As network bandwidth demands continue to grow, many enterprises, data centers, and telecom operators are turning to DWDM SFP transceivers to maximize fiber capacity while keeping infrastructure costs under control. By transmitting multiple wavelengths over a single fiber, DWDM SFP modules enable long-distance, high-density connectivity without the need to deploy additional fiber links.
However, buying the right DWDM SFP is not just about choosing a wavelength. Factors such as data rate, transmission distance, ITU channel spacing, device compatibility, and cost all play a critical role in ensuring stable network performance and long-term scalability. Selecting the wrong module can lead to compatibility issues, signal degradation, or unnecessary expenses.
This buying guide is designed to help you compare, evaluate, and confidently purchase SFP DWDM transceivers. Whether you are upgrading a metro network, building a data center interconnect, or optimizing an existing fiber infrastructure, this article will walk you through the key specifications, pricing considerations, and compatibility checks you need to know before making a purchase decision.
💡 What Is a SFP DWDM Transceiver?
A DWDM SFP transceiver is a small form-factor pluggable optical module designed to transmit and receive data over a single-mode fiber using Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) technology. It operates on a specific ITU-T C-band wavelength, allowing multiple data channels to coexist on the same fiber without interference. DWDM SFP modules are commonly available for 1G SFP and 10G SFP+ data rates, making them a flexible and cost-effective solution for high-capacity optical networks.
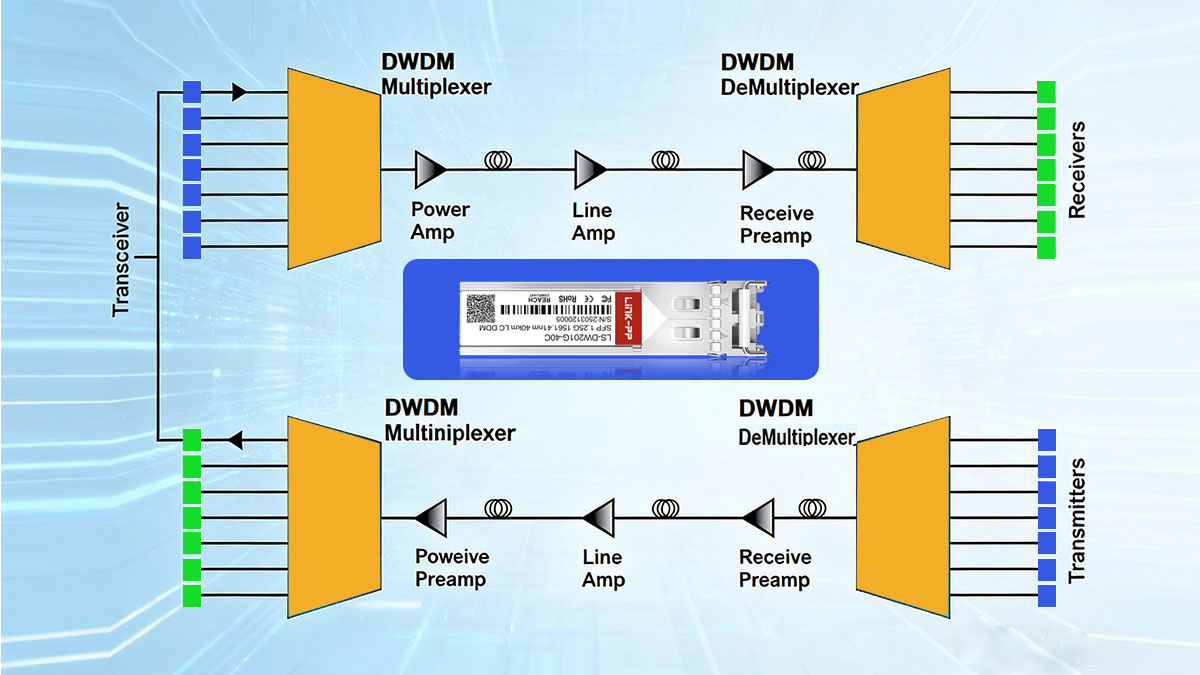
How DWDM SFP Works in DWDM Systems
In a DWDM system, each DWDM SFP transceiver transmits data on a precisely spaced wavelength (typically 100GHz or 50GHz channel spacing). These wavelengths are multiplexed together using a DWDM MUX, sent over a single fiber, and then demultiplexed at the receiving end. Because each wavelength carries an independent data stream, DWDM SFP enables massive bandwidth expansion without deploying additional fiber, while maintaining high signal integrity over long distances.
DWDM SFP vs CWDM SFP vs Standard SFP
Compared with other SFP modules, DWDM SFP offers significantly higher capacity and longer reach:
-
DWDM SFP uses tightly spaced wavelengths, supports long-haul transmission (40–100km or more), and is ideal for high-density networks.
-
CWDM SFP uses wider wavelength spacing (20nm), typically supports shorter distances, and is more suitable for cost-sensitive, lower-density deployments.
-
Standard SFP uses a single wavelength per fiber and does not support wavelength multiplexing, limiting scalability.
For networks where fiber resources are limited or future expansion is required, DWDM SFP is the most scalable option.
Typical Applications of DWDM SFP
DWDM SFP transceivers are widely deployed in scenarios that demand high capacity and long-distance transmission, including:
-
Long-haul and metro networks for telecom and service providers
-
Data Center Interconnect (DCI) to link geographically separated data centers
-
Enterprise backbone networks requiring reliable, scalable fiber links
These applications benefit from DWDM SFP’s ability to maximize fiber utilization while maintaining carrier-grade performance, making it a preferred choice for modern optical infrastructures.
💡 Why Choose DWDM SFP? Key Benefits for High-Capacity Networks
DWDM SFP transceivers are chosen when networks need maximum capacity, long reach, and efficient fiber utilization. By leveraging dense wavelength spacing, they allow operators to scale bandwidth without increasing physical infrastructure, making them ideal for carrier, data center, and enterprise backbone deployments.

Key Takeways
Why choose DWDM SFP?
-
High channel density on a single fiber
-
Long-distance transmission up to 100km+
-
Lower fiber and infrastructure costs
-
Easy scalability for future bandwidth needs
High Channel Density on a Single Fiber
One of the biggest advantages of DWDM SFP is its ability to support multiple independent channels on a single fiber pair. With channel spacing as tight as 100GHz or 50GHz, a single fiber can carry dozens of wavelengths simultaneously. Each wavelength operates as a separate data path, enabling dramatic bandwidth expansion without adding new fiber links—an essential benefit in fiber-constrained environments.
Extended Transmission Distances (40km / 80km / 100km+)
DWDM SFP modules are engineered for long-distance transmission. Standard models commonly support 40km, 80km, and even 100km or longer when used with optical amplification. This makes DWDM SFP ideal for metro and long-haul networks where signal integrity, low attenuation, and stable performance over distance are critical.
Lower Fiber Cost Compared to Single-Wavelength Solutions
By transmitting multiple wavelengths over the same fiber, DWDM SFP significantly reduces the cost per bit. Instead of deploying additional fiber for each new link, network operators can increase capacity by adding DWDM channels. This approach minimizes fiber leasing costs, construction expenses, and ongoing maintenance, delivering a strong return on investment.
Scalability for Future Bandwidth Growth
DWDM SFP provides a future-proof foundation for network expansion. New wavelengths can be added incrementally as bandwidth demand grows, without disrupting existing traffic. Whether upgrading from 1G to 10G or expanding channel count, DWDM SFP enables seamless scalability—making it a strategic choice for networks planning long-term growth.
💡 DWDM SFP vs CWDM SFP: Which One Should You Buy?
When choosing between DWDM SFP and CWDM SFP, the right decision depends on your network’s distance requirements, fiber availability, scalability goals, and budget. While both technologies use wavelength multiplexing to increase fiber capacity, they are designed for very different deployment scenarios.
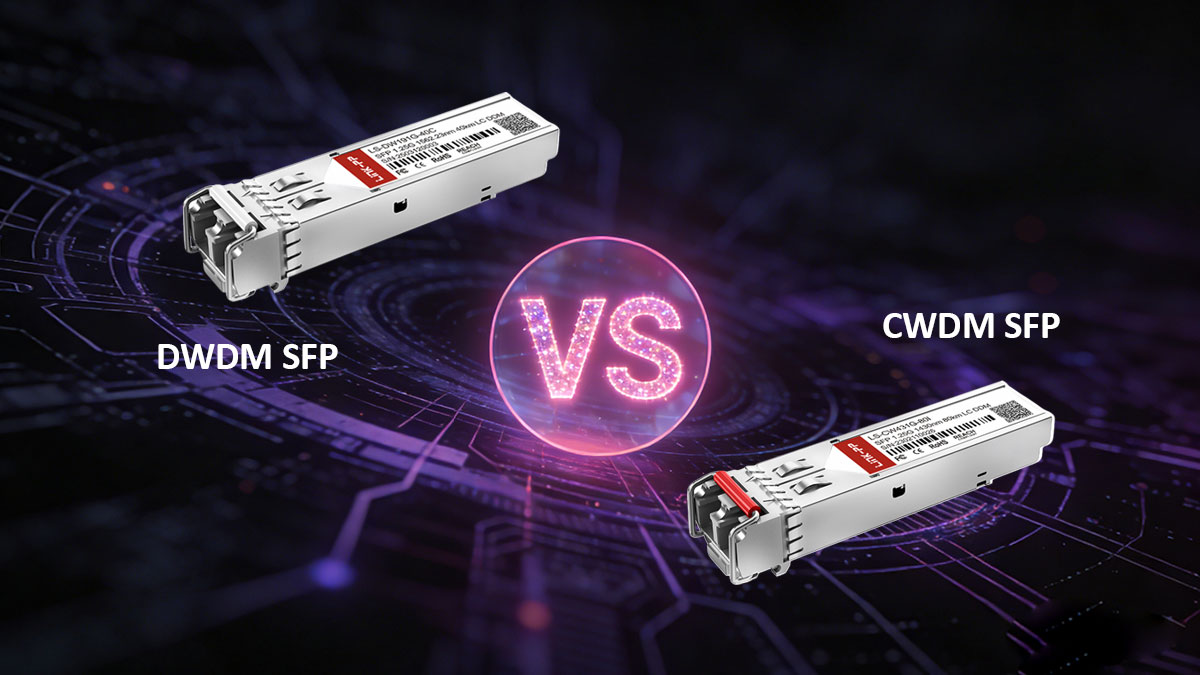
Wavelength Spacing: 0.8nm vs 20nm
The most fundamental difference lies in wavelength spacing:
-
DWDM SFP uses tightly spaced wavelengths—typically 0.8nm (100GHz) or even 0.4nm (50GHz)—within the C-band. This allows many channels to coexist on a single fiber.
-
CWDM SFP uses much wider spacing of 20nm, resulting in fewer available channels but simpler optics.
Tighter spacing enables higher channel density, which is why DWDM is preferred in high-capacity networks.
Transmission Distance and Power Budget
Distance capability is another key differentiator:
-
DWDM SFP supports longer transmission distances, commonly 40km, 80km, or 100km+, thanks to higher optical power and better receiver sensitivity.
-
CWDM SFP is typically limited to 10–40km, as wider spacing and uncooled lasers reduce power efficiency.
-
Standard SFP modules usually operate over shorter distances and do not support wavelength multiplexing at all.
For metro and long-haul links, DWDM SFP offers a clear advantage in both reach and signal stability.
Cost Differences and Use-Case Recommendations
From a cost perspective:
-
CWDM SFP modules generally have a lower upfront cost, making them attractive for small-scale or budget-sensitive deployments.
-
DWDM SFP modules cost more per unit, but they deliver a lower cost per transmitted bit in high-capacity networks.
-
Standard SFP appears inexpensive initially but becomes costly when additional fiber is required to scale bandwidth.
Use-case guidance:
-
Choose DWDM SFP when fiber is scarce, distances are long, or future expansion is planned.
-
Choose CWDM SFP for shorter links with moderate capacity requirements.
-
Choose Standard SFP only for simple, point-to-point connections.
Decision Table: DWDM vs CWDM vs Standard SFP
| Feature |
DWDM SFP |
CWDM SFP |
Standard SFP |
| Wavelength Spacing |
0.8nm / 0.4nm |
20nm |
Single wavelength |
| Channel Density |
Very high |
Medium |
Single channel |
| Typical Distance |
40–100km+ |
10–40km |
Short to medium |
| Scalability |
Excellent |
Limited |
Very limited |
| Fiber Utilization |
Maximum |
Moderate |
Low |
| Cost per Module |
Higher |
Lower |
Lowest |
| Best Use Case |
Long-haul, metro, DCI |
Enterprise, campus |
Simple point-to-point |
According to the table, you will see the differences clearly among DWDM, CWDM and standard SFP
Summary
DWDM SFP vs CWDM SFP: which should you buy?
-
Choose DWDM SFP for long distances, high capacity, and future scalability.
-
Choose CWDM SFP for shorter links with lower bandwidth needs.
-
Standard SFP is best for simple, non-multiplexed connections.
💡 Key Specifications to Check Before Buying a DWDM SFP
Choosing the right DWDM SFP transceiver requires more than matching a wavelength. To ensure reliable performance, long-term scalability, and compatibility with your network equipment, you should carefully evaluate the following key specifications before making a purchase.
Data Rate Compatibility
DWDM SFP modules are available in different data rates, and selecting the correct one is critical for seamless integration.
1G DWDM SFP
-
Designed for Gigabit Ethernet (1GbE) and legacy DWDM deployments
-
Lower power consumption and cost-effective for existing 1G optical links
-
Commonly used in metro access and enterprise backbone networks
10G DWDM SFP+
-
Supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GbE) applications
-
Higher bandwidth per wavelength, ideal for modern data centers and DCI
-
Often preferred when upgrading network capacity without adding fiber
Backward Compatibility Considerations
-
10G SFP+ ports generally do not support 1G SFP modules, unless explicitly stated by the device vendor
-
Always verify switch or router port specifications before buying
-
Mismatched data rates can result in link failure or unstable performance
Buyer tip: Match the DWDM SFP data rate exactly to your device port and network speed to avoid compatibility issues.
Wavelength (ITU-T Channel Selection)
DWDM SFP transceivers operate on standardized ITU-T C-band channels, which ensures interoperability across DWDM systems.
C-Band Channel Grid Overview
-
Typical wavelength range: 1530.33nm to 1565.50nm
-
Channel spacing: 100GHz (≈0.8nm) or 50GHz (≈0.4nm)
-
Each channel corresponds to a fixed ITU channel number
Fixed Wavelength vs Tunable DWDM SFP
| Feature |
Fixed DWDM SFP |
Tunable DWDM SFP |
| Wavelength |
Single, pre-set channel |
Adjustable across C-band |
| Inventory |
One SKU per wavelength |
One SKU for all channels |
| Cost |
Lower per module |
Higher upfront |
| Flexibility |
Limited |
Very high |
| Best For |
Stable, fixed networks |
Dynamic or large-scale networks |
How to Select the Correct Channel
-
Ensure both ends of the link use matching or paired wavelengths, depending on network design
-
Confirm compatibility with existing DWDM MUX/DEMUX channel plan
-
Consider tunable DWDM SFP if channel requirements may change in the future
Transmission Distance
DWDM SFP modules are available in multiple distance options, determined by optical power and receiver sensitivity.
-
40km: Suitable for metro access and short inter-city links
-
80km: Common choice for metro core and regional networks
-
100km+: Designed for long-haul or DCI applications
When to Choose Amplified Solutions
-
For distances beyond standard reach
-
When fiber attenuation or connector loss is high
-
When deploying DWDM SFPs in long-haul backbone networks
In such cases, optical amplifiers (such as EDFA) can extend reach while maintaining signal quality.
Optical Power & Receiver Sensitivity
Understanding optical performance parameters is essential for stable DWDM operation.
Link Budget Planning
-
Link budget = Transmit power – Receiver sensitivity
-
Must account for fiber loss, connector loss, splice loss, and system margin
-
A properly calculated link budget prevents signal degradation and link failure
OSNR Considerations
-
Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (OSNR) is critical in DWDM environments
-
Dense channel spacing increases sensitivity to noise and interference
-
Higher OSNR ensures better signal integrity, especially over long distances
Best practice: Always verify that your DWDM SFP provides sufficient OSNR margin for your planned transmission distance and channel density.
💡 Fixed DWDM SFP vs Tunable DWDM SFP: Buying Guide
When purchasing DWDM optics, one of the most important decisions is whether to choose a fixed DWDM SFP or a tunable DWDM SFP. Both options deliver high-capacity wavelength-division multiplexing, but they differ significantly in flexibility, cost structure, and inventory strategy.

What Is a Fixed DWDM SFP?
A fixed DWDM SFP operates on a single, pre-defined ITU-T wavelength. Each module is manufactured and coded for one specific channel and cannot be adjusted after deployment.
Key characteristics:
Fixed DWDM SFPs are widely deployed in established metro and long-haul networks where wavelength assignments rarely change.
What Is a Tunable DWDM SFP?
A tunable DWDM SFP can be programmed to operate on multiple ITU-T C-band wavelengths. Using software or hardware commands, the wavelength can be adjusted to match different DWDM channels.
Key characteristics:
-
Covers a wide range of C-band channels in a single module
-
High flexibility for dynamic or growing networks
-
Simplifies provisioning and network expansion
Tunable DWDM SFPs are especially popular in data center interconnect (DCI) and environments where wavelength planning may change over time.
Pros and Cons of Fixed vs Tunable DWDM SFP
| Feature |
Fixed DWDM SFP |
Tunable DWDM SFP |
| Wavelength Flexibility |
None (single channel) |
High (multiple channels) |
| Initial Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
| Inventory Complexity |
High (many SKUs) |
Low (fewer SKUs) |
| Deployment Speed |
Slower |
Faster |
| Power Consumption |
Lower |
Slightly higher |
| Best Use Case |
Stable, long-term networks |
Dynamic, scalable networks |
Cost Comparison and Inventory Optimization Benefits
From a unit price perspective, fixed DWDM SFP modules are usually less expensive. However, cost should be evaluated across the entire network lifecycle.
-
Fixed DWDM SFP:
-
Lower upfront cost per module
-
Requires stocking multiple wavelengths
-
Higher inventory and logistics overhead
-
Tunable DWDM SFP:
For large-scale or fast-growing networks, tunable DWDM SFPs often deliver lower total cost of ownership (TCO) by simplifying inventory management and reducing downtime caused by unavailable wavelengths.
💡 Compatibility Matters: Will a DWDM SFP Work with Your Switch or Router?
Even if a DWDM SFP meets all optical specifications, compatibility with your switch or router is critical for successful deployment. Device vendors often enforce specific requirements at the firmware and hardware level, making compatibility checks an essential step before purchasing DWDM optics—especially when using third-party transceivers.

MSA Compliance Overview
Most DWDM SFP transceivers are designed to follow MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) standards, which define the physical form factor, electrical interface, and optical parameters of SFP and SFP+ modules.
What MSA compliance ensures:
-
Standardized mechanical dimensions and port fit
-
Consistent electrical signaling and power requirements
-
Interoperability at the hardware level
However, MSA compliance alone does not guarantee full compatibility. Many network vendors implement additional software-level checks that go beyond the MSA specification.
Compatibility with Major Network Vendors
Major switch and router vendors often use proprietary firmware to validate installed optics:
-
Cisco: Enforces strict transceiver identification and may display warnings or disable ports if optics are not recognized
-
Juniper: Generally more open but still performs EEPROM validation
-
Arista: Supports third-party optics but requires proper coding
-
Huawei: Often requires vendor-specific EEPROM profiles
Without correct coding, even a technically compliant DWDM SFP may fail to function or operate with limited features.
Importance of EEPROM Coding
Each DWDM SFP contains an EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) that stores key identification data, including:
Network devices read this information to determine whether the module is supported. Proper EEPROM coding ensures the DWDM SFP is recognized as compatible, preventing port shutdowns, alarms, or performance restrictions.
How to Avoid Compatibility Issues When Buying Third-Party DWDM SFP
Third-party DWDM SFP modules can offer significant cost savings, but compatibility must be carefully managed. Follow these best practices:
-
Verify your switch or router model and firmware version before purchasing
-
Choose third-party suppliers that offer vendor-specific EEPROM coding
-
Ensure modules are tested in real devices, not just on optical test equipment
-
Confirm availability of warranty and technical support in case firmware updates affect compatibility
When sourced from a reputable supplier, third-party DWDM SFP transceivers can deliver OEM-level performance at a lower cost, without compromising network reliability.
Buyer Takeaway
Will a DWDM SFP work with your switch or router?
-
MSA compliance is necessary but not sufficient
-
Vendor-specific EEPROM coding is critical
-
Properly coded third-party DWDM SFPs can be fully compatible and cost-effective
💡 Common Use Cases for DWDM SFP Modules
DWDM SFP modules are best suited for networks that require high capacity, long reach, and efficient fiber utilization. They are widely used across telecom, data center, and enterprise environments where scalability and cost control are critical. Below are the most common deployment scenarios.
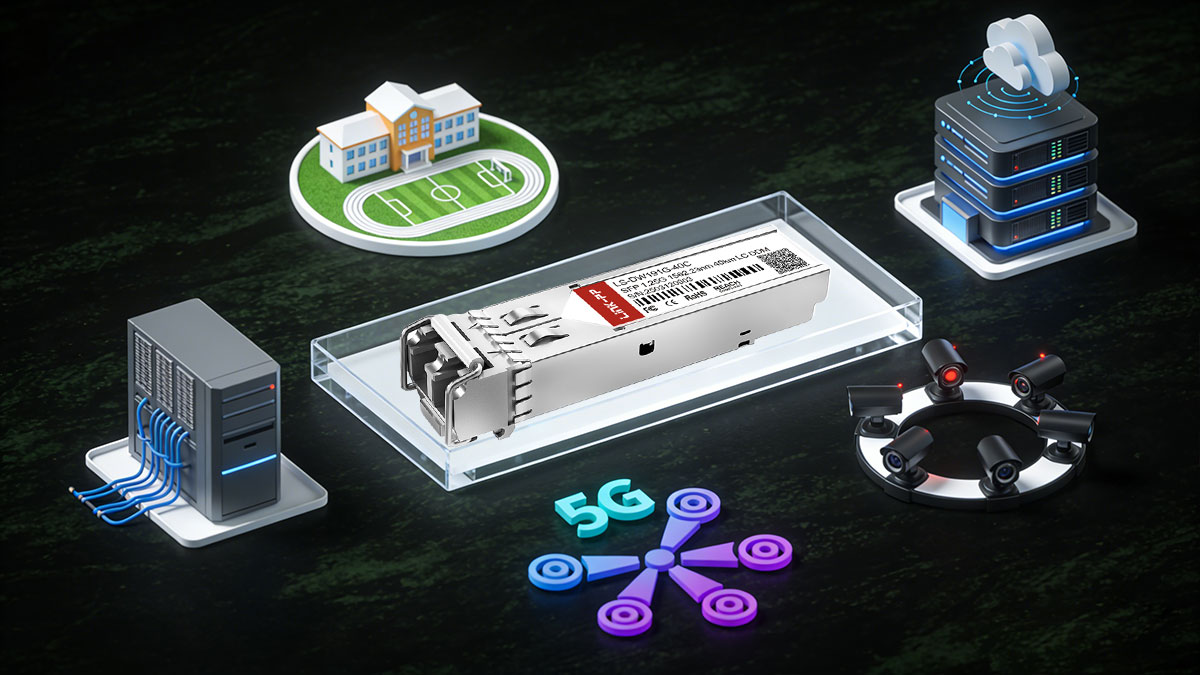

DWDM SFP is commonly used in telecom and metro networks to aggregate multiple services over a single fiber.
Service providers deploy DWDM SFP modules to support high traffic volumes across city-wide and regional optical networks.
Key reasons to use DWDM SFP in telecom networks:
-
High wavelength density on limited fiber infrastructure
-
Long-distance transmission for metro and regional coverage
-
Compatibility with DWDM MUX/DEMUX and optical amplifiers
This makes DWDM SFP a standard solution for carrier-grade optical transport.
Data Center Interconnect (DCI)
DWDM SFP is ideal for data center interconnect (DCI) deployments.
It enables high-bandwidth, low-latency connectivity between geographically separated data centers.
Benefits for DCI environments:
-
Scalable bandwidth by adding wavelengths instead of new fiber
-
Reduced fiber leasing and operational costs
-
Support for long-distance, high-capacity links
DWDM SFP modules allow data center operators to expand inter-site capacity efficiently and predictably.
Enterprise Long-Distance Fiber Links
Enterprises use DWDM SFP modules to extend network reach across campuses or remote buildings.
When standard SFP optics cannot meet distance or capacity requirements, DWDM SFP provides a reliable alternative.
Typical enterprise use cases include:
-
Campus-to-campus backbone connections
-
Building-to-building fiber links
-
Consolidation of multiple services on a single fiber pair
DWDM SFP helps enterprises future-proof their networks while controlling infrastructure costs.
Network Upgrades Without Laying New Fiber
DWDM SFP enables network upgrades without installing additional fiber.
This is especially valuable where fiber resources are limited or construction is impractical.
Why DWDM SFP is used for fiber-constrained upgrades:
-
Increases bandwidth on existing fiber infrastructure
-
Avoids construction, permitting, and downtime costs
-
Enables incremental expansion with minimal disruption
By deploying DWDM SFP modules, networks can achieve significant capacity growth without physical fiber expansion.
💡 How to Buy the Right DWDM SFP: Step-by-Step Checklist
Buying the right DWDM SFP transceiver requires a structured approach. Following this step-by-step checklist helps ensure compatibility, optimal performance, and long-term cost efficiency—while reducing the risk of deployment issues.

How to buy the right DWDM SFP
-
Confirm data rate and port type
-
Identify the correct wavelength/channel
-
Calculate distance and power budget
-
Check device compatibility
-
Choose fixed or tunable optics
-
Buy from a trusted supplier
Step 1: Confirm Data Rate and Port Type
Start by verifying the data rate and port type on your switch or router.
-
Identify whether the port supports 1G SFP or 10G SFP+
-
Check vendor documentation for supported optical modules
-
Confirm power class and form-factor requirements
Best practice: Always match the DWDM SFP data rate exactly to the device port to avoid link failures or performance limitations.
Step 2: Identify the Required Wavelength and Channel
Next, determine the ITU-T wavelength or channel number required for your DWDM system.
-
Review your existing DWDM channel plan
-
Ensure both ends of the link use matching or paired wavelengths
-
Decide whether fixed or tunable wavelengths are needed
Accurate wavelength selection is essential for proper integration with DWDM MUX/DEMUX equipment.
Step 3: Calculate Link Distance and Power Budget
Proper link budget calculation ensures stable transmission over the desired distance.
-
Measure total fiber length
-
Account for fiber attenuation, connector loss, and splice loss
-
Include a system margin for reliability
If the required distance exceeds standard DWDM SFP capabilities (40km / 80km / 100km), consider optical amplification solutions.
Step 4: Check Device Compatibility
Compatibility is critical when deploying DWDM SFP modules.
-
Verify compatibility with your specific switch or router model
-
Confirm support for third-party optics if applicable
-
Ensure proper EEPROM coding for vendor recognition
Choosing a DWDM SFP tested on real hardware reduces the risk of port errors or shutdowns.
Step 5: Decide Between Fixed or Tunable DWDM SFP
Select the DWDM SFP type that best fits your operational needs.
-
Fixed DWDM SFP: Lower cost, ideal for stable networks with fixed channels
-
Tunable DWDM SFP: Higher flexibility, reduced inventory, faster provisioning
Consider long-term scalability and inventory management when making this decision.
Step 6: Choose a Reliable Supplier
Finally, select a supplier that ensures quality and long-term support.
-
Look for full optical and compatibility testing
-
Confirm warranty and technical support availability
-
Evaluate lead times and supply consistency
A reliable supplier helps ensure your DWDM SFP modules deliver OEM-level performance with lower total cost of ownership.
💡 Why Buy DWDM SFP from a Trusted Third-Party Supplier?
For many network operators and enterprises, choosing third-party DWDM SFP transceivers is a strategic decision rather than a compromise. When sourced from a trusted supplier, third-party optics can deliver OEM-level performance at a significantly lower cost, while offering greater flexibility and faster availability.

Cost Savings vs OEM Optics
One of the primary reasons to choose third-party DWDM SFP modules is cost efficiency.
-
Third-party DWDM SFPs typically cost 30–70% less than original vendor optics
-
Lower unit cost reduces capital expenditure, especially in large-scale deployments
-
Savings can be redirected toward network expansion or redundancy
For networks deploying multiple wavelengths, third-party (like LINK-PP) DWDM SFPs offer a much lower cost per transmitted bit without sacrificing performance.
Quality Control and Testing Standards
Reputable third-party suppliers follow strict quality control and testing processes to ensure reliability.
-
Optical performance testing (power, sensitivity, wavelength accuracy)
-
Compatibility testing on real switches and routers
-
Environmental and stability testing for long-term operation
These measures help ensure third-party DWDM SFP modules meet or exceed industry standards and perform reliably in production networks.
Warranty and Technical Support
Trusted suppliers stand behind their products with strong warranty and support services.
-
Multi-year warranties comparable to OEM offerings
-
Access to technical support for deployment and troubleshooting
-
Rapid replacement options to minimize downtime
This level of support reduces operational risk and provides confidence when deploying third-party DWDM SFPs in mission-critical networks.
Lead Time and Availability Advantages
Third-party DWDM SFP suppliers often provide shorter lead times and better availability than OEM vendors.
-
Broad inventory across fixed and tunable wavelengths
-
Faster delivery for urgent network expansions or replacements
-
Reduced dependency on vendor-specific supply chains
This flexibility is especially valuable in fast-growing networks or time-sensitive deployments.
💡 FAQs About Buying DWDM SFP

Below are answers to the most common questions buyers ask when selecting DWDM SFP transceivers.
Can DWDM SFP Be Used in Standard SFP Ports?
Yes, DWDM SFP modules can be used in standard SFP or SFP+ ports, as long as the data rate and form factor match the port specifications.
-
1G DWDM SFP works in 1G SFP ports
-
10G DWDM SFP+ works in 10G SFP+ ports
-
The port must support single-mode fiber optics
Always verify vendor documentation, as some devices enforce firmware-based restrictions on supported optics.
Do Both Ends Need the Same Wavelength?
Yes, both ends of a DWDM link must use matching wavelengths, unless the network design specifically requires paired channels.
-
For point-to-point DWDM links, transmit and receive wavelengths must align
-
In MUX/DEMUX systems, channel assignments must match the configured ITU channels
-
Mismatched wavelengths will result in link failure
Accurate wavelength planning is essential for successful DWDM deployment.
Are Third-Party DWDM SFP Modules Reliable?
Yes, third-party DWDM SFP modules are reliable when sourced from a trusted supplier.
-
Reputable suppliers perform full optical and compatibility testing
-
Modules are coded to ensure device recognition
-
Performance and reliability are comparable to OEM optics
The key is selecting a supplier that provides documented testing, warranty coverage, and technical support.
When Should I Choose a Tunable DWDM SFP?
You should choose a tunable DWDM SFP when flexibility and scalability are required.
-
When wavelength assignments may change
-
When reducing inventory complexity is a priority
-
When deploying large-scale or dynamic DWDM networks
Tunable DWDM SFPs simplify provisioning and help lower long-term operational costs.
💡 Summary: Is DWDM SFP the Right Choice for Your Network?
DWDM SFP is the right choice if your network requires high capacity, long-distance transmission, and efficient fiber utilization. It enables multiple wavelengths on a single fiber, supports 40 km to 100 km+ links, and provides a scalable path for future bandwidth growth without laying new fiber.
For telecom, data center interconnect, and enterprise backbone networks, DWDM SFP offers a strong balance between performance, flexibility, and cost—especially when paired with properly planned wavelengths, verified compatibility, and reliable suppliers. Fixed DWDM SFP works well for stable deployments, while tunable DWDM SFP is ideal for dynamic, fast-growing environments.
👉 If you’re ready to purchase DWDM SFP transceivers, choosing a trusted third-party source can significantly reduce costs without sacrificing quality. Explore fully tested, vendor-compatible DWDM SFP modules at the LINK-PP Official Store to build a high-capacity optical network with confidence.