QSFP 40G SR4 is a short-reach 40Gbps optical transceiver designed for high-density data center interconnects using multimode fiber and parallel optics.
It operates at 850nm, transmits data over four parallel 10Gbps lanes, and typically supports distances up to 100m on OM3 and 150m on OM4 fiber, making it ideal for switch-to-switch links within racks or rows.
As one of the most widely deployed 40G transceiver types, QSFP 40G SR4 is commonly used in leaf–spine architectures where low latency, high port density, and cost efficiency are more critical than long-reach capability. Its MPO interface and support for breakout connectivity also make it a flexible option for both native 40G links and 4×10G deployments.
This article explains what QSFP 40G SR4 is, how it works, its key specifications, typical use cases, and how it compares with other 40G transceiver options—helping you determine when SR4 is the right choice for your network design.
↪️ What Is a QSFP 40G SR4 Transceiver?
A QSFP 40G SR4 transceiver is a 40Gbps optical module that uses short-reach multimode fiber and parallel optics to transmit data over four independent lanes.
It follows the QSFP+ form factor, operates at 850nm, and is primarily designed for high-density, short-distance links inside data centers rather than long-haul or campus networks.

What Does “QSFP 40G SR4” Mean?
The term “QSFP 40G SR4” describes the module’s form factor, speed, reach, and lane architecture.
Each part of the name directly reflects a technical characteristic:
-
QSFP+: Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus, a hot-swappable transceiver form factor
-
40G: Aggregate data rate of 40Gbps
-
SR (Short Reach): Optimized for short-distance transmission over multimode fiber
-
4: Four parallel optical lanes, each running at 10Gbps
This naming convention helps distinguish SR4 modules from single-lane long-reach options such as LR4 or ER4.
How QSFP 40G SR4 Fits Into 40G Ethernet Standards
QSFP 40G SR4 is defined by the IEEE 802.3ba standard as 40GBASE-SR4, which specifies short-reach 40GbE transmission over multimode fiber using four parallel optical lanes. This standard ensures consistent electrical interfaces, optical characteristics, and interoperability across compliant switches and transceivers.
Under IEEE 802.3ba, 40GBASE-SR4 operates at 850nm and is designed for OM3 and OM4 multimode fiber, supporting typical link distances of up to 100m on OM3 and 150m on OM4. The standard also mandates the use of parallel optics with an MPO interface, which differentiates SR4 from duplex single-mode variants such as LR4.
By adhering to this standard, QSFP 40G SR4 modules from different vendors can be mixed within the same network environment, provided that fiber type, distance, and polarity requirements are met.
Why QSFP 40G SR4 Uses Parallel Optics
QSFP 40G SR4 relies on parallel optics to achieve high bandwidth without increasing per-lane speed.
Instead of sending 40Gbps over a single optical channel, the module splits the signal into four 10Gbps lanes, transmitting and receiving them simultaneously.
This design offers several advantages:
-
Lower signal loss over short distances
-
Reduced power consumption per lane
-
Better signal integrity compared to single-lane high-speed optics
-
Natural support for breakout applications (40G to 4×10G)
Because of these characteristics, SR4 has become the default choice for short-reach 40G deployments in modern data centers.
↪️ Key Specifications of QSFP 40G SR4
QSFP 40G SR4 is defined by a set of standardized optical and electrical specifications optimized for short-reach, high-density 40GbE links in data center environments. These specifications determine transmission distance, cabling requirements, power behavior, and overall interoperability.

Core Technical Parameters
From a practical deployment perspective, the most important QSFP 40G SR4 specifications relate to speed, wavelength, fiber type, and reach.
| Parameter |
Specification |
| Data Rate |
40Gbps (4×10Gbps) |
| Wavelength |
850nm |
| Fiber Type |
OM3 / OM4 multimode |
| Maximum Distance |
100m (OM3), 150m (OM4) |
| Connector Type |
MPO / MTP |
These parameters explain why QSFP 40G SR4 is primarily used inside data centers rather than across campuses or metro links. The use of 850nm optics and multimode fiber limits reach but significantly reduces cost and power consumption.
Electrical Interface and Form Factor
QSFP 40G SR4 uses the QSFP+ form factor with a standardized electrical interface to ensure broad platform compatibility.
| Parameter |
Specification |
| Form Factor |
QSFP+ |
| Lane Architecture |
4 transmit + 4 receive |
| Host Interface |
4×10Gbps electrical lanes |
| Hot-Swappable |
Yes |
This electrical design allows switches to support multiple 40G ports in a compact footprint, enabling high port density in spine and leaf switches.
Power Consumption and Thermal Characteristics
Power efficiency is a key reason QSFP 40G SR4 remains widely deployed in 40G networks.
| Parameter |
Typical Value |
| Power Consumption |
≤1.5W |
| Cooling Requirement |
Standard airflow |
| Thermal Monitoring |
Digital diagnostics (DDM) |
Compared with long-reach 40G modules, SR4 transceivers generate less heat, simplifying thermal design and reducing overall operating costs in dense switch environments.
↪️ How Does QSFP 40G SR4 Work?
QSFP 40G SR4 works by transmitting data over four parallel optical lanes, each carrying 10Gbps, to achieve an aggregate bandwidth of 40Gbps over short distances. This parallel optics approach avoids pushing a single optical channel to very high speeds, improving signal stability and efficiency in dense data center environments.
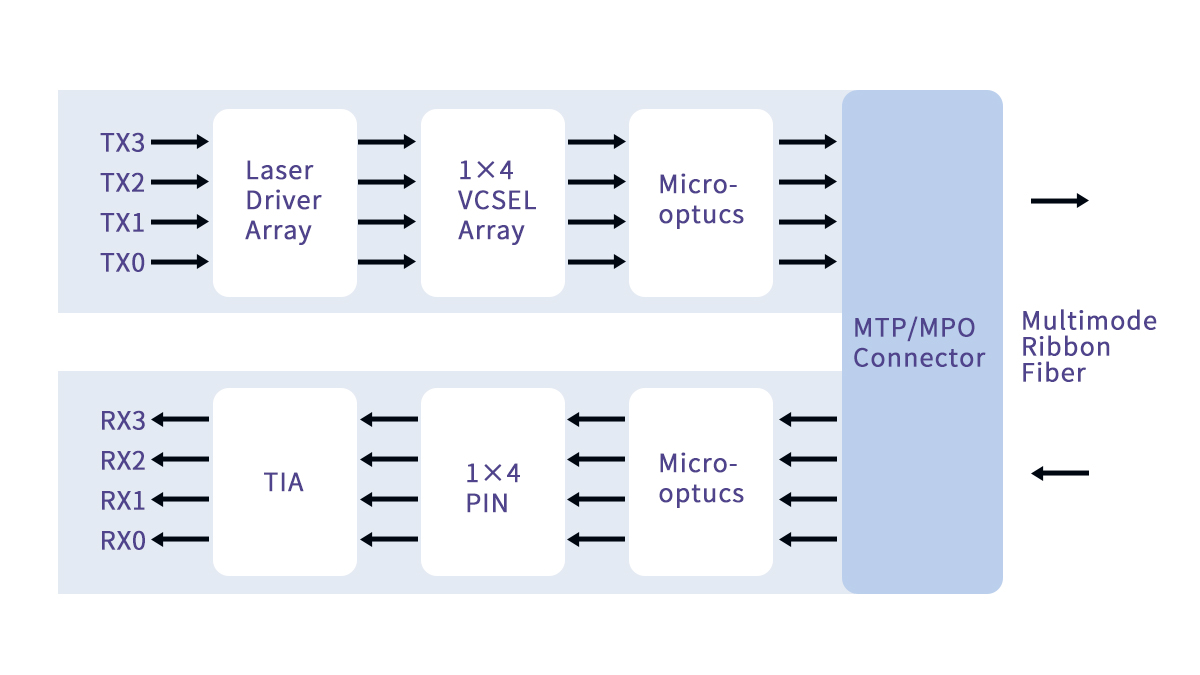
Parallel Optics Transmission Explained
Instead of using one high-speed laser, QSFP 40G SR4 splits the data stream into multiple lower-speed optical lanes.
On the transmit side, the electrical 40Gbps signal from the host is divided into four 10Gbps lanes, each modulated onto an 850nm laser. On the receive side, four corresponding photodiodes convert the optical signals back into electrical data and recombine them into a single 40Gbps stream.
This architecture reduces per-lane signal distortion and makes short-reach multimode transmission more reliable compared to single-lane designs at higher speeds.
Transmit and Receive Lane Architecture
QSFP 40G SR4 uses eight fibers in total: four for transmission and four for reception.
These fibers are grouped within an MPO connector, enabling compact and high-density cabling.
-
4 transmit lanes (Tx): each operating at 10Gbps
-
4 receive lanes (Rx): each operating at 10Gbps
-
All lanes operate simultaneously to deliver full-duplex 40Gbps communication
This fixed lane mapping is defined by the 40GBASE-SR4 standard, ensuring consistent polarity and interoperability across compliant devices.
Why MPO Connectivity Is Required
MPO connectors are essential for QSFP 40G SR4 because parallel optics require multiple fibers to operate at the same time.
Unlike duplex LC connectors used in single-lane optics, MPO interfaces can carry multiple fibers within a single connector, supporting high port density without increasing cable count.
In practice, QSFP 40G SR4 modules typically use an MPO-12 connector, where eight fibers are actively used for data transmission and reception, while the remaining fibers provide alignment and future compatibility.
Breakout and Aggregation Scenarios
The parallel lane design of QSFP 40G SR4 naturally supports breakout configurations.
A single 40G SR4 port can be broken out into four independent 10G links using an MPO-to-LC breakout cable.
Common breakout scenarios include:
-
40G switch port to 4×10G server or access switches
-
Gradual migration from 10G to 40G infrastructure
-
Efficient utilization of high-density spine ports
These breakout capabilities add deployment flexibility and extend the practical value of QSFP 40G SR4 in evolving data center networks.
↪️ QSFP 40G SR4 vs Other 40G Transceivers
QSFP 40G SR4 is optimized for short-distance, high-density data center links, while other 40G transceivers prioritize longer reach or different cabling models. Choosing the right 40G module depends primarily on transmission distance, fiber type, and deployment scenario rather than raw bandwidth, since all options deliver 40Gbps.

QSFP 40G SR4 vs QSFP 40G LR4
The primary difference between SR4 and LR4 lies in reach and fiber type, which directly impacts cost and deployment flexibility.
| Feature |
QSFP 40G SR4 |
QSFP 40G LR4 |
| Fiber Type |
Multimode (OM3/OM4) |
Single-mode |
| Wavelength |
850nm |
1310nm |
| Maximum Distance |
Up to 150m |
Up to 10km |
| Typical Use Case |
Intra–data center links |
Campus / inter-building links |
SR4 is preferred when fiber distances are short and port density is high, while LR4 is used when links must span longer distances or existing single-mode infrastructure is already in place.
QSFP 40G SR4 vs QSFP 40G ZR4
SR4 and ZR4 serve similar short-reach environments but differ in physical medium and cabling constraints.
| Feature |
QSFP 40G SR4 |
QSFP 40G ZR4 |
| Medium |
Multimode fiber |
Single mode fiber |
| Maximum Distance |
Up to 150m |
Up to 80km |
| Cabling Flexibility |
High |
High |
| Typical Deployment |
Structured cabling |
Top-of-rack |
ZR4 is suitable for long connections, while SR4 offers significantly more flexibility for cross-rack and row-level connections.
When SR4 Is the Better Choice
QSFP 40G SR4 is the most practical option when balancing distance, density, and cost in modern data centers.
It is typically the right choice when:
-
Link distances fall within 100–150m
-
Multimode fiber infrastructure is available
-
High port density and airflow efficiency are required
-
Breakout support (40G to 4×10G) is needed
In contrast, LR4 or other long-reach transceivers become necessary only when distance requirements exceed the limits of multimode fiber.
↪️ Typical Use Cases for QSFP 40G SR4
QSFP 40G SR4 is primarily used in short-reach, high-bandwidth data center environments where port density and cost efficiency are critical. Its parallel-optics design and multimode fiber support make it especially suitable for intra-data center connections rather than long-distance or carrier-grade netwo
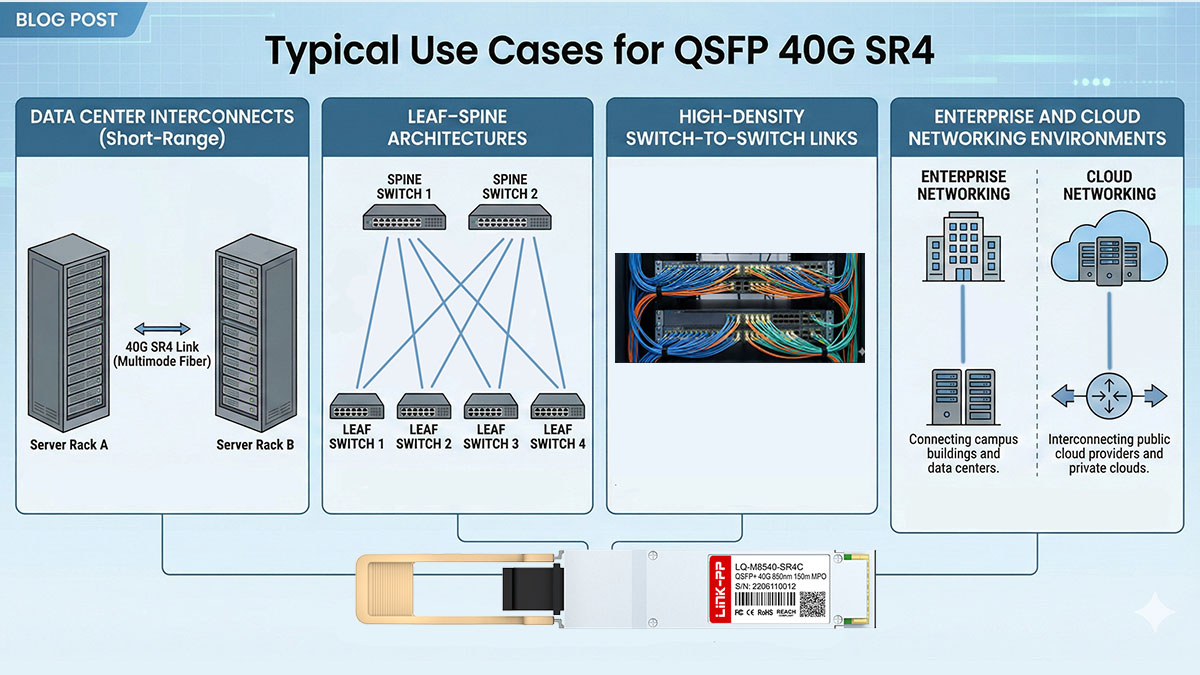
Leaf–Spine Data Center Architectures
QSFP 40G SR4 is widely deployed as a spine-to-leaf interconnect in modern data center designs.
In leaf–spine architectures, SR4 modules are typically used for:
-
High-capacity links between leaf and spine switches
-
Low-latency east–west traffic within the data center
-
Dense switch configurations requiring efficient airflow
The short reach of SR4 aligns well with the physical layout of most data centers, where switch-to-switch distances rarely exceed 100–150m.
Switch-to-Switch Links Within Racks or Rows
SR4 is an optimal choice for switch-to-switch connections within the same rack or across adjacent rows.
Common deployment scenarios include:
-
Aggregation layer to access layer switches
-
Inter-rack links in medium-to-large data halls
-
High-bandwidth uplinks from top-of-rack switches
Compared with copper-based alternatives, SR4 provides greater distance and better signal stability without sacrificing port density.
40G to 4×10G Breakout Deployments
QSFP 40G SR4 naturally supports breakout configurations due to its four-lane optical architecture.
Typical breakout use cases include:
-
Connecting a 40G switch port to four 10G server NICs
-
Gradual migration from 10G to 40G infrastructure
-
Maximizing utilization of high-capacity switch ports
This flexibility allows network operators to scale bandwidth incrementally while preserving existing 10G equipment.
Enterprise and Private Cloud Networks
Beyond hyperscale environments, QSFP 40G SR4 is also common in enterprise and private cloud data centers.
It is often selected for:
-
Internal data center connectivity
-
Virtualized and containerized workloads with high east–west traffic
-
Cost-sensitive deployments requiring reliable 40G performance
In these scenarios, SR4 strikes a practical balance between performance, cost, and operational simplicity.
↪️ Fiber and Cabling Requirements for QSFP 40G SR4
QSFP 40G SR4 requires multimode fiber and MPO-based cabling to support its parallel optics architecture and short-reach transmission model. Correct fiber type, connector selection, and polarity management are essential to achieve the expected distance and interoperability.
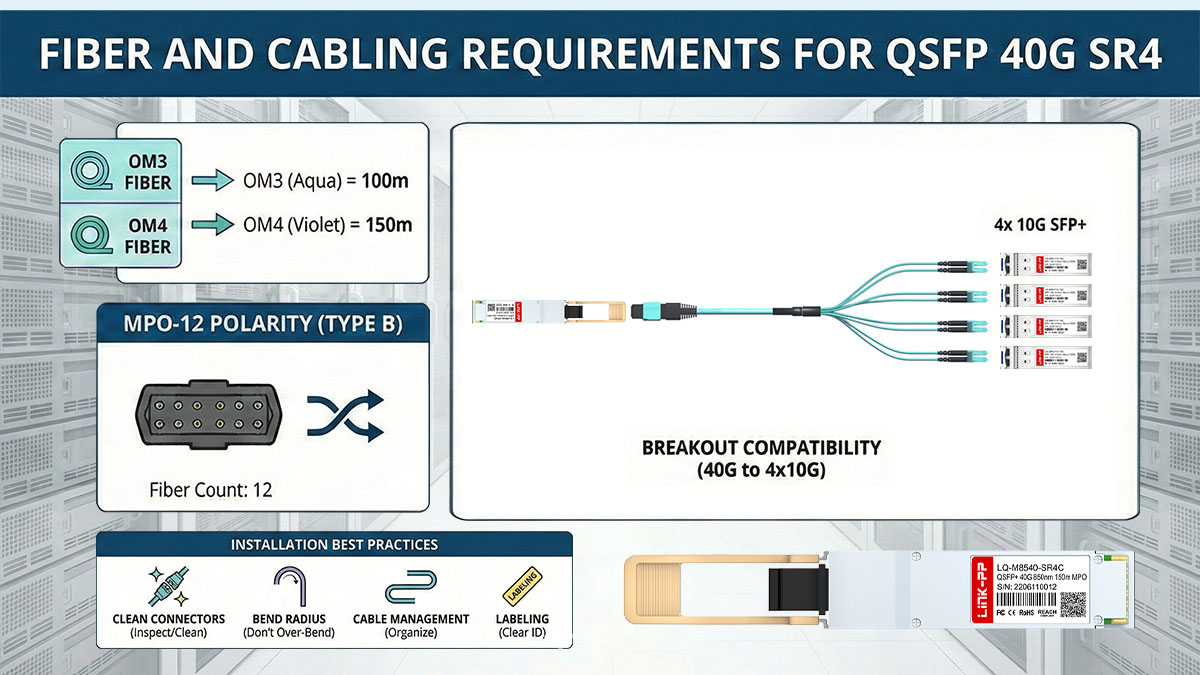
OM3 vs OM4 Multimode Fiber Support
Transmission distance for QSFP 40G SR4 is primarily determined by the multimode fiber grade.
| Fiber Type |
Core Size |
Maximum Distance |
| OM3 |
50/125µm |
Up to 100m |
| OM4 |
50/125µm |
Up to 150m |
OM4 fiber offers extended reach and greater link margin compared to OM3, making it the preferred option for new installations or larger data halls, while OM3 remains common in existing infrastructures.
MPO Connector and Fiber Count Requirements
QSFP 40G SR4 uses an MPO interface to accommodate multiple optical lanes within a single connector.
Although the module typically features an MPO-12 connector, only eight fibers are actively used for data transmission.
-
4 fibers for transmit (Tx)
-
4 fibers for receive (Rx)
-
Remaining fibers reserved for alignment and standard compliance
This design enables high-density cabling while maintaining compatibility with standardized MPO systems.
Polarity and Cabling Considerations
Correct polarity is critical for QSFP 40G SR4 links because transmit and receive lanes must be properly aligned end-to-end.
Key cabling considerations include:
-
Selecting the correct MPO polarity method (commonly Type B)
-
Ensuring consistent fiber mapping across patch panels
-
Verifying Tx/Rx alignment during installation and testing
Improper polarity is one of the most common causes of link failures in SR4 deployments.
Breakout Cable Compatibility
QSFP 40G SR4 supports breakout cabling to convert one 40G link into multiple 10G connections.
Common breakout configurations:
-
MPO-to-4×LC for 40G to 4×10G
-
Direct connection to SFP+ 10G SR modules
-
Structured cabling environments with MPO trunks
Breakout cables must be matched with compatible switch configurations and supported firmware to function correctly.
↪️ Compatibility and Interoperability Considerations
QSFP 40G SR4 transceivers are broadly interoperable across vendors, but practical compatibility depends on switch support, coding compliance, and proper cabling. Understanding these factors helps avoid link issues and ensures predictable performance in multi-vendor environments.

Switch and Platform Compatibility
QSFP 40G SR4 modules must be supported by the host switch or network device at both the hardware and software levels.
Key compatibility checks include:
-
The switch port supports QSFP+ 40G operation
-
The platform firmware recognizes SR4 optical modules
-
Port speed and breakout mode are correctly configured
Even when physical insertion is possible, unsupported firmware or port configurations can prevent the link from coming up.
MSA Compliance and Optical Standards
MSA compliance is the foundation of cross-vendor interoperability for QSFP 40G SR4.
| Aspect |
Requirement |
| Form Factor |
QSFP+ MSA compliant |
| Optical Standard |
IEEE 802.3ba (40GBASE-SR4) |
| Electrical Interface |
4×10Gbps lanes |
| Management Interface |
I²C with DDM support |
Modules that fully adhere to MSA and IEEE standards can typically interoperate without issue, provided that fiber and distance limits are respected.
OEM vs Third-Party QSFP 40G SR4 Modules
Both OEM and third-party QSFP 40G SR4 modules can function reliably if compatibility requirements are met.
Key differences to consider:
-
OEM modules are vendor-branded and pre-approved
-
Third-party modules rely on EEPROM coding to match specific platforms
-
Compatibility testing reduces risk in mixed environments
From a technical standpoint, standards-compliant third-party modules perform the same optical functions as OEM versions when properly coded and validated.
Interoperability Testing and Deployment Best Practices
Interoperability is best ensured through controlled testing rather than assumptions.
Recommended practices include:
-
Validating modules on target switch models before full rollout
-
Testing links at maximum expected distance
-
Verifying DDM readings such as optical power and temperature
These steps help identify potential issues early and ensure stable operation in production networks.
↪️ How to Choose the Right QSFP 40G SR4 Module
Choosing the right QSFP 40G SR4 module depends less on bandwidth and more on distance, cabling, platform compatibility, and deployment intent. Since all SR4 modules deliver the same 40Gbps performance, the correct choice is primarily about fit and risk control rather than speed.
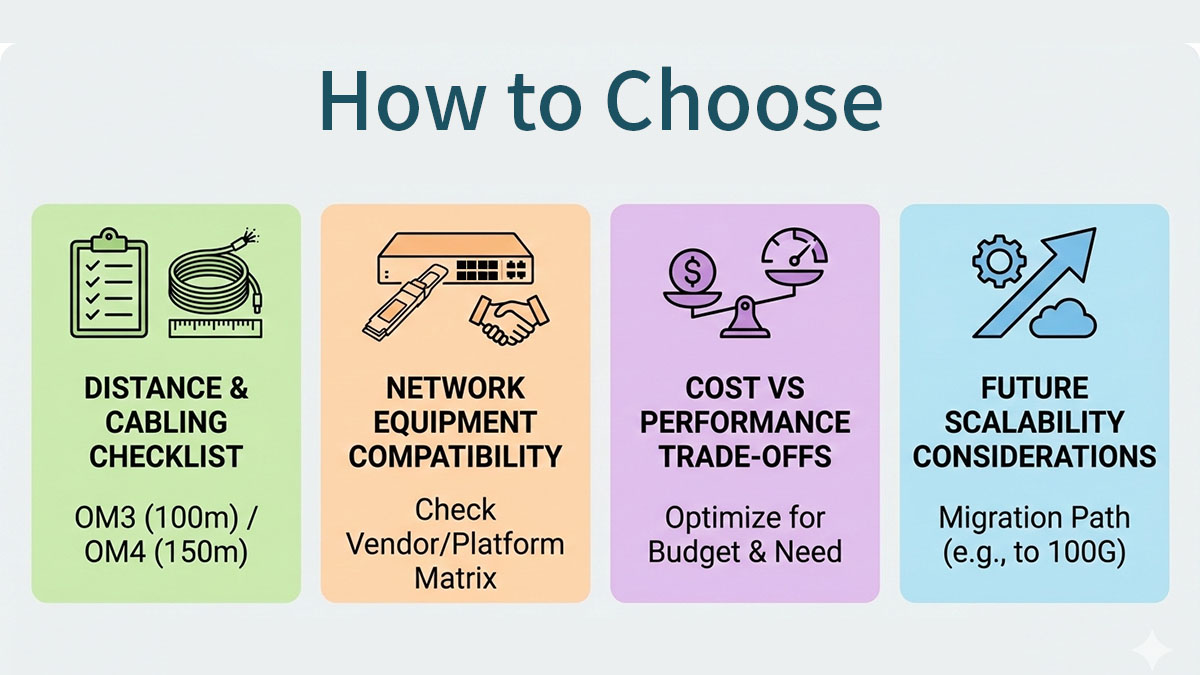
Confirm Link Distance and Fiber Infrastructure
The first decision point is whether your link falls within SR4 distance limits and uses compatible multimode fiber.
Before selecting a module, verify:
-
Maximum link length does not exceed 100m on OM3 or 150m on OM4
-
Existing cabling is multimode, not single-mode
-
Fiber quality and connector cleanliness meet data center standards
If distance or fiber type is uncertain, SR4 may not be the appropriate option.
Check Switch and NIC Compatibility
Platform compatibility is critical to avoid link failures or unsupported-module warnings.
Key checks include:
-
The switch supports QSFP+ 40G SR4 optics
-
Firmware version allows SR4 or third-party modules
-
Breakout mode is supported if 40G to 4×10G is required
Verifying compatibility at this stage prevents unnecessary troubleshooting after deployment.
Decide Between OEM and Third-Party Modules
From a technical perspective, standards-compliant OEM and third-party SR4 modules function identically.
Your decision should consider:
-
Budget constraints and total deployment scale
-
Vendor lock-in policies
-
Availability of platform-specific coding
-
Access to pre-deployment compatibility testing
In large-scale data centers, validated third-party modules are often chosen to reduce cost while maintaining reliability.
Consider Power, Density, and Thermal Constraints
In high-density environments, power consumption and thermal behavior directly affect switch performance.
When comparing SR4 modules:
-
Confirm typical power consumption remains within switch limits
-
Ensure adequate airflow for densely populated ports
-
Monitor DDM values during pilot deployments
SR4 modules are generally power-efficient, but consistency matters in large installations.
Plan for Future Network Evolution
A good SR4 selection should support not only current needs but also future transition paths.
Consider whether:
-
Breakout support will be needed during migration phases
-
Existing 10G infrastructure must be preserved
-
40G links may later be replaced or upgraded to 100G
Selecting a module that aligns with long-term architecture reduces rework and operational complexity.
↪️ FAQs About QSFP 40G SR4 Transceivers
Q1: Is QSFP 40G SR4 single-mode or multimode?
QSFP 40G SR4 is a multimode transceiver designed specifically for OM3 and OM4 fiber.
It operates at 850nm and does not support single-mode fiber, which is why its transmission distance is limited compared to LR4 or ER4 modules.
Q2: What is the maximum distance of QSFP 40G SR4?
The maximum distance is up to 100m on OM3 fiber and up to 150m on OM4 fiber.
Actual reach may vary depending on fiber quality, connector loss, and installation conditions, but SR4 is not intended for long-distance links.
Q3: Does QSFP 40G SR4 require an MPO connector?
Yes, QSFP 40G SR4 requires an MPO interface because it uses parallel optical lanes.
Eight fibers are actively used—four for transmit and four for receive—making MPO cabling mandatory for native 40G SR4 links.
Q4: Can QSFP 40G SR4 be broken out to 4×10G?
Yes, QSFP 40G SR4 fully supports breakout into four 10Gbps links.
Using an MPO-to-4×LC breakout cable, a single 40G port can connect to four SFP+ 10G SR interfaces, provided the switch supports breakout mode.
Q5: Is QSFP 40G SR4 compatible with LC connectors?
QSFP 40G SR4 does not natively support LC connectors for 40G links.
LC connectors are only used on the 10G side in breakout configurations; the 40G interface itself always uses MPO.
Q6: Is QSFP 40G SR4 still relevant compared to 100G?
QSFP 40G SR4 remains relevant in existing 40G infrastructures and cost-sensitive environments.
While new deployments increasingly favor 100G, SR4 continues to be used where 40G switching platforms are already in place.
↪️ Conclusion: When QSFP 40G SR4 Is the Right Choice
QSFP 40G SR4 is the right choice for short-reach 40GbE deployments where high port density, multimode fiber, and cost efficiency are key priorities. With its parallel optics design, 850nm operation, and support for MPO cabling and breakout scenarios, SR4 fits naturally into modern data center architectures such as leaf–spine networks and high-density switch-to-switch links.
While SR4 is not intended for long-distance transmission, it remains highly practical in environments where link distances stay within 100–150m and existing OM3 or OM4 fiber infrastructure is available. When selected with proper attention to cabling, polarity, and platform compatibility, QSFP 40G SR4 delivers stable performance and predictable interoperability.
For network planners and operators evaluating reliable QSFP 40G SR4 options, exploring standards-compliant, fully tested modules can simplify deployment and reduce operational risk. You can review compatible QSFP 40G SR4 transceiver solutions and deployment-ready options at the LINK-PP Official Store, where detailed specifications and platform support information are available to support informed purchasing decisions.