A 10GBASE-LRM SFP module is designed to deliver 10G Ethernet over legacy multimode fiber, solving a common problem in enterprise and data center networks: achieving longer reach without replacing existing cabling. It fills the gap between short-reach 10G SR optics and long-reach single-mode solutions by extending 10G transmission to up to 220m on older multimode fiber types.
As networks upgrade from 1G to 10G, many environments still rely on OM1 or OM2 multimode fiber originally deployed for earlier generations. Standard 10G SR modules are often limited by distance on these fibers, while single-mode LR requires new cabling and higher costs. This is where 10GBASE-LRM becomes relevant, offering a practical upgrade path based on the IEEE 802.3aq standard.
In this guide, you will learn what a 10GBASE-LRM SFP module is, how it works, its key technical specifications, and when it makes sense to use it instead of other 10G optics. The goal is to help network planners and engineers clearly determine whether 10GBASE-LRM is the right solution for their infrastructure before moving on to detailed comparisons and use cases.
🚀 What Is a 10GBASE-LRM SFP Module?
A 10GBASE-LRM SFP module is a 10GbE optical transceiver designed to transmit data over multimode fiber at extended distances, specifically targeting legacy fiber infrastructure. It operates at 1310nm and supports link lengths of up to 220m, making it suitable for environments where standard short-reach optics cannot reliably meet distance requirements.
Definition of 10GBASE-LRM
10GBASE-LRM is an Ethernet physical layer specification that enables 10G Ethernet over multimode fiber beyond traditional SR limits. Unlike 10GBASE-SR, which is optimized for short distances at 850nm, LRM uses a longer wavelength and signal compensation techniques to maintain performance over older fiber types.
Meaning of “LRM” (Long Reach Multimode)
“LRM” stands for Long Reach Multimode, highlighting the module’s primary purpose: extending 10G transmission on multimode fiber. By using 1310nm optics combined with electronic dispersion compensation, LRM minimizes modal dispersion issues that typically limit distance on legacy multimode cabling.
Form Factor: SFP+ vs XFP (Historical Context)
Originally, 10GBASE-LRM was implemented in the XFP form factor, which was common in early 10G deployments. As SFP+ became the industry standard for higher port density and lower power consumption, LRM optics transitioned to the SFP+ form factor, allowing seamless integration with modern switches and routers while maintaining backward compatibility in functionality.
IEEE 802.3aq Standard Overview
10GBASE-LRM is defined under the IEEE 802.3aq standard, which specifies:
-
Operation at 10GbE data rates
-
Support for multimode fiber types such as OM1, OM2, and OM3
-
A maximum reach of 220m
-
Compliance requirements for dispersion compensation and link performance
This standardization ensures interoperability across compliant devices and positions 10GBASE-LRM as a reliable solution for upgrading existing multimode fiber networks without extensive re-cabling.
🚀 Key Technical Specifications of 10GBASE-LRM
The 10GBASE-LRM SFP module is defined by a specific set of technical parameters that distinguish it from other 10G optical transceiver. Understanding these specifications is essential for determining compatibility, performance expectations, and deployment suitability.
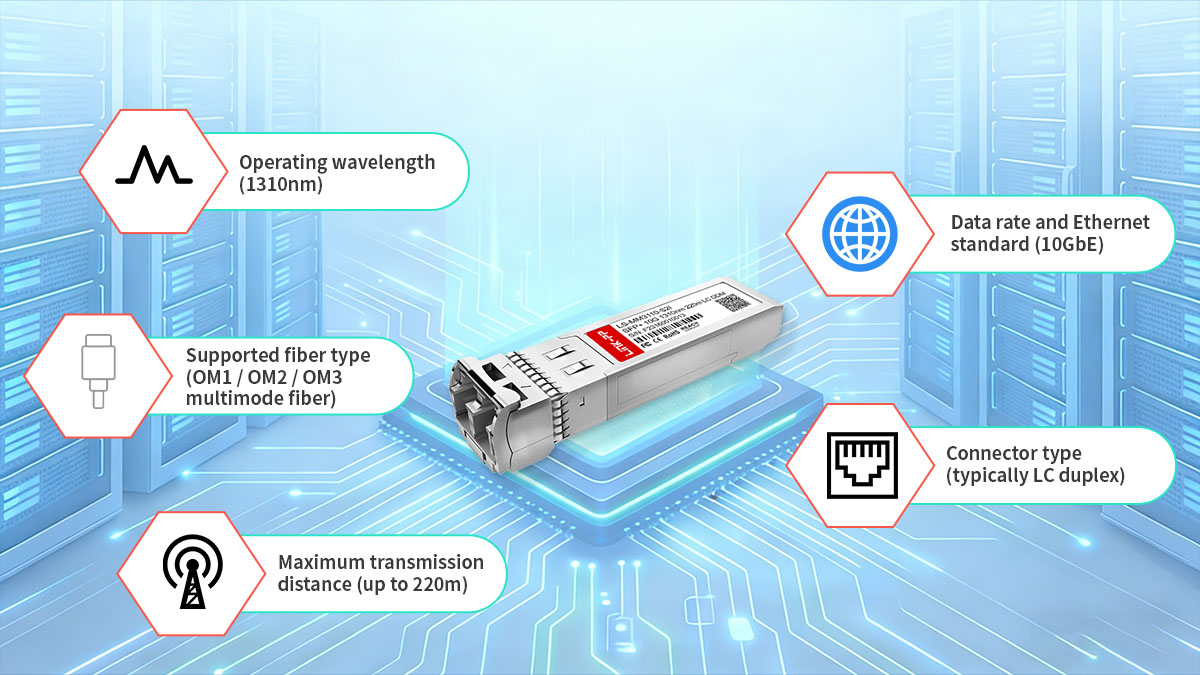
Operating Wavelength (1310nm)
10GBASE-LRM operates at a 1310nm wavelength, which allows signals to travel farther on multimode fiber compared to 850nm-based SR optics. This longer wavelength helps reduce modal dispersion on legacy fibers, enabling more stable transmission over extended distances.
Supported Fiber Types (OM1 / OM2 / OM3)
10GBASE-LRM is designed to work with multimode fiber, including:
This broad compatibility makes it particularly useful in environments where older multimode cabling is already installed. While it can also function on newer fiber types, its primary value lies in extending the usability of existing OM1 and OM2 infrastructure.
Maximum Transmission Distance (Up to 220m)
The maximum supported distance for 10GBASE-LRM is up to 220m on multimode fiber, depending on fiber quality and link conditions. This extended reach significantly exceeds what standard 10GBASE-SR modules can achieve on legacy fiber, making LRM a practical alternative when distance becomes a limiting factor.
Data Rate and Ethernet Standard (10GbE)
10GBASE-LRM supports a 10GbE data rate in compliance with Ethernet standards defined by IEEE. It is fully compatible with 10G Ethernet switching and routing platforms that support SFP+ optics, ensuring seamless integration into modern network architectures.
Connector Type (Typically LC Duplex)
Most 10GBASE-LRM SFP modules use an LC duplex connector, which is the industry standard for 10G optical links. This connector type supports reliable bidirectional communication over separate transmit and receive fibers and is widely supported across enterprise and data center cabling systems.
Together, these specifications define the operational boundaries of 10GBASE-LRM and explain why it remains relevant for upgrading legacy multimode fiber networks to 10G speeds.
🚀 How 10GBASE-LRM Works on Multimode Fiber
10GBASE-LRM enables longer 10G transmission on multimode fiber by combining a 1310nm optical signal with electronic signal processing, rather than relying solely on short-wavelength optics. This design allows it to overcome the physical limitations that affect traditional 10G SR modules on legacy fiber.
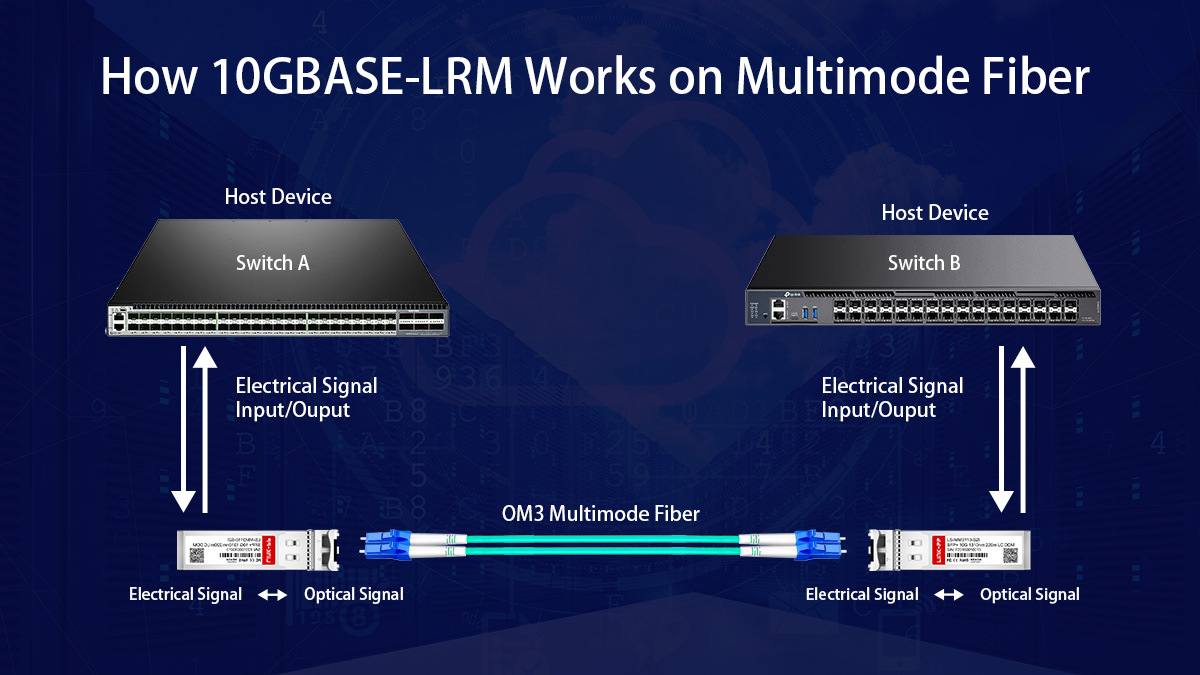
Difference Between LRM and Traditional SR Optics
The key difference between 10GBASE-LRM and 10GBASE-SR lies in how each handles signal dispersion on multimode fiber:
-
10GBASE-SR operates at 850nm and is optimized for short distances, performing best on OM3 and OM4 fiber.
-
10GBASE-LRM operates at 1310nm, which experiences less modal dispersion on older multimode fiber.
As a result, SR optics often fail to reach required distances on OM1 or OM2 fiber, while LRM is specifically engineered to extend reach under these conditions.
Use of Electronic Dispersion Compensation (EDC)
A defining feature of 10GBASE-LRM is its use of Electronic Dispersion Compensation (EDC). EDC actively corrects signal distortion caused by modal dispersion as the light travels through multimode fiber. By compensating for these distortions at the receiver, LRM maintains signal integrity over longer distances that would otherwise be unreliable for 10G transmission.
Why 1310nm Is Used on Multimode Fiber
Although 1310nm is commonly associated with single-mode optics, it offers advantages on multimode fiber when combined with EDC. At this wavelength, the effects of modal dispersion are reduced compared to 850nm, allowing the signal to propagate more evenly across multiple fiber modes. This makes 1310nm a practical choice for extending reach on legacy multimode cabling.
Signal Performance Over Legacy Fiber Infrastructure
On older multimode fiber installations, factors such as fiber quality, connector condition, and link loss can significantly affect performance. 10GBASE-LRM is designed to tolerate these real-world conditions better than SR optics, providing more consistent signal performance on existing infrastructure. However, proper cabling practices and, in some cases, mode conditioning patch cords are still important to ensure optimal results.
By combining wavelength selection and electronic compensation, 10GBASE-LRM delivers a reliable solution for running 10G Ethernet over multimode fiber networks that were never originally designed for such speeds.
🚀 10GBASE-LRM vs Other 10G SFP+ Modules
10GBASE-LRM sits between SR and LR optics, offering extended reach on multimode fiber without the cost and complexity of single-mode deployment. The differences are easiest to understand when compared side by side.
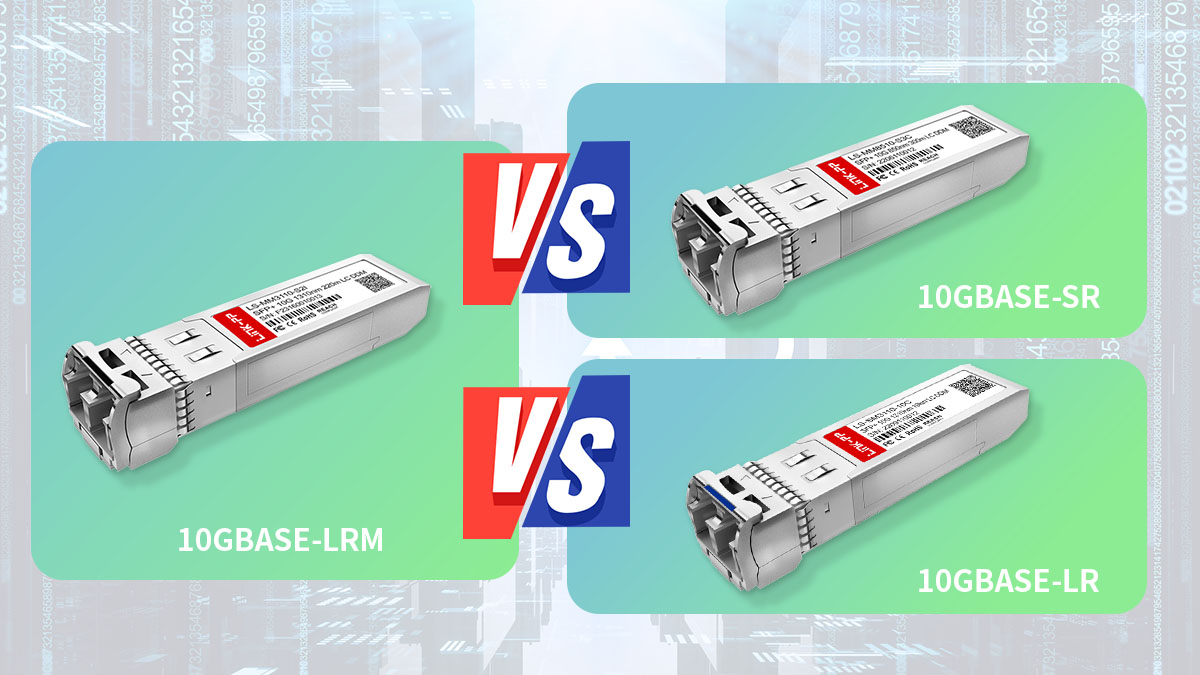
10GBASE-LRM vs 10GBASE-SR vs 10GBASE-LR
| Feature |
10GBASE-SR |
10GBASE-LRM |
10GBASE-LR |
| Operating wavelength |
850nm |
1310nm |
1310nm |
| Fiber type |
Multimode (OM3 / OM4) |
Multimode (OM1 / OM2 / OM3) |
Single-mode |
| Maximum distance |
Short on legacy fiber |
Up to 220m |
Up to 10km |
| Optimized for legacy MMF |
❌ |
✅ |
❌ |
| Typical use case |
Modern data centers |
Legacy MMF upgrades |
Long-distance links |
| Infrastructure cost impact |
Low on new fiber |
Low on existing MMF |
High (new fiber often required) |
Key Differences Explained
-
Distance
-
SR performs well on modern multimode fiber but is distance-limited on OM1 and OM2.
-
LRM extends reach to 220m on legacy multimode fiber.
-
LR far exceeds both but targets completely different use cases.
-
Fiber Type
-
LRM is the only option specifically designed for longer reach on multimode fiber.
-
LR requires single-mode fiber, making it unsuitable for reuse of legacy MMF.
-
Cost Considerations
-
While SR modules are typically the least expensive optics, they may force costly fiber replacement.
-
LRM reduces total upgrade cost by eliminating re-cabling.
-
LR optics and single-mode deployment usually represent the highest overall investment.
When 10GBASE-LRM Is the Better Choice
10GBASE-LRM is the preferred option when:
-
Your network relies on OM1 or OM2 multimode fiber
-
Link distances exceed what SR can reliably support
-
Replacing fiber with single-mode is not practical or budget-friendly
-
You need a low-disruption path to 10G Ethernet
In these scenarios, 10GBASE-LRM delivers a practical balance between performance, compatibility, and cost, making it a targeted solution rather than a general-purpose optic.
🚀 Typical Use Cases for 10GBASE-LRM SFP Modules
10GBASE-LRM SFP modules are best suited for environments where legacy multimode fiber must be preserved while upgrading to 10G Ethernet. Rather than being a general-purpose 10G optic, LRM addresses very specific deployment challenges.
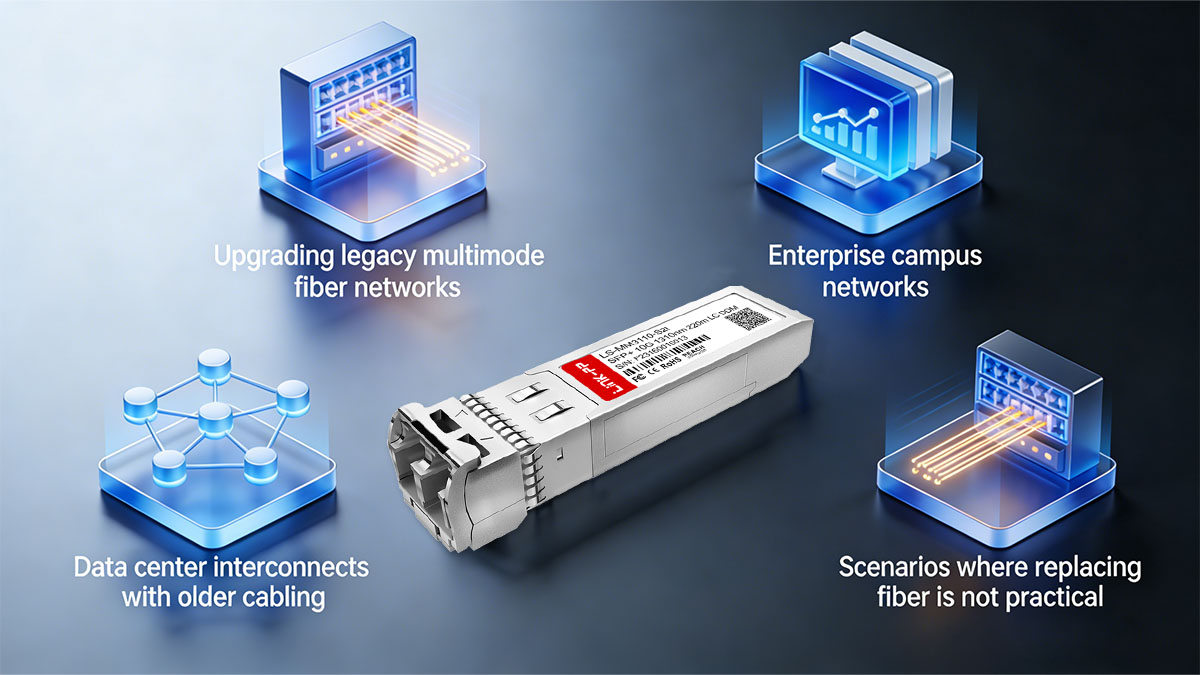
Upgrading Legacy Multimode Fiber Networks
One of the most common use cases for 10GBASE-LRM is upgrading existing OM1 or OM2 multimode fiber from 1G to 10G. In many older buildings and facilities, fiber was installed long before 10G standards existed. LRM enables higher speeds on this infrastructure without requiring disruptive and costly re-cabling projects.
Enterprise Campus Networks
Enterprise campus networks often span multiple buildings with fiber runs that exceed the practical limits of 10GBASE-SR on legacy fiber. 10GBASE-LRM provides sufficient reach for inter-building and floor-to-floor links while maintaining compatibility with installed multimode cabling commonly found in campus environments.
Data Center Interconnects with Older Cabling
In data centers that were originally built for earlier Ethernet generations, multimode fiber layouts may not support SR at 10G speeds over required distances. 10GBASE-LRM is frequently used to connect switches or aggregation layers within the same facility when upgrading older racks or zones that still rely on legacy multimode fiber.
Scenarios Where Replacing Fiber Is Not Practical
Replacing fiber is not always feasible due to:
-
Physical constraints in conduits or ceilings
-
Downtime restrictions in production environments
-
Budget limitations for large-scale infrastructure changes
In these scenarios, 10GBASE-LRM offers a low-risk, cost-efficient upgrade path that extends the useful life of existing multimode fiber while meeting 10G performance requirements.
Overall, 10GBASE-LRM is most valuable when the goal is maximizing return on existing fiber investments rather than deploying new, future-proof cabling.
🚀 Fiber Compatibility and Cabling Considerations
Proper fiber selection and cabling practices are critical to achieving reliable performance with 10GBASE-LRM. While LRM is designed to tolerate legacy multimode fiber, incorrect cabling or poor link conditions can still limit reach and stability.
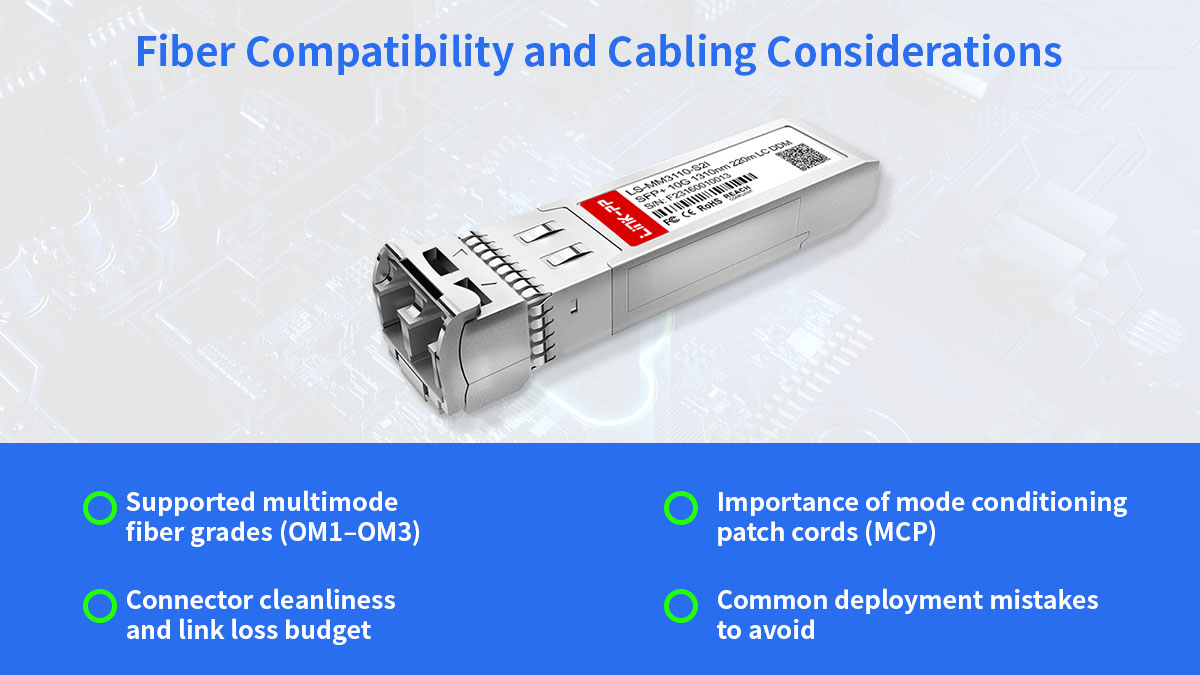
Supported Multimode Fiber Grades (OM1–OM3)
10GBASE-LRM is specified to operate on multimode fiber types OM1, OM2, and OM3. Its primary advantage is support for older OM1 and OM2 fiber, which are commonly found in legacy installations. Although OM3 can also be used, LRM is generally chosen when OM3 or OM4 is unavailable or when distance limitations prevent the use of SR optics.
Importance of Mode Conditioning Patch Cords (MCP)
In some deployments, especially on OM1 and OM2 fiber, a mode conditioning patch cord (MCP) may be required. MCPs help align the launch condition of the 1310nm signal to reduce differential mode delay and improve signal stability. While not always mandatory, MCPs are often recommended when link performance is marginal or when operating near the maximum supported distance.
Connector Cleanliness and Link Loss Budget
Legacy fiber networks often suffer from connector contamination and higher insertion loss. For 10GBASE-LRM links:
-
Ensure all connectors are properly cleaned before installation
-
Verify that total link loss stays within the allowed loss budget
-
Minimize unnecessary patch panels and splices where possible
Even small losses can significantly impact 10G performance on older fiber.
Common Deployment Mistakes to Avoid
To ensure a successful 10GBASE-LRM deployment, avoid the following mistakes:
-
Assuming LRM behaves like SR and ignoring fiber quality
-
Skipping mode conditioning when required on OM1 or OM2
-
Mixing incompatible fiber types within the same link
-
Overlooking connector cleanliness and inspection
By addressing these cabling considerations, 10GBASE-LRM can deliver consistent and reliable 10G connectivity over multimode fiber infrastructure that would otherwise be unsuitable for higher-speed upgrades.
🚀 Advantages and Limitations of 10GBASE-LRM SFP Module
10GBASE-LRM sfp module is a purpose-built solution with clear strengths and well-defined boundaries. Understanding both its advantages and limitations helps ensure it is used in the right scenarios and not misapplied where other optics are more suitable.

Advantages of 10GBASE-LRM
-
Extends the life of existing multimode fiber
10GBASE-LRM allows organizations to continue using legacy OM1 and OM2 multimode fiber while upgrading to 10G Ethernet. This significantly delays the need for large-scale cabling replacements.
-
Longer reach than SR on legacy fiber
Compared to 10GBASE-SR, LRM provides a much longer and more reliable reach on older multimode fiber, supporting links of up to 220m where SR may fall short.
-
Avoids costly fiber replacement
By leveraging existing infrastructure, LRM reduces both material costs and operational disruption. In many cases, the savings from avoiding re-cabling outweigh the higher price of the transceiver itself.
Limitations of 10GBASE-LRM
-
Shorter reach compared to single-mode LR
With a maximum distance of 220m, 10GBASE-LRM cannot replace single-mode 10GBASE-LR for long-distance links, which can extend up to 10km.
-
Higher cost than SR in some cases
LRM modules are often more expensive than SR optics. In environments with modern OM3 or OM4 fiber, SR is usually the more cost-effective option.
-
Not ideal for new greenfield deployments
In new network builds, it is generally better to deploy fiber and optics optimized for future scalability, such as single-mode or high-grade multimode. LRM is best viewed as a transitional technology rather than a long-term standard for new installations.
When used in the right context, 10GBASE-LRM offers significant value, but its benefits diminish when applied outside its intended use cases.
🚀 Compatibility with Network Switches and Vendors
10GBASE-LRM SFP modules are generally interoperable across platforms, but real-world compatibility depends on both standards compliance and vendor-specific requirements. Understanding these factors helps avoid deployment issues and unexpected link failures.

MSA Compliance and Interoperability
Most 10GBASE-LRM SFP modules follow MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) specifications, which define mechanical, electrical, and optical characteristics. MSA-compliant modules are designed to work across a wide range of switches and routers, allowing LRM optics from different vendors to interoperate when basic standards are met.
Vendor-Specific Compatibility Considerations
Despite MSA compliance, some network equipment vendors implement proprietary compatibility checks. These checks may restrict or limit the use of third-party optics, even when the module itself is technically compatible. As a result, it is important to verify that the selected 10GBASE-LRM module is explicitly supported—or at least tested—with the target switch platform.
Importance of Firmware and EEPROM Coding
Each optical module contains an EEPROM that stores identification and capability information. Network switches read this data during initialization to determine whether the module is acceptable. Proper EEPROM coding that matches vendor expectations is essential for:
-
Successful module recognition
-
Stable link initialization
-
Avoiding warning messages or port shutdowns
In some cases, firmware updates on switches can also affect optical compatibility, making validation even more important.
Third-Party vs OEM Optics (High-Level Overview)
OEM optics are designed and branded by the switch manufacturer, offering guaranteed compatibility but often at a premium cost. Third-party 10GBASE-LRM modules, when correctly coded and tested, can deliver equivalent performance at a lower price point. The key is choosing reputable suppliers that provide compatibility assurance and testing rather than relying on generic, unverified modules.
Overall, careful attention to compatibility ensures that 10GBASE-LRM optics function reliably across diverse network environments, regardless of the vendor ecosystem.
🚀 When Should You Choose a 10GBASE-LRM SFP Module?
You should choose a 10GBASE-LRM SFP module when your network relies on legacy multimode fiber and needs a reliable 10G upgrade without re-cabling. The decision is primarily driven by fiber type, link distance, and the feasibility of infrastructure changes.

Decision Checklist Based on Fiber Type and Distance
10GBASE-LRM is a suitable choice if most of the following conditions apply:
-
Existing links use OM1 or OM2 multimode fiber
-
Required link distance is greater than what 10GBASE-SR can reliably support
-
The target distance is within 220m
-
Replacing fiber or switching to single-mode is not practical
-
Network equipment supports or can accept LRM optics
If these conditions are met, LRM is often the most straightforward path to 10G.
Comparison with Modern Alternatives
While 10GBASE-LRM solves specific problems, it is not always the optimal solution:
-
On OM3 or OM4 fiber, 10GBASE-SR is typically simpler and more cost-effective
-
For distances beyond 220m, 10GBASE-LR on single-mode fiber is the appropriate choice
-
In new deployments, higher-grade multimode or single-mode fiber offers better long-term scalability
LRM should be viewed as a targeted solution rather than a universal replacement for other 10G optics.
Ideal Scenarios vs Cases to Avoid
Ideal scenarios:
-
Upgrading legacy buildings with fixed multimode cabling
-
Enterprise or campus networks with moderate link distances
-
Environments where downtime and construction must be minimized
Cases to avoid:
-
New greenfield installations
-
Networks already equipped with OM3 or OM4 fiber
-
Long-distance links that exceed 220m
By applying these criteria, network planners can quickly determine whether 10GBASE-LRM is the right fit or whether a more modern alternative would deliver better value.
🚀 Frequently Asked Questions About 10GBASE-LRM

1. Is 10GBASE-LRM still relevant today?
Yes. 10GBASE-LRM remains relevant in networks that rely on legacy multimode fiber, especially OM1 and OM2. While newer fiber types favor SR or LR optics, LRM continues to be a practical upgrade option when replacing existing cabling is not feasible.
2. Can 10GBASE-LRM run on OM3 or OM4 fiber?
Yes, 10GBASE-LRM can operate on OM3 multimode fiber, and in many cases also works on OM4. However, it is usually not the optimal choice in these environments, as 10GBASE-SR is typically more cost-effective and simpler to deploy on modern multimode fiber.
3. Do both ends of the link need to use 10GBASE-LRM modules?
Yes. Both ends of the link must use compatible 10GBASE-LRM optics. Mixing LRM with SR or LR modules will not establish a proper 10G link due to differences in wavelength and signaling.
4. Is a mode conditioning patch cord always required?
No. A mode conditioning patch cord (MCP) is not always required, but it may be recommended on OM1 or OM2 fiber, particularly when operating near the maximum distance or when link stability issues are observed. Its necessity depends on fiber quality and link conditions.
5. What is the maximum supported distance of 10GBASE-LRM?
The maximum supported distance for 10GBASE-LRM is up to 220m on multimode fiber, as defined by the IEEE 802.3aq standard. Actual performance may vary depending on fiber condition, connector quality, and overall link loss.
6. Is 10GBASE-LRM more expensive than other 10G SFP+ modules?
The module itself is often more expensive than 10GBASE-SR, but typically less costly than deploying single-mode solutions when fiber replacement is required. In many cases, the total project cost with LRM is lower due to reduced infrastructure changes.
🚀 Summary: Is a 10GBASE-LRM SFP Module Right for Your Network?
A 10GBASE-LRM SFP module is the most practical 10G solution for extending Ethernet over legacy multimode fiber without replacing existing cabling, making it ideal for cost-sensitive upgrades in established network environments.
Key Takeaways
-
1310nm wavelength + EDC enables stable 10G transmission over OM1, OM2, and OM3 multimode fiber
-
Up to 220m reach fills the distance gap where 10GBASE-SR is unreliable on legacy fiber
-
IEEE 802.3aq compliant for standardized performance and interoperability
-
Lower total upgrade cost by avoiding disruptive fiber replacement projects
-
Purpose-built, not universal—best used in clearly defined scenarios
When to Choose / When Not
Choose 10GBASE-LRM if:
-
Your network uses legacy multimode fiber (OM1 or OM2)
-
Link distances exceed SR limits but stay within 220m
-
Re-cabling to single-mode fiber is impractical or cost-prohibitive
Avoid 10GBASE-LRM if:
-
You are deploying a new greenfield network
-
Your infrastructure already uses OM3 or OM4 fiber
-
You require distances beyond 220m, where 10GBASE-LR is more appropriate
Final Recommendation
For enterprises, campuses, and data centers upgrading older multimode fiber links, 10GBASE-LRM SFP modules offer a balanced combination of reach, compatibility, and cost efficiency. If you are evaluating reliable, vendor-compatible LRM optics for real-world deployments, the LINK-PP Official Store provides tested solutions designed to integrate smoothly into existing network environments without unnecessary complexity.