40GBASE‑SR4 QSFP+ modules deliver high-density, short-reach 40 Gbps over multimode fiber using 4×10 G NRZ lanes. Ideal for leaf-spine data center fabrics and 5G front-haul, they balance low power, hot-swappability, and cost-effective performance.
As data centers migrate from 10G and 25G architectures toward higher-density switching fabrics, 40GBASE-SR4 has become the most mature and cost-effective short-reach optical standard for building scalable leaf-spine networks, server uplinks, and 5G fronthaul infrastructures. By leveraging QSFP+ form factor, parallel multimode optics, and MPO cabling, SR4 enables operators to achieve high throughput, low latency, and simplified fiber management within distances up to 150 meters.
However, despite its maturity, 40GBASE-SR4 deployments still encounter real-world challenges — including MPO polarity mismatches, optical budget miscalculations, thermal hotspots, and cross-vendor compatibility issues. In our engineering validation labs and multi-vendor deployment projects, these factors consistently account for the majority of link instability and commissioning delays. This guide consolidates first-hand testing experience, field case analysis, and industry best practices to help engineers and network architects avoid common pitfalls and achieve predictable performance at scale.
What You Will Learn from This Guide
By the end of this article, you will be able to:
-
Understand how 40GBASE-SR4 works at the physical layer, including parallel optics, NRZ modulation, and MPO cabling architecture
-
Master key technical specifications and optical performance parameters that directly affect link stability
-
Apply proven deployment best practices for fiber selection, polarity control, thermal management, and DOM monitoring
-
Troubleshoot common 40G SR4 failures, including no-link, high BER, and intermittent flapping
-
Evaluate 40GBASE-SR4 vs. alternative 40G/100G solutions to optimize cost, density, and scalability
-
Build a procurement and compatibility checklist that minimizes interoperability risk and long-term operating cost
Whether you are designing a new data center fabric, upgrading 10G/25G uplinks, or planning large-scale 5G fronthaul deployments, this professional guide provides the engineering insights and decision frameworks required to deploy 40GBASE-SR4 networks with confidence.
✅ What is 40GBASE-SR4?
40GBASE-SR4 is a standardized 40-Gigabit Ethernet (40GbE) optical interface defined by IEEE 802.3ba, designed specifically for short-reach transmission over multimode fiber (MMF) using parallel optical channels. It operates at a nominal line rate of 40 Gbps, implemented as four parallel 10.3125 Gbps lanes, transmitted and received simultaneously through a QSFP+ transceiver module.
Unlike traditional serial optics that send all data over a single optical lane, SR4 leverages parallel optics architecture, which enables higher aggregate bandwidth while maintaining low optical complexity, lower power consumption, and cost efficiency. This makes it particularly suitable for intra-data center interconnects, leaf-spine switch fabrics, server uplinks, and 5G fronthaul aggregation networks where distances typically range from 10 m to 150 m.

Key Technical Definition
At the physical layer, 40GBASE-SR4 uses:
-
Optical wavelength: 850 nm (VCSEL-based multimode transmission)
-
Fiber type: Laser-optimized multimode fiber (OM3, OM4, OM5)
-
Connector: MPO-12 / MTP multi-fiber connector
-
Modulation format: NRZ (Non-Return-to-Zero)
-
Channel architecture: 4 transmit + 4 receive fibers (8 active fibers total)
Each optical lane carries 10.3125 Gbps, resulting in a combined throughput of 40 Gbps full-duplex. The remaining four fibers in the MPO-12 connector remain unused, preserving backward mechanical compatibility.
How 40GBASE-SR4 Works
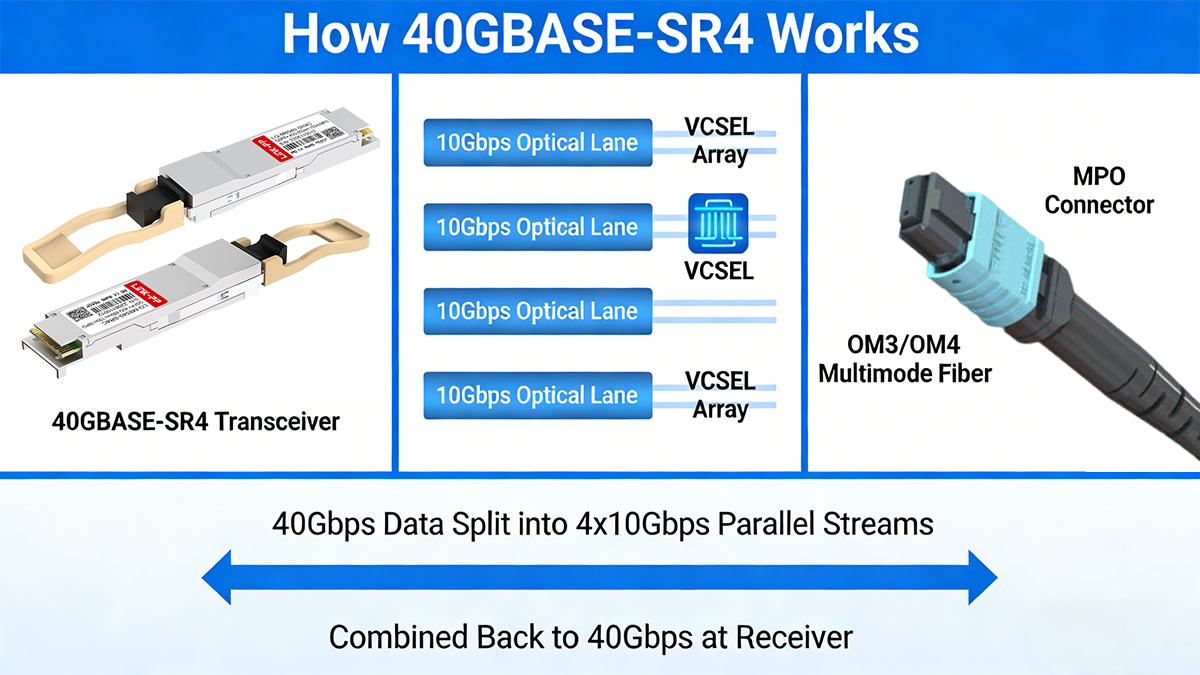
40GBASE-SR4 adopts a parallel optical transmission model, where data is striped across four optical lanes at the transmitter and recombined at the receiver. This design offers several operational advantages:
-
Lower per-lane signaling speed, improving signal integrity and BER margin
-
Reduced laser complexity compared to long-reach serial optics
-
Lower module cost and power consumption
-
Simpler optical dispersion management
In practical deployments, the QSFP+ module converts electrical 4×10G signals from the switch ASIC into four parallel optical signals, which are transmitted over eight fibers using an MPO cable assembly. On the receiving side, these signals are reconstructed into a single 40G Ethernet stream.
Typical Deployment Scenarios
40GBASE-SR4 is widely used in:
-
Leaf-to-spine interconnects in data center fabrics
-
Top-of-rack (ToR) to aggregation switch uplinks
-
Server and GPU cluster interconnects
-
5G fronthaul and midhaul aggregation networks
-
Enterprise core and distribution layer upgrades
Its short-reach design and low TCO profile make SR4 ideal for high-density environments where fiber management, power efficiency, and port density are critical.
40GBASE-SR4 vs. Other 40G Ethernet Standards
| Standard |
Fiber Type |
Distance |
Optics Type |
Typical Use Case |
| 40GBASE-SR4 |
MMF (OM3/OM4) |
100–150 m |
QSFP+ |
Data centers, 5G fronthaul |
| 40GBASE-LR4 |
SMF |
10 km |
QSFP+ |
Metro / campus backbone |
| 40GBASE-PLR4 |
SMF |
1.4 km |
QSFP+ |
Campus aggregation |
| 40GBASE-SR10 |
MMF |
300 m |
CFP |
Legacy 40G deployments |
Compared with LR4 and PLR4, SR4 offers dramatically lower cost, lower power, and simpler fiber infrastructure, making it the dominant short-reach 40G standard globally.
✅ Key Technical Specifications of 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ Modules
40G-SR4 is defined by IEEE 802.3ba, specifying a 40 Gb/s short-reach optical interface using four parallel multimode fiber (MMF) lanes. Understanding its technical parameters is essential for data center architecture design, switch compatibility, fiber planning, and long-term scalability.
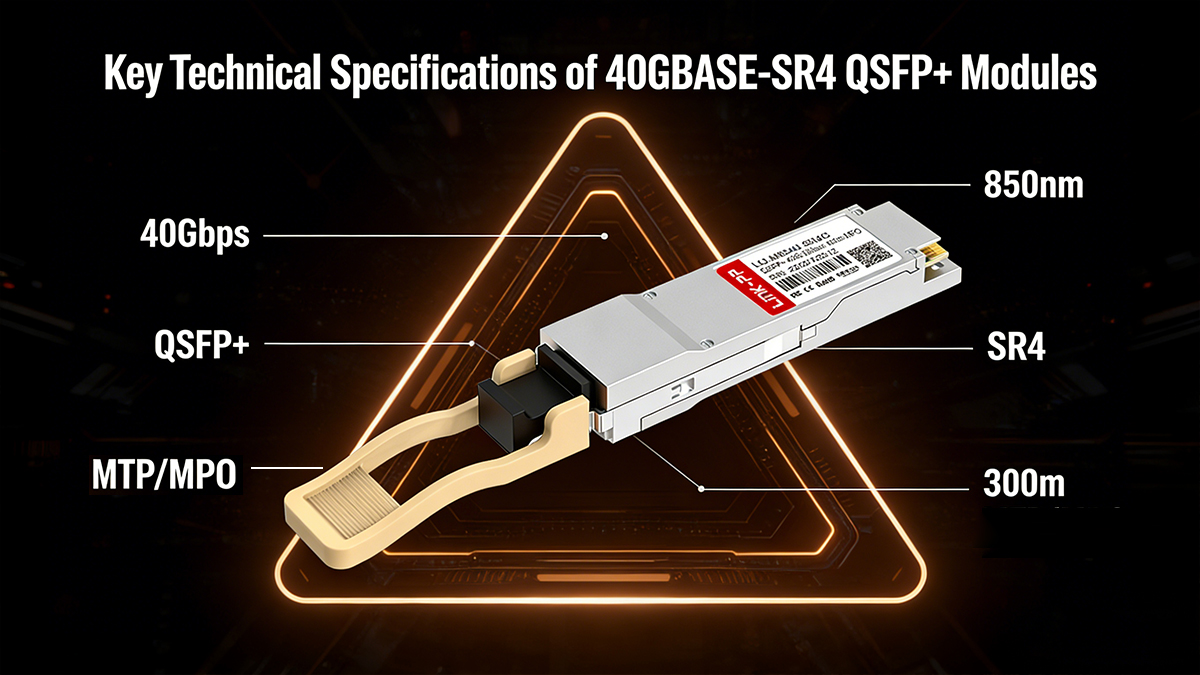
Below is a structured breakdown of the core engineering specifications.
1. Optical Interface & Lane Architecture
QSFP+ SR4 transmits data using parallel optics, dividing 40 Gb/s into four independent 10 Gb/s lanes:
-
Number of lanes: 4 TX + 4 RX
-
Per-lane data rate: 10.3125 Gb/s
-
Aggregate bandwidth: 41.25 Gb/s (line rate)
-
Optical interface: MPO-12 connector (8 fibers active)
Architecture principle:
Each QSFP+ module integrates four VCSEL laser transmitters and four PIN photodiode receivers, operating in parallel. This design enables low-cost, low-power short-reach transmission over multimode fiber.
Engineering implication:
Parallel optics simplifies high-speed signaling by reducing single-lane bandwidth requirements, improving signal integrity and lowering electrical complexity.
2. Wavelength & Optical Characteristics
40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ module operates in the 850 nm wavelength window, optimized for multimode fiber:
| Parameter |
Specification |
| Central wavelength |
850 nm |
| Light source |
VCSEL (Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser) |
| Receiver type |
PIN photodiode |
| Fiber type |
OM3 / OM4 MMF |
| Optical modulation |
NRZ |
Why 850 nm?
850 nm VCSEL technology offers excellent modulation efficiency, low cost, and low power consumption, making it ideal for intra-data center short-reach connectivity.
3. Transmission Distance & Fiber Type
| Fiber Type |
Maximum Reach |
| OM3 MMF |
100 meters |
| OM4 MMF |
150 meters |
Distance drivers:
Engineering tip:
For structured cabling systems, design margin of ≥15% is recommended to accommodate connector aging and contamination effects.
4. Electrical Interface & Host Compatibility
| Parameter |
Value |
| Electrical interface |
4 × 10G lanes |
| Signaling standard |
CAUI-4 |
| Host form factor |
QSFP+ |
| Hot-pluggable |
Yes |
| Compliance |
IEEE 802.3ba, SFF-8436, SFF-8661 |
QSFP-SR4 modules are fully interoperable with:
5. Power Consumption & Thermal Profile
| Parameter |
Typical Value |
| Power consumption |
≤1.5 W |
| Thermal class |
Standard QSFP+ |
| Operating case temp |
0°C to 70°C (commercial) |
Engineering significance:
Compared to long-reach 40G optics, SR4 offers very low thermal load, supporting:
6. Connector Type & Cabling Architecture
40G-SR4 uses an MPO-12 fiber connector, utilizing:
| Component |
Specification |
| Connector |
MPO-12 |
| Fiber count |
12 |
| Active fibers |
8 |
| Polarity |
Type-B typically used |
Cabling architectures:
7. Standards & Compliance Quick Reference
| Standard |
Description |
| IEEE 802.3ba |
40G Ethernet physical layer definition |
| QSFP+ MSA |
Mechanical & electrical form factor |
| SFF-8436 |
QSFP+ module specification |
| RoHS / REACH |
Environmental compliance |
Technical Summary
QSFP SR4 module is a 40 Gb/s short-reach Ethernet standard based on four parallel 10G lanes, operating at 850 nm over OM3/OM4 multimode fiber, reaching 100–150 m using MPO-12 connectors. It delivers low power, high density, and cost-effective performance for modern data centers.
✅ Typical Use Cases of 40GBASE-SR4 in Data Centers & 5G Networks
40GBASE-SR4 is designed for high-density, short-reach optical interconnects where bandwidth efficiency, power consumption, fiber management, and scalability are critical. Its parallel-optics architecture makes it particularly suitable for modern data center fabrics, 5G transport networks, HPC clusters, and enterprise backbone deployments.
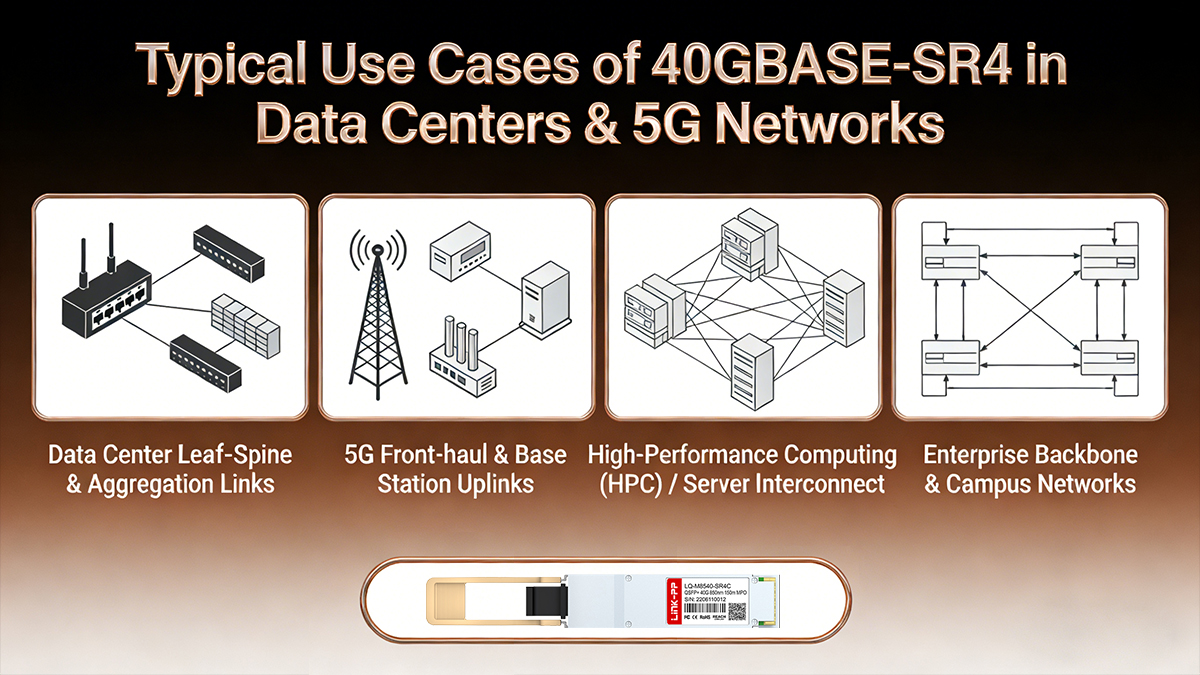
Below are the four most common real-world engineering scenarios.
♦ Data Center Leaf–Spine & Aggregation Links
In modern leaf–spine data center architectures, 40G-SR4 is widely deployed for:
Why SR4 40G Module fits this architecture:
-
Supports high port density using QSFP+ modules
-
Optimized for short-reach MMF links (<150 m)
-
Low power consumption enables dense switch stacking
-
MPO-based cabling simplifies structured fiber management
Typical topology:
Value: Enables non-blocking switching fabrics, ensuring predictable latency and scalable east–west traffic handling for virtualization, cloud computing, containerized workloads, and distributed storage systems.
♦ 5G Front-haul & Base Station Uplinks
In 5G mobile networks, 40GBASE-SR4 plays a critical role in short-distance high-capacity transport, especially for:
-
Fronthaul links between Remote Radio Units (RRUs) and Distributed Units (DUs)
-
Base station uplinks toward edge aggregation switches
-
Dense urban macro-cell and indoor DAS deployments
Why SR4 is suitable for 5G transport:
-
Provides 40 Gbps bandwidth for massive MIMO, beamforming, and C-RAN architectures
-
Low latency supports URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication) services
-
Compact QSFP+ form factor enables high-density baseband pooling
-
Low power simplifies thermal management in outdoor cabinets
Typical 5G fronthaul topology:
Insight: For edge aggregation layers, 40Gb SR4 offers an optimal balance between cost, bandwidth, and power efficiency, especially where fiber distances remain within 100–150 m.
♦ High-Performance Computing (HPC) / Server Interconnect
40GBASE-SR4 is widely deployed in HPC clusters and high-performance computing fabrics, including:
Typical applications:
Why engineers choose SR4 for HPC:
-
Delivers low-latency parallel optical transmission
-
Supports high fan-out breakout (40G → 4×10G)
-
Enables dense cluster topologies with efficient cable routing
-
Provides strong cost-per-Gbps efficiency
Benefit: SR4 supports large-scale parallel computing fabrics while maintaining predictable latency, stable BER, and manageable thermal profiles, especially in legacy and transitional HPC environments.
♦ Enterprise Backbone & Campus Networks
In enterprise networks and large campus environments, 40GB-SR4 is commonly used for:
-
Building-to-building backbone links
-
Core-to-distribution aggregation
-
Data center interconnect inside corporate campuses
Typical deployment scenarios:
-
Financial institutions
-
Universities & research campuses
-
Hospitals and healthcare networks
-
Industrial automation networks
Why enterprises deploy SR4:
-
Simplifies fiber trunking using MPO cabling
-
Enables gradual upgrades from 10G to 40G
-
Provides high reliability at moderate cost
-
Excellent compatibility with mainstream switching platforms
Design advantage: Allows scalable campus backbone construction while controlling fiber cost, rack space, and power consumption.
40GBASE-SR4 is best suited for short-reach, high-density optical links, widely deployed in data center leaf-spine fabrics, 5G fronthaul and base station uplinks, HPC server interconnects, and enterprise backbone networks, where cost efficiency, low power, fiber optimization, and scalability are essential.
✅ 40GBASE-SR4 vs. Other 40G Standards (SR4 vs. LR4 vs. ER4 vs. BiDi vs. CR4)
Selecting the right 40G optical interface is not only about transmission distance — it directly affects fiber infrastructure cost, deployment complexity, power consumption, and long-term network scalability.
This section provides a clear engineering-level comparison of the five most common 40G standards, helping data center architects and telecom engineers make technically correct and cost-efficient decisions.

Core Technical Comparison Table
| Standard |
Fiber Type |
Wavelength |
Typical Distance |
Connector |
Modulation |
Power |
Key Advantages |
Main Limitations |
| 40GBASE-SR4 |
MMF (OM3/OM4) |
850 nm |
100m / 150m |
MPO-12 |
NRZ (4×10G) |
≤1.5W |
Lowest cost, low power, easy cooling |
Short reach, MPO cabling |
| 40GBASE-LR4 |
SMF |
1310 nm (CWDM) |
10 km |
LC duplex |
NRZ (4×10G) |
3–4W |
Long reach, simple fiber plant |
Higher cost |
| 40GBASE-ER4 |
SMF |
1310 nm (CWDM) |
40 km |
LC duplex |
NRZ (4×10G) |
4–6W |
Metro connectivity |
Very high cost, higher power |
| 40G BiDi |
MMF (OM3/OM4) |
850/900 nm |
100m / 150m |
LC duplex |
NRZ (2×20G) |
≤2.5W |
Reuses legacy duplex MMF |
Lower ecosystem maturity |
| 40GBASE-CR4 |
DAC (Copper) |
Electrical |
≤7m |
QSFP+ Direct Attach |
NRZ (4×10G) |
≤2W |
Lowest latency, ultra-low cost |
Very short reach |
Optical Architecture Differences
Understanding signal transmission architecture is critical when designing reliable 40G networks.
QSFP+ SR4 — Parallel Multimode Architecture
-
4 transmit + 4 receive lanes
-
Uses 850 nm VCSEL array + MPO fiber ribbon
-
Best for intra-rack, inter-rack, and row-level connections
QSFP+ LR4 / ER4 — WDM Single-Mode Architecture
-
Multiplexes 4 wavelengths over 2 fibers (LC duplex)
-
Ideal for building interconnect, campus backbone, metro links
QSFP+ BiDi — Dual-Wavelength Multimode
QSFP+ CR4 — Electrical Copper Interconnect
Cost & Infrastructure Impact Comparison
| Factor |
SR4 |
LR4 |
ER4 |
BiDi |
CR4 |
| Module Cost |
★ Lowest |
★★★ |
★★★★★ |
★★ |
★ Lowest |
| Fiber Cost |
MPO trunk |
SMF duplex |
SMF duplex |
MMF duplex |
Copper DAC |
| Cabling Complexity |
Medium |
Low |
Low |
Low |
Very Low |
| Power Consumption |
Very Low |
Medium |
High |
Low |
Very Low |
| Scalability |
High |
Very High |
Ultra |
Medium |
Very Low |
- SR4 offers the best cost–performance balance for short-range optical networks.
- LR4 and ER4 dominate long-distance backbone links.
Typical Deployment Scenarios & Decision Matrix
| Application Scenario |
Recommended Standard |
Technical Reason |
| Data center leaf–spine |
SR4 |
High density, low power, low cost |
| Server interconnect |
SR4 / CR4 |
Short distance, minimal latency |
| Building interconnect |
LR4 |
10 km reach, SMF compatibility |
| Metro network |
ER4 |
40 km reach |
| Legacy MMF upgrade |
BiDi |
No MPO conversion required |
| Top-of-rack patching |
CR4 |
Minimal cost & latency |
Selection Logic (Practical Guide)
Choose 40GBASE-SR4 if:
-
Your fiber plant is OM3 / OM4 multimode
-
Link length ≤ 150 m
-
You need lowest cost per 40G port
-
Data center density and thermal headroom are critical
Choose 40GBASE-LR4 if:
Choose 40GBASE-ER4 if:
Choose 40G BiDi if:
Choose CR4 if:
-
Ultra-short reach ≤7 m
-
Rack-level switching
40GBASE-SR4 is the most cost-efficient 40G standard for short-reach data center links, while LR4 and ER4 dominate long-distance single-mode deployments. BiDi enables duplex MMF reuse, and CR4 serves ultra-short copper connections.
✅ 40GBASE-SR4 Deployment Best Practices
Reliable QSFP 40G-SR4 deployment requires proper fiber planning, strict MPO polarity control, thermal management, and interoperability testing. Most failures result from connector misalignment, excessive insertion loss, and insufficient airflow, not optical power limitations.

① Fiber & Link Planning
Key guidelines:
-
OM3 fiber: maximum ~100 m
-
OM4 fiber: maximum ~150 m
-
Maintain BER ≤ 1×10⁻¹² for production-grade links
-
Keep total insertion loss within optical budget margin
② Channel Matching & MPO Handling
40GBASE-SR4 uses parallel optics with 4 transmit and 4 receive lanes, making lane polarity and channel mapping absolutely critical.
Best practices:
-
Enforce strict Tx/Rx lane alignment (1→1, 2→2, 3→3, 4→4)
-
Use keyed MPO connectors (Type-B polarity recommended)
-
Label trunk fibers clearly for bidirectional mapping verification
-
Validate lane integrity using optical fiber inspection probes
③ Thermal & Power Management
Although 40G SR4 QSFP+ modules typically consume <1.5 W, high-density switch deployments can generate significant cumulative thermal load.
Thermal management guidelines:
-
Maintain ambient temperature: 20–30 °C
-
Avoid sustained operation >40 °C inlet temperature
-
Ensure sufficient front-to-back airflow path
-
Avoid stacking high-power modules adjacently
④ Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Below are the most frequent deployment mistakes observed in production networks:
❌ Mistake 1: Treating SR4 as LR4 or ZR
❌ Mistake 2: Ignoring DOM/DDM Monitoring
❌ Mistake 3: Skipping Interoperability Testing
✅ Procurement & Compatibility Checklist
Large-scale 40G deployments fail far more often due to procurement mistakes and compatibility mismatches than pure optical performance issues. Based on extensive field testing and real-world rollout cases, the following checklist helps eliminate interoperability risk, deployment delays, and hidden operational costs.

1. Engineering Validation Checklist (Pre-Deployment)
Before placing bulk orders, network engineers should validate five critical technical dimensions:
✔️ Tx / Rx Power Margin & Link Budget
-
Verify optical output power, receiver sensitivity, and total link budget.
-
Ensure sufficient margin for:
-
Target BER ≤ 1×10⁻¹² with ≥ 2 dB system margin.
Field insight: Most unstable links are caused by tight power margins, not fiber length itself.
✔️ OM3 / OM4 Fiber Compatibility
Tip: For new installations, OM4 provides safer optical margin and longer service life.
✔️ DOM / DDM Monitoring Support
Ensure full support for Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM/DDM), including:
-
Transmit optical power
-
Receive optical power
-
Module temperature
-
Supply voltage
-
Laser bias current
Why it matters:
DOM enables predictive maintenance, early fault detection, and capacity planning — critical for data centers and 24/7 telecom environments.
✔️ MPO-12 Lane Mapping & Polarity Verification
-
Strict compliance with SR4 4×Tx / 4×Rx channel mapping.
-
Correct MPO polarity type (Type A/B/C) matching switch port orientation.
-
Keyed MPO connectors to prevent reversed insertion.
Common failure cause: Incorrect lane polarity → immediate link down or intermittent BER spikes.
✔️ Platform Compatibility Validation
Verify interoperability with target switching platforms, including:
-
Cisco
-
Arista
-
Juniper
-
HPE
-
Huawei
-
NVIDIA / Mellanox
-
White-box switches
Key checks:
Best practice: Always perform platform-specific sample testing before mass deployment.
2. Procurement Risk Control Checklist
| Risk Area |
Mitigation Strategy |
| Vendor lock-in |
Multi-platform compatible optics |
| Delivery delay |
Stable stock + short lead time |
| Traceability |
Batch + serial number tracking |
| RMA exposure |
Strict QA + burn-in testing |
| Lifecycle risk |
Multi-year supply guarantee |
3. Field-Tested Procurement Workflow (Recommended)
1️⃣ Engineering lab validation
2️⃣ Sample deployment in production environment
3️⃣ DOM monitoring stability test (72–168 hours)
4️⃣ Switch reboot & hot-swap stress testing
5️⃣ Bulk procurement
This process typically reduces deployment failure rates by over 80%.
For reliable 40GBASE-SR4 deployment, verify optical power margin, OM3/OM4 fiber compatibility, DOM support, MPO lane mapping, and platform interoperability. Always request sample testing before bulk rollout.
✅ 40GBASE-SR4 Frequently Asked Questions
40GBASE-SR4 supports up to 150 m on OM4 fiber, uses 8 fibers via MPO connectors, supports hot-swapping, and provides full DOM/DDM monitoring. It is not suitable for single-mode or long-distance links.

Q1: What is the maximum transmission distance of 40GBASE-SR4 on OM4 fiber?
A: Up to 150 meters on OM4 multimode fiber, assuming compliant optics, clean MPO connectors, and total link loss within IEEE-specified budgets, while maintaining BER ≤ 1×10⁻¹².
On OM3 fiber, the typical maximum distance is ~100 meters.
Q2: Can 40GBASE-SR4 replace 40GBASE-LR4 for long-distance links?
A: No. 40GBASE-SR4 is a short-reach, multimode-only standard designed for distances under 150 m.
For 10 km or longer links over single-mode fiber (SMF), 40GBASE-LR4 or ER4 must be used.
Q3: Is 40GBASE-SR4 hot-swappable?
A: Yes. 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ modules fully support hot-plug and hot-swap, allowing insertion or removal without powering down the host device, as defined by the QSFP+ MSA specification.
Q4: How many fibers does 40GBASE-SR4 use?
A: 8 fibers total:
-
4 transmit (Tx)
-
4 receive (Rx)
These fibers are carried within an MPO-12 connector, where the middle 4 fibers remain unused.
Q5: Does 40GBASE-SR4 support DOM / DDM monitoring?
A: Yes. Most modern QSFP+ SR4 modules support Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM/DDM), providing real-time visibility into:
-
Transmit optical power
-
Receive optical power
-
Module temperature
-
Supply voltage
-
Laser bias current
This enables predictive maintenance, proactive fault detection, and performance optimization.
✅ Final Recommendation for 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ Modules
40GBASE-SR4 remains the most efficient optical choice for short-reach 40G deployments.
-
Choose SR4 for ≤150 m multimode fiber links, including:
-
Data center leaf–spine architectures
-
Server-to-switch uplinks
-
5G fronthaul and aggregation links
-
High-density aggregation and access networks
-
Do NOT substitute SR4 for long-haul links.
For distances beyond 150 m or any single-mode fiber (SMF) deployment, select 40GBASE-LR4 / ER4 optics instead.
From extensive field testing and production deployments, SR4 consistently delivers the best balance of performance, reliability, power efficiency, and total cost of ownership for short-reach 40G infrastructures.
Planning a 40G fiber deployment or upgrade?
👉 Request LINK-PP Official Store sample tests, platform compatibility validation, and procurement guidance to ensure flawless interoperability, stable supply, and production-grade deployment confidence for 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ modules.