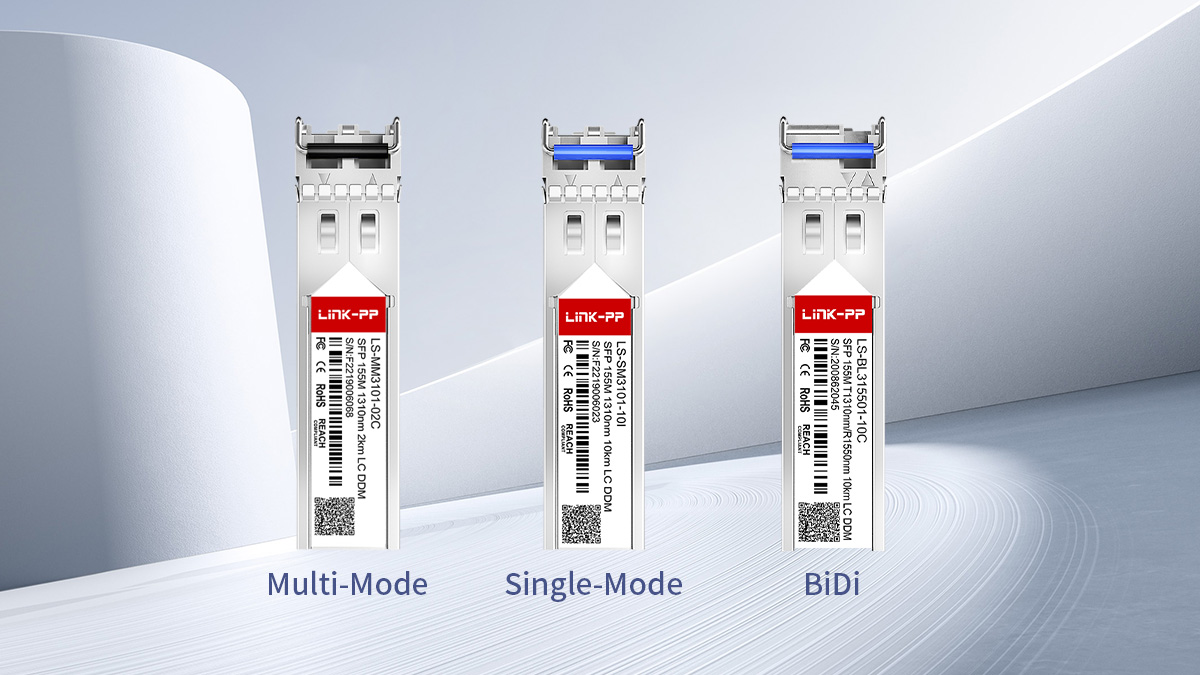
Below are the most common 155M SFP module types used in real-world deployments.
Multi-Mode 155M SFP (MMF)
Best for: Short-distance, indoor, or campus environments
Multi-mode 155M SFP modules typically operate at 850nm and are designed for short-reach optical links.
Key characteristics:
-
Uses multi-mode fiber (MMF)
-
Typical reach: up to 2km
-
Lower optical cost for short distances
-
Common in equipment rooms or local access networks
When to choose MMF:
If your existing infrastructure already uses MMF and the link distance is short, this is the most cost-effective option.
Single-Mode 155M SFP (SMF)
Best for: Access networks and medium-distance links
Single-mode 155M SFP modules are the most widely deployed type, commonly operating at 1310nm.
Key characteristics:
-
Uses single-mode fiber (SMF)
-
Typical reach: 15km or 40km
-
Balanced cost and transmission stability
-
Suitable for most SDH STM-1 access links
When to choose SMF:
If the link exceeds a few kilometers or requires higher signal stability, SMF is the default and safest choice.
Long-Reach 155M SFP (1550nm)
Best for: Metro and long-distance SDH links
1550nm 155M SFP modules are designed for long-haul transmission, often supporting distances up to 80km.
Key characteristics:
When to choose 1550nm:
If the fiber span is long and signal loss is a concern, 1550nm provides greater margin and reliability.
BiDi 155M SFP Modules
Best for: Fiber-constrained environments
BiDi (Bidirectional) 155M SFP modules transmit and receive data over a single strand of fiber, using two different wavelengths.
Key characteristics:
-
Single-fiber transmission
-
Requires paired wavelengths (Tx/Rx matched)
-
Reduces fiber usage by 50%
-
Useful for legacy or limited fiber routes
When to choose BiDi:
When fiber resources are limited or adding new fiber is impractical, BiDi SFP modules offer a cost-effective alternative.
CWDM 155M SFP Modules
Best for: Legacy metro networks with wavelength multiplexing
CWDM 155M SFP modules support Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing, allowing multiple optical signals to share a single fiber.
Key characteristics:
When to choose CWDM:
If your network already uses CWDM infrastructure, these modules allow you to extend capacity without redesigning the optical layer.
How to Choose the Right Type Quickly
As a practical rule:
-
Short distance + existing MMF → 155M Multi-mode SFP
-
General access networks → 155M 1310nm single mode SFP
-
Long-distance links → 155M 1550nm SFP
-
Limited fiber availability → 155M BiDi SFP
-
Wavelength-multiplexed networks → CWDM 155M SFP
Selecting the correct type upfront reduces deployment risk and avoids costly troubleshooting later.
🔰 155M SFP vs Higher-Speed SFP Modules
A 155M SFP module is not outdated by default—but it is specialized. Whether a higher-speed SFP (such as 1G or 10G) makes sense depends entirely on network requirements, platform compatibility, and lifecycle constraints, not on speed alone.

The table below highlights the practical differences between 155M SFP and higher-speed SFP modules.
155M SFP vs 1G / 10G SFP: Practical Comparison
| Aspect |
155M SFP |
1G SFP / 10G SFP |
| Designed Data Rate |
155Mbps (STM-1 / OC-3) |
1Gbps / 10Gbps |
| Primary Protocols |
SDH / SONET |
Ethernet |
| Typical Use Case |
Legacy & industrial networks |
Modern IP networks |
| Rate Adaptation |
Not supported |
Supported (depending on model) |
| Hardware Compatibility |
SDH/SONET-specific platforms |
Ethernet switches & routers |
| Upgrade Requirement |
None |
Often requires platform replacement |
| Cost Impact |
Lower and predictable |
Higher total upgrade cost |
| Network Risk |
Minimal if correctly matched |
Higher if legacy systems involved |
When 155M SFP Is the Better Choice
A 155M SFP is the correct and safer option when:
-
The network is built around SDH STM-1 or SONET OC-3
-
Existing equipment does not support Ethernet optics
-
Bandwidth demand is stable and unlikely to change
-
Service uptime and certification outweigh performance upgrades
-
Long-term maintenance and spare availability are priorities
In these environments, replacing a 155M SFP with a higher-speed module is technically impossible or operationally risky.
When Higher-Speed SFP Modules Make Sense
Upgrading to 1G or 10G SFP modules is justified when:
-
You are deploying a new Ethernet-based network
-
Traffic growth requires higher throughput
-
Network equipment fully supports higher-speed optics
-
Downtime during migration is acceptable
-
Future scalability is a key design requirement
In this case, the decision is architectural—not incremental.
Cost and Risk Perspective
From a total cost of ownership (TCO) standpoint:
For networks with long service lifecycles, avoiding unnecessary upgrades can be more strategic than chasing speed.
Key Takeaway
If your network already operates on STM-1 / OC-3, a 155M SFP module remains the most rational choice. Higher-speed SFPs should be considered only when the entire network architecture is designed to support them.
🔰 Common Applications of 155M SFP in Modern Networks
A 155M SFP module continues to be widely deployed—not because networks resist change, but because many critical systems are designed for long-term stability rather than continuous upgrades.
Below are the most common modern use cases where 155M SFP modules remain a practical and intentional choice.
SDH / SONET Access and Aggregation Networks
Primary application: STM-1 / OC-3 transmission
Telecom operators still rely on SDH and SONET infrastructure for access and aggregation layers, especially in:
In these environments, 155M SFP modules provide:
-
Guaranteed protocol compatibility
-
Stable clock synchronization
-
Predictable long-term performance
Replacing SDH optics with Ethernet-based modules is often not feasible without redesigning the entire network.
Industrial and Utility Communication Systems
Primary application: Mission-critical, low-bandwidth links
Industrial networks prioritize deterministic performance and uptime, not bandwidth density. Typical examples include:
-
Power grid monitoring and protection systems
-
Transportation signaling networks
-
Oil, gas, and pipeline communication systems
-
Factory and process automation backbones
Here, a 155M SFP offers:
-
Stable point-to-point transmission
-
Support for industrial temperature ranges
-
Long service lifecycles aligned with infrastructure depreciation
Legacy Metro and Backbone Links
Primary application: Long-distance optical spans
Many metro networks deployed SDH decades ago and continue to operate reliably. In these scenarios:
Long-reach 1550nm 155M SFP modules are still used to maintain these links without introducing unnecessary operational risk.
Government, Transportation, and Public Infrastructure
Primary application: Networks with strict certification and compliance
Public-sector networks often face:
As a result, certified SDH equipment paired with 155M SFP modules remains in service far longer than commercial IT networks.
Backup, Redundancy, and Protection Paths
Primary application: Secondary or failover links
Even in networks that have partially migrated to Ethernet, 155M SFP modules are often retained for:
Their predictable behavior and low operating cost make them suitable for always-on but rarely saturated links.
Why These Applications Still Matter
The continued use of 155M SFP modules reflects a broader reality:
-
Not all networks need higher bandwidth
-
Not all systems can be upgraded safely
-
Reliability often outweighs performance
In these modern yet conservative environments, 155M SFP modules remain the most appropriate optical interface.
🔰 Compatibility Considerations for 155M SFP Modules
A 155M SFP module must be fully compatible with the host equipment to operate reliably. Unlike modern Ethernet optics, SDH/SONET platforms are often less tolerant of parameter mismatches, making compatibility a critical selection factor.
Ignoring compatibility considerations can result in link instability, equipment alarms, or complete service failure—even if the module appears to meet basic specifications.

MSA Compliance Is Necessary—but Not Always Sufficient
Most 155M SFP modules are designed to be MSA-compliant, which ensures:
However, MSA compliance alone does not guarantee full interoperability with all SDH/SONET equipment, especially on older platforms.
Equipment Vendor and Platform Sensitivity
Many SDH devices:
-
Are tightly validated against specific optical parameters
-
Enforce strict tolerance for transmit power and receiver sensitivity
-
May reject modules that deviate slightly from expected values
In some cases, equipment firmware may:
For this reason, proven compatibility testing is often more important than nominal specifications.
OEM vs Third-Party 155M SFP Modules
Using third-party 155M SFP modules can significantly reduce cost—but only when compatibility is properly addressed.
Key considerations include:
-
Accurate EEPROM programming
-
Matching optical characteristics to OEM equivalents
-
Pre-deployment testing on target platforms
High-quality third-party suppliers validate their modules against multiple SDH systems to minimize interoperability risk.
Optical Budget and Link Margin Matching
Compatibility is not limited to the host device—it also involves the entire optical link.
Ensure that:
-
Transmit power aligns with the receiver’s acceptable range
-
Optical budget supports the full fiber span with margin
-
Attenuation is controlled on short links to avoid receiver saturation
Improper optical power levels are a common cause of unexplained link issues.
Environmental and Operational Compatibility
Many 155M SFP deployments occur in:
In such cases, selecting modules with:
-
Appropriate temperature ratings
-
Long-term reliability testing
-
Stable optical components
is essential for continuous operation.
Practical Compatibility Checklist
Before purchasing a 155M SFP module, confirm:
-
Target equipment model and firmware version
-
Required wavelength and distance
-
Optical power budget compatibility
-
Temperature and environmental requirements
-
Supplier testing and validation scope
A small amount of upfront verification can prevent costly troubleshooting and downtime later.
🔰 How to Choose the Right 155M SFP Module
Choosing the right 155M SFP module is less about comparing brands and more about eliminating mismatch risks. When the key parameters are aligned correctly, a 155M SFP deployment is straightforward and highly reliable.
The following step-by-step framework helps ensure you select a module that fits both technical requirements and long-term operational needs.
Step 1: Confirm Network Standard and Application
Start by confirming the exact protocol and application:
-
SDH STM-1 or SONET OC-3
-
Access, aggregation, or backbone link
-
Primary link or backup/protection path
A 155M SFP must be purpose-matched to the SDH/SONET environment—there is no flexibility for protocol mismatch.
Step 2: Select Fiber Type and Transmission Distance
Next, determine:
-
Existing fiber type (MMF or SMF)
-
Actual fiber length, not just estimated distance
-
Presence of splices, connectors, or patch panels
Choose:
-
MMF (850nm) for short indoor links
-
SMF (1310nm) for most access networks
-
SMF (1550nm) for long-distance spans
Always allow sufficient optical margin for long-term stability.
Step 3: Evaluate Compatibility with Host Equipment
Compatibility is critical for 155M SFP modules, especially on legacy platforms.
Verify:
-
Supported optical specifications from the equipment vendor
-
Known compatibility references or test reports
-
EEPROM coding requirements, if any
If using third-party modules, select suppliers that actively test against real SDH equipment, not just generic SFP interfaces.
Step 4: Consider Environmental Conditions
Assess where the module will operate:
Choose:
Environmental mismatch is a common cause of premature failure.
Step 5: Balance Cost with Lifecycle Requirements
For long-lived networks, upfront price should not be the only factor.
Consider:
-
Expected service life of the equipment
-
Availability of replacement modules over time
-
Consistency of specifications across batches
A slightly higher-quality 155M SFP can reduce maintenance effort and operational risk over the system’s lifetime.
Quick Decision Checklist
A 155M SFP module is the right choice when:
-
The network standard is fixed at STM-1 / OC-3
-
Fiber type and distance are clearly defined
-
Host equipment compatibility is verified
-
Environmental conditions are understood
-
The supplier offers consistent quality and support
Selecting the right 155M SFP upfront ensures stable performance, predictable costs, and minimal operational risk throughout the network lifecycle.
🔰 LINK-PP 155M SFP Modules Overview
LINK-PP 155M SFP modules are designed to support stable, long-term SDH/SONET deployments where compatibility, consistency, and lifecycle reliability matter more than peak performance.
Rather than positioning 155M SFPs as legacy products, LINK-PP treats them as purpose-built optical interfaces for networks that must remain operational for many years.

LINK-PP 155M SFP Product Coverage
| Category |
LINK-PP Support |
Deployment Value |
| Data Rate |
155Mbps (STM-1 / OC-3) |
Exact match for SDH/SONET platforms |
| Fiber Type |
MMF / SMF |
Compatible with existing fiber infrastructure |
| Wavelength |
850nm / 1310nm / 1550nm |
Covers short to long-distance links |
| Reach Options |
2km / 15km / 40km / 80km |
Flexible replacement for legacy spans |
| Transmission Type |
Dual-fiber / BiDi / CWDM |
Supports fiber-limited and metro networks |
| Connector |
LC |
Standard integration with patch panels |
This range allows operators to replace or extend 155M links without modifying network architecture.
Proven Compatibility with SDH Equipment
Compatibility is a primary design focus for LINK-PP 155M SFP modules.
Key compatibility practices include:
-
Strict adherence to SFP MSA electrical and mechanical standards
-
Optical parameter tuning aligned with SDH/SONET platform tolerances
-
EEPROM programming validated against common telecom systems
These measures help ensure plug-and-play operation on a wide range of SDH and SONET devices.
Reliability and Long-Term Availability
LINK-PP designs 155M SFP modules with long service lifecycles in mind.
Key reliability considerations:
-
Stable laser and receiver components
-
Consistent specifications across production batches
-
Options for industrial temperature operation
-
Quality control focused on telecom-grade deployments
This approach reduces the risk of unexpected behavior when replacing modules years after the original installation.
Cost Efficiency Without Compromising Stability
Compared with OEM-branded optics, LINK-PP 155M SFP modules offer:
For operators maintaining large SDH infrastructures, this balance between cost control and operational stability is often a key purchasing factor.
When LINK-PP 155M SFP Is the Right Choice
LINK-PP 155M SFP modules are particularly suitable when:
-
You need reliable replacements for existing SDH links
-
OEM modules are costly or difficult to source
-
Long-term availability matters more than brand labeling
-
Compatibility assurance is required for legacy platforms
🔰 Pricing Factors and Cost Advantages of 155M SFP
The price of a 155M SFP module is influenced by a limited and well-defined set of factors. Understanding these factors helps buyers evaluate true cost, rather than focusing only on unit price.
For networks built on SDH/SONET, 155M SFP modules often deliver lower total cost of ownership (TCO) compared with higher-speed alternatives.

Key Pricing Factors for 155M SFP Modules
| Pricing Factor |
Impact on Cost |
Buyer Consideration |
| Transmission Distance |
Moderate to high |
Longer reach requires higher optical budget |
| Wavelength |
Moderate |
1550nm typically costs more than 1310nm |
| Fiber Type |
Low |
SMF is more common and scalable |
| Module Type |
Moderate |
BiDi and CWDM add complexity |
| Temperature Rating |
Moderate |
Industrial-grade modules carry a premium |
| Compatibility Testing |
Indirect |
Reduces post-deployment risk and cost |
These factors explain why 155M SFP pricing varies—even within the same data rate category.
Why 155M SFP Has a Cost Advantage
From a procurement perspective, 155M SFP modules offer several structural cost benefits:
-
No platform upgrade required
Replacing a like-for-like 155M SFP avoids chassis, line card, and software costs.
-
Lower operational risk
Stable, fixed-rate operation reduces troubleshooting and downtime.
-
Predictable maintenance cost
Fewer configuration variables mean fewer unexpected issues over time.
-
Extended infrastructure lifespan
Existing SDH systems continue to deliver value without forced upgrades.
OEM vs Compatible 155M SFP Modules
One of the biggest pricing differences comes from OEM-branded vs compatible modules.
| Aspect |
OEM 155M SFP |
Compatible 155M SFP |
| Unit Price |
Higher |
Lower |
| Lead Time |
Often longer |
Typically shorter |
| Performance |
Equivalent |
Equivalent when validated |
| Compatibility Risk |
Low |
Low with tested suppliers |
| Long-Term Supply |
Vendor-dependent |
Often more flexible |
For many operators, compatible 155M SFP modules provide better cost control without compromising reliability.
Long-Term Cost Perspective
Because 155M SFP modules are often used in long-lived networks, long-term considerations matter more than initial savings.
When evaluating cost, consider:
-
Consistency across future replacement orders
-
Availability of the same specifications over time
-
Supplier stability and support
A reliable supplier can reduce hidden costs related to qualification, retesting, and operational disruption.
Key Takeaway
The cost advantage of 155M SFP modules lies not just in lower unit pricing, but in avoiding unnecessary upgrades and minimizing operational risk. For SDH/SONET networks with stable bandwidth requirements, 155M SFP remains a financially rational and technically sound choice.
🔰 Where to Buy Reliable 155M SFP Transceiver Modules
The most reliable 155M SFP transceiver modules come from suppliers that combine strict compatibility testing, long-term supply stability, and clear technical support, not simply the lowest price.
For SDH/SONET networks, choosing the right source is just as important as choosing the right specification.

What to Look for in a Reliable 155M SFP Supplier
Before purchasing, buyers should evaluate suppliers based on the following criteria:
-
Standards compliance
Full support for OC-3 / STM-1 (155Mbps) specifications.
-
Compatibility validation
Proven interoperability with mainstream SDH equipment from major vendors.
-
Consistent product lifecycle
Ability to supply the same model and specification over long periods.
-
Quality control and testing
Factory-level optical and electrical performance verification.
-
Technical documentation
Clear datasheets, wavelength options, and distance specifications.
A supplier that meets these conditions significantly reduces deployment risk and future replacement issues.
OEM vs Specialized Optical Module Manufacturers
Buyers typically choose between OEM vendors and specialized third-party manufacturers.
| Supplier Type |
Strengths |
Limitations |
| OEM Vendors |
Guaranteed compatibility |
Higher cost, limited flexibility |
| Specialized Manufacturers |
Cost-effective, flexible supply |
Requires proper validation |
Well-established optical module manufacturers often provide OEM-equivalent performance with better pricing and faster lead times, making them a preferred choice for long-term SDH networks.
Online Sourcing vs Direct Manufacturer Supply
Where you buy also affects reliability and cost structure.
-
Online distributors
Suitable for small quantities or urgent replacement needs.
-
Direct manufacturers
Better for bulk orders, consistent specifications, and long-term projects.
Direct sourcing often ensures:
-
Stable pricing
-
Customizable options (distance, wavelength, temperature)
-
Faster technical response
Why LINK-PP Is a Trusted Source for 155M SFP Modules
LINK-PP provides carrier-grade 155M SFP transceiver modules designed for long-term SDH/SONET deployment.
Key advantages include:
-
Full OC-3 / STM-1 compliance
-
Broad compatibility testing
-
Stable production and supply continuity
-
Cost-effective alternative to OEM modules
This combination makes LINK-PP a reliable partner for operators maintaining or expanding legacy optical networks.
Final Buying Recommendation
If your network requires stable 155Mbps optical transmission, the best purchasing strategy is to work with a supplier that prioritizes compatibility, consistency, and long-term availability, rather than short-term price advantages.
A reliable source ensures your 155M SFP modules remain deployable, replaceable, and supportable throughout the entire network lifecycle.
🔰 Conclusion: Is 155M SFP Still the Right Choice for Your Network?
If your network is built on SDH/SONET infrastructure and does not require higher bandwidth, 155M SFP transceiver modules remain a reliable, cost-effective, and operationally stable solution.
Throughout this guide, we’ve seen that 155M SFP modules continue to play an important role in:
-
Legacy OC-3 / STM-1 networks
-
Utility, transportation, and industrial systems
-
Long-distance, low-bandwidth optical links
Their advantages lie in predictable performance, broad compatibility, and lower total cost of ownership, especially when upgrading the platform is unnecessary or impractical.
Make a Smart Purchasing Decision
To maximize long-term value, buyers should focus on:
-
Proven standards compliance
-
Vendor compatibility validation
-
Stable supply and consistent specifications
-
Reliable technical support
Choosing the right supplier ensures that 155M SFP modules remain deployable and replaceable over the full lifecycle of your network.
Buy with Confidence from LINK-PP Official Store
For operators and system integrators seeking reliable 155M SFP transceiver modules, the LINK-PP offers:
-
Carrier-grade OC-3 / STM-1 SFP modules
-
Broad compatibility with mainstream SDH equipment
-
Stable production and long-term availability
-
Competitive pricing without compromising quality
👉 Visit the LINK-PP Official Store to explore available 155M SFP options and get expert support for your specific network requirements.