In today’s high-speed digital networks, flexibility and scalability are key to maintaining reliable data transmission. SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) modules play a vital role in achieving this. They allow network operators to adapt their systems easily — enabling seamless connectivity between switches, routers, and other networking devices. Whether for enterprise networks or data centers, the SFP module offers an efficient way to expand link capacity without replacing entire devices.
Among various optical module types, the fiber optic SFP module stands out for its ability to deliver reliable, high-speed data over long distances. It uses fiber optic cables to transmit data through light signals, offering lower latency and greater bandwidth compared to copper-based alternatives. Whether used in enterprise networks, data centers, or telecommunication systems, fiber optic SFP modules are crucial for building efficient and future-proof network environments.
In the following sections, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the fiber optic SFP module — from its working principles and key specifications to the different types available on the market. You’ll also learn how to choose the right SFP module based on transmission speed, fiber type, distance, compatibility, and so on. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how this small yet powerful SFP transceiver module keeps modern communication networks running smoothly.
❇️ What Is A Fiber Optic SFP Module
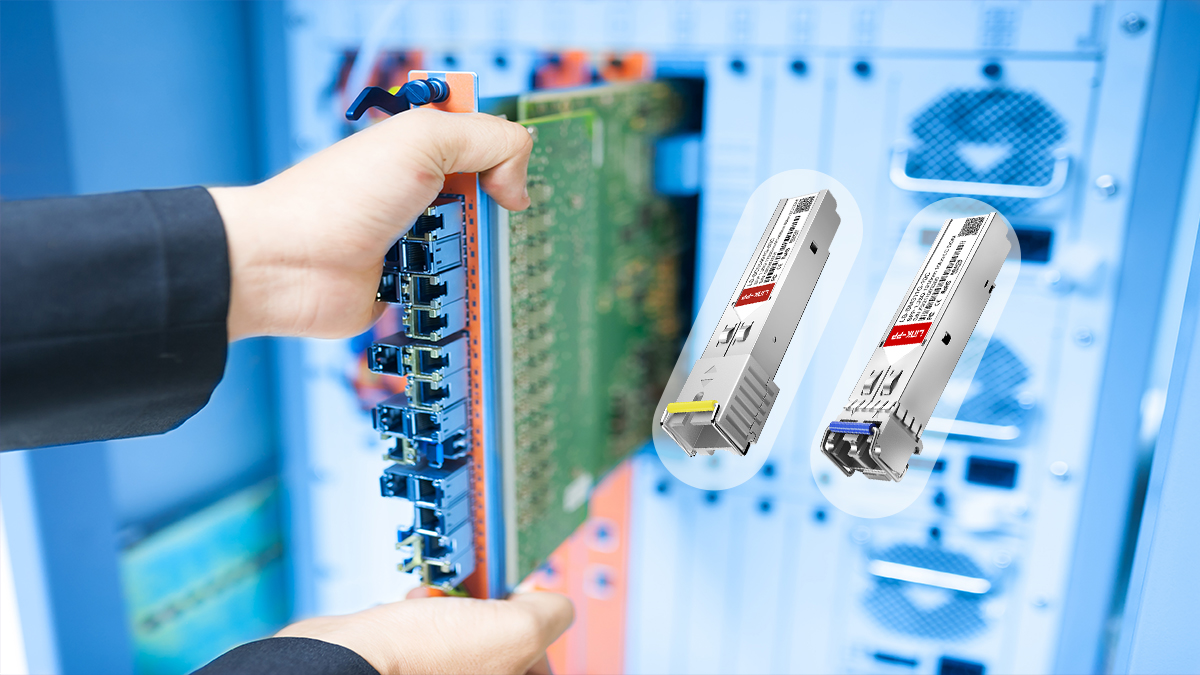

A fiber optic SFP module is a compact, hot pluggable optical module used to connect network devices such as switches, routers, and servers through optical fiber. It enables data transmission over long distances with high speed, stability, and minimal signal loss.
Meaning of SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable)
The SFP, or Small Form-factor Pluggable, is a standardized interface that allows quick plug-and-play installation. It replaces older GBIC modules with a smaller footprint, enabling higher port density and greater network flexibility.
SFP modules are widely adopted because they can be easily swapped to support different transmission types or distances without changing the main hardware, improving system scalability and cost efficiency.
Basic of A Fiber Optic SFP Module
A fiber optic SFP module converts electrical signals into optical signals for transmission through fiber optic cables, and vice versa. This design acts as a bridge between network hardware and fiber infrastructure, enabling efficient and stable communication. The ability of the fiber SFP module to perform efficient optical–electrical conversion relies on a number of functional components. The following table outlines these components and their corresponding functions.
| Component |
Function |
| TOSA (Optical Transmitter Assembly) |
Responsible for converting electrical signals into optical signals. It uses a laser or LED light source to emit data through the optical fiber. |
| Laser Driver |
Controls the operation of the laser diode inside the transmitter. It ensures stable optical output power and precise modulation for reliable signal transmission. |
| ROSA (Optical Receiver Assembly) |
Converts incoming optical signals back into electrical signals, allowing the network device to process the transmitted data. |
| Limiting Amplifier |
Amplifies weak electrical signals received from the optical input and restores them to standard logic levels suitable for processing. |
| PCB (Printed Circuit Board) |
Acts as the central platform that interconnects all internal components of the fiber SFP module. The PCB provides electrical pathways for signal transmission and power distribution. |
| Optical Interface |
Provides the physical connection point to the fiber optic cable, usually through standardized connectors such as LC, SC or RJ-45, enabling secure and low-loss signal coupling. |
❇️ How Does A Fiber Optic SFP Module Transmit Data
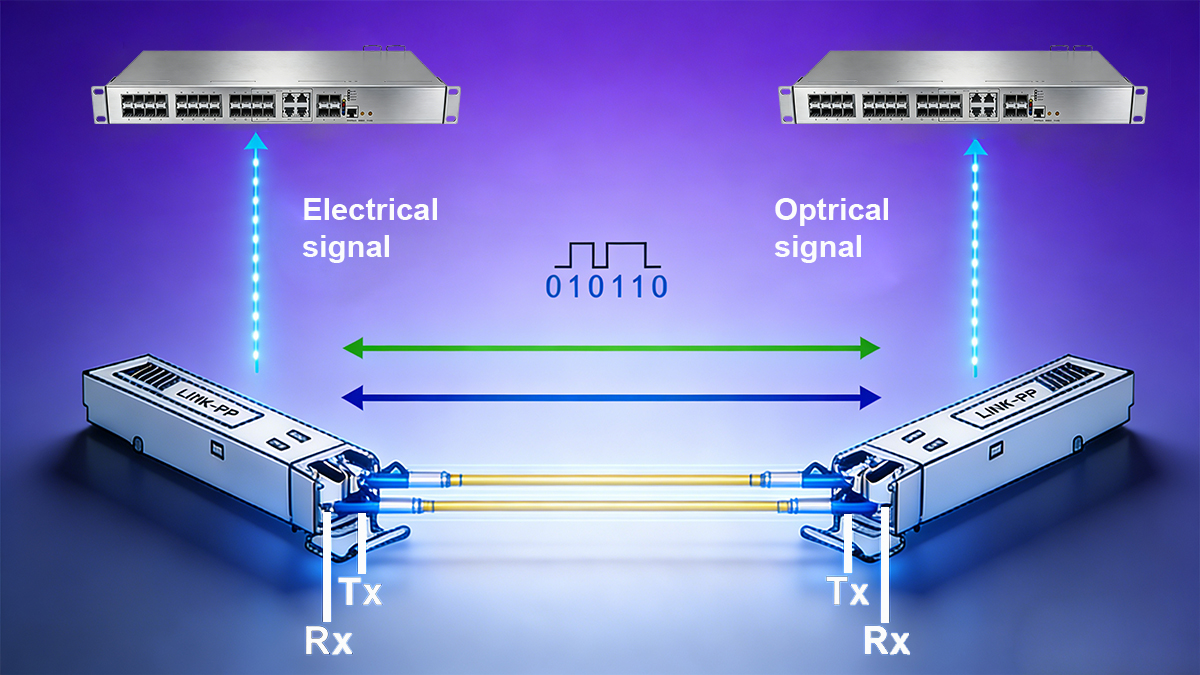
A fiber optic SFP module transmits data through two processes — electro-optical conversion at the transmitting end and opto-electrical conversion at the receiving end. This two-way conversion enables high-speed, low-loss communication across long optical fiber links.
Role of Transmitter Optical Subassembly in SFP Module
At the transmitting end, the SFP fiber optic module receives electrical signals from network devices such as switches or routers. These signals are processed by a laser driver, which controls a semiconductor light source like a DFB laser or FP laser.
The laser driver modulates the intensity or phase of the emitted light according to the digital input, representing “1” and “0” as optical pulses. This process converts the electrical signal into a stable optical signal that is transmitted through the optical fiber.
Role of Receiver Optical Subassembly in SFP Module
At the receiving end, the Receiver Optical Subassembly (ROSA) uses a photodetector, such as a PIN photodiode or an Avalanche Photodiode (APD), to detect incoming light signals from the fiber. The photodetector converts these optical pulses into weak electrical currents.
A Transimpedance Amplifier (TIA) then converts the current into a voltage signal and amplifies it, while a Limiting Amplifier (LA) further strengthens and shapes it to meet the required electrical levels. Through this conversion chain, the SFP module restores the original electrical data for the network device to interpret and process.
❇️ Important Parameters of Fiber Optic SFP Module
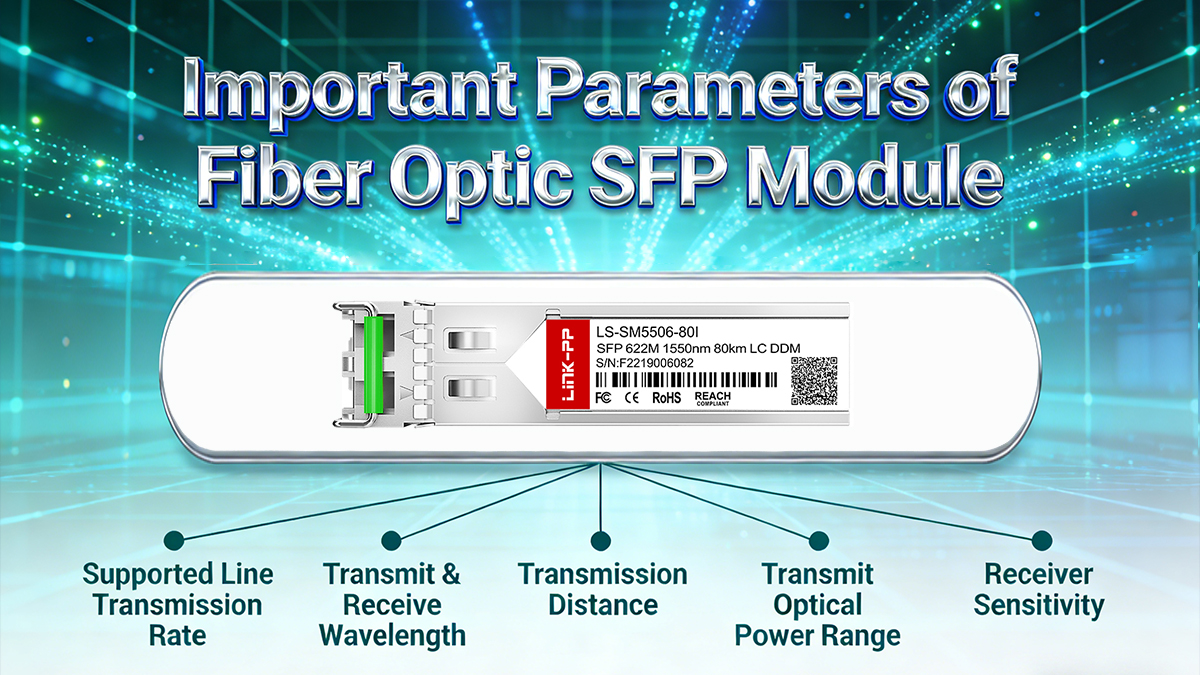
Understanding key performance parameters of a fiber optic SFP module is essential for ensuring compatibility and optimal network performance. The following technical metrics determine how effectively the network SFP module transmits and receives data across fiber links.
Supported Line Transmission Rate
The supported line transmission rate indicates the maximum speed at which data can be transmitted. Common fiber optic SFP modules support rates such as 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 2.5Gbps, or 4Gbps, depending on network requirements. Matching the module’s rate to your device ports ensures seamless and stable data communication.
Transmit & Receive Wavelength
The transmit and receive wavelength defines the light frequency used for data transmission. Typical wavelengths include 850nm or 1300nm for Multimode Fiber (MMF), and 1310nm or 1550nm for Single Mode Fiber (SMF). Selecting the correct wavelength pair is crucial for achieving proper optical coupling and preventing signal loss.
Transmission Distance
The transmission distance of a fiber optic SFP module is generally classified as short range or long range. Distances up to 2km are considered short, while those beyond 10km are regarded as long- range transmission.
In practical applications, transmission distance is limited by optical loss and dispersion during propagation through the fiber.
- Optical Loss refers to the gradual attenuation of optical signal strength, caused by factors such as material absorption, scattering, bending, or connector loss.
- Optical Dispersion describes the spreading of light pulses at different frequencies or modes, which can lead to pulse overlap, higher bit‑error rates, and signal distortion.
Transmit Optical Power Range
The transmit optical power range refers to the optical intensity emitted by the transmitter at the output end of the SFP module. It is a key factor influencing transmission distance. Higher optical power enables longer transmission reach, while excessive output may cause signal distortion or receiver overload.
Receiver Sensitivity
The receiver sensitivity represents the minimum optical power required for the receiver to accurately detect incoming data. A more sensitive receiver can capture weaker signals, enabling longer transmission distances and more stable communication, especially in high-loss or long-haul fiber systems.
❇️ Different Types of Fiber Optic SFP Module
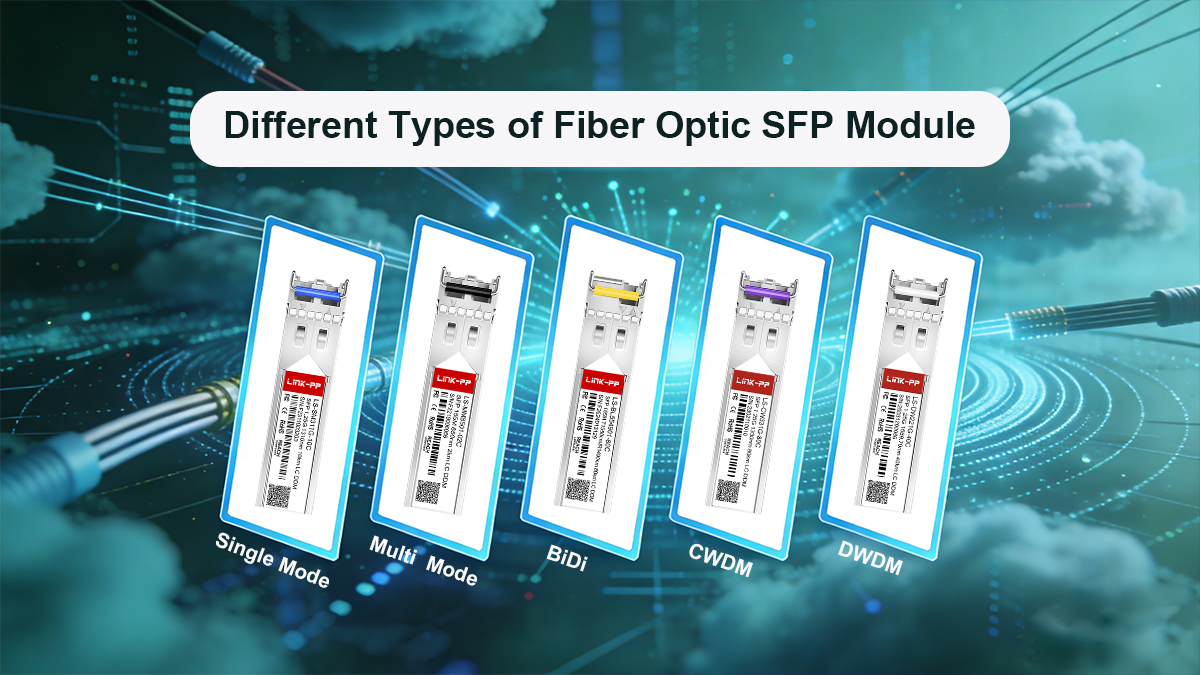
Fiber optic SFP modules come in various types to meet different transmission distances, network applications, and wavelength requirements. Each type is designed for specific optical fiber characteristics and operating environments, ensuring flexible deployment across diverse network infrastructures.
Single Mode Fiber Optic SFP Module
Single Mode SFP module is designed for long-distance transmission using single-mode fiber. Operating typically at 1310nm or 1550nm wavelengths, it supports distances from 10km to over 80km. It is ideal for MAN, WAN, and telecom networks requiring high-performance long-haul connectivity.
Multi Mode Fiber Optic SFP Module
Multimode SFP module is suitable for short-range communication using multimode fiber. It commonly operates at 850nm and supports distances up to 550m, depending on the data rate and fiber type (OM2, OM3, or OM4). It’s widely used in data centers and enterprise LAN environments.
BiDi Fiber Optic SFP Module
Bidirectional SFP module enables full-duplex transmission over a single fiber strand by using different wavelengths for transmitting and receiving (e.g., 1310nm TX / 1550nm RX). This design reduces fiber demand and cost while maintaining high data efficiency, making it ideal for fiber-limited networks.
CWDM Fiber Optic SFP Module
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) SFP module uses multiple wavelengths spaced widely apart, typically 20nm, to transmit multiple data channels over the same fiber. It supports up to 18 channels between 1271nm and 1611nm, allowing for scalable bandwidth in the network, and is widely deployed in metro area networks (MANs) and enterprise backbone networks.
DWDM Fiber Optic SFP Module
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) SFP module employs closely spaced wavelengths, typically 0.4nm, 0.8nm, or 1.6nm apart, allowing dozens of high-capacity channels to operate simultaneously over the same fiber. This technology supports long-distance transmission with exceptional bandwidth efficiency and is typically used in carrier-grade and telecom core networks.
❇️ What Is Fiber Optic SFP Module Used for
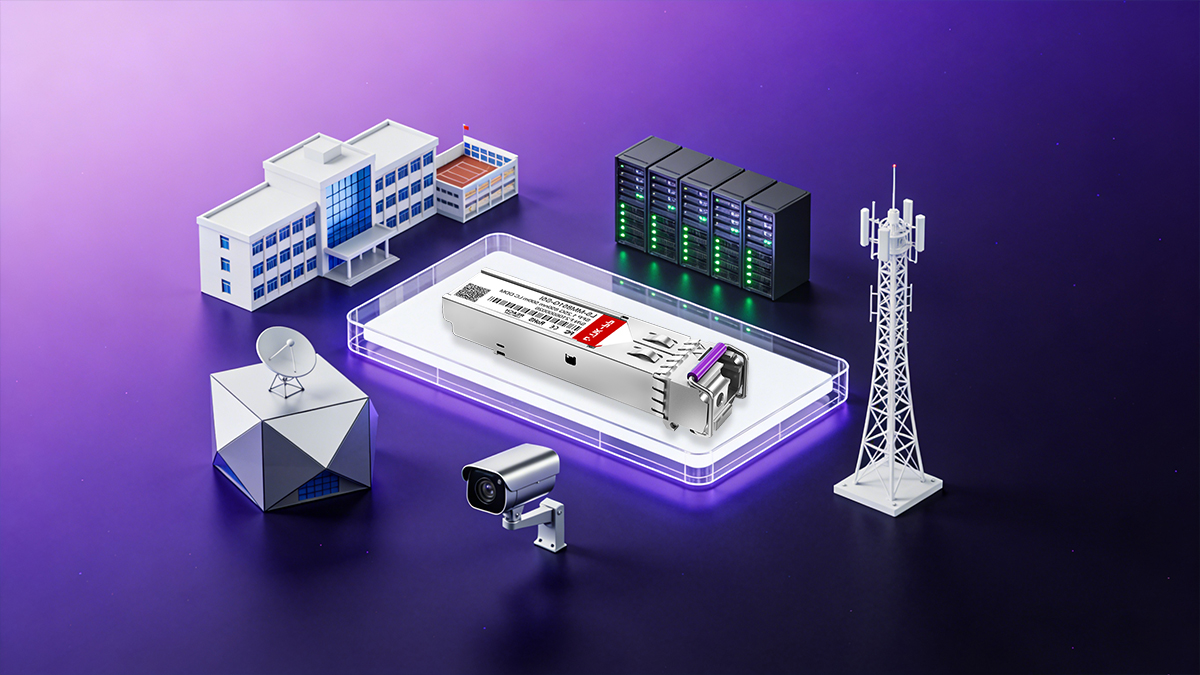
Fiber optic SFP module is a versatile component widely applied across different network environments, offering flexible connectivity, high bandwidth, and reliable data transmission. Its modular design allows easy upgrades and replacement, making it vital for scalable and cost-effective network infrastructure.
Data Centers
In data centers, the SFP optical module provides high-speed interconnections between servers, switches, and storage systems. It enables low-latency data transfer and efficient bandwidth utilization across top-of-rack and core network architectures. Its hot-pluggable design ensures quick maintenance and upgrades without disrupting critical operations.
Enterprise Networks
Within enterprise networks, fiber optic SFP modules deliver stable and high-performance links between buildings or departments. They support both short and long-distance connections, ensuring network flexibility as organizations grow. Their compatibility with existing network devices minimizes deployment costs while optimizing network scalability and reliability.
Telecom Access Networks
In telecom access networks, the fiber optic SFP module is used to connect subscriber access points with central offices. It offers long-distance data transmission with minimal signal loss, supporting voice, video, and internet services. Its wide range of power levels and wavelengths makes it ideal for high-density, high-availability carrier networks.
Industrial Ethernet
For industrial Ethernet applications, fiber SFP modules enable robust and interference-free communication in harsh environments. They are designed to withstand vibration, temperature extremes, and electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable performance in automation systems, transportation, and energy infrastructure. Their durability and stability make them a preferred choice for mission-critical field operations.
❇️ How to Choose The Right Fiber Optic SFP Module
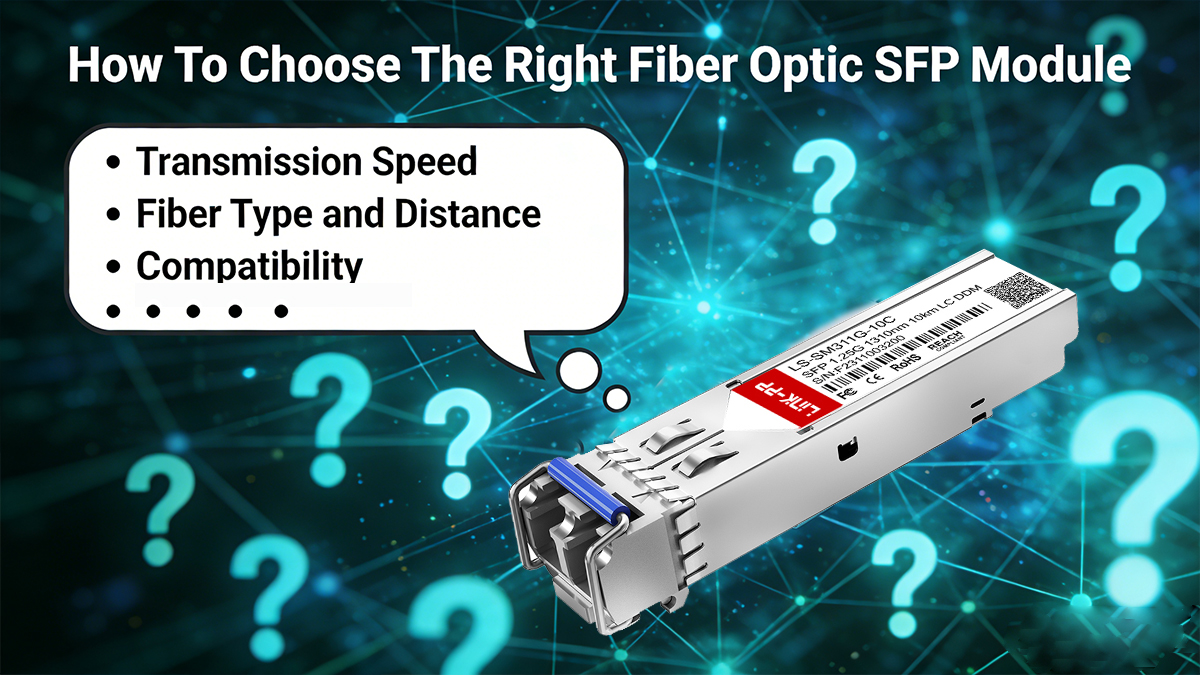
Selecting the right fiber optic SFP module is crucial for achieving reliable, high-performance, and cost-effective network connectivity. The ideal SFP module must match both the technical specifications and environmental requirements of your system to deliver efficient and stable communication.
Transmission Speed
The first step is to determine the required data rate. Fiber optic SFP module is available for various transmission speeds, such as 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 2.5Gbps, 10Gbps, or higher. Using mismatched speeds can lead to link failures or degraded performance, so always match the module’s speed to the switch or outer port capability to ensure seamless data transmission.
Fiber Type and Distance
Single mode fiber (SMF) is designed for long-distance communication. With its small core diameter, it carries light along a single transmission path, significantly reducing signal loss and dispersion. This characteristic makes SMF ideal for backbone or metro networks between remote locations.
For deployments that exceed several kilometers — sometimes up to 80km or more — Small Form Pluggable SFP modules such as SFP LX, SFP EX, or SFP ZX are recommended. Each type supports varying transmission distances and wavelengths, ensuring reliable performance and data integrity over long hauls.
Multimode fiber (MMF), by contrast, is optimized for short-range communication. Its larger core diameter allows multiple light signals to travel simultaneously through different paths. While this design supports higher bandwidth at short distances, it also introduces modal dispersion, which limits transmission range.
MMF is commonly used within data centers, campus networks, or enterprise environments where cable runs are shorter — typically under 550m, depending on the SFP wavelength. Cost-effective fiber optic SFP module like the SFP SX is well-suited for these situations, offering efficient performance at a lower price point.
Compatibility
Compatibility with network devices such as switches, routers, or media converters is critical. Some devices only support specific SFP module types or brands. Always verify compatibility through the manufacturer’s approved vendor list (AVL) or ensure the module adheres to MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) standards for cross-brand interoperability.
Environmental Specs
Environmental specifications define the conditions under which the fiber optic SFP module can operate reliably. Modules used in industrial or outdoor environments should support extended temperature ranges (e.g., –40 °C to +85 °C), strong vibration resistance, and robust housing to withstand harsh conditions and maintain stable performance.
Monitoring and Diagnostics
Some quality SFP fiber modules include DDM (Digital Diagnostics Monitoring) or DOM (Digital Optical Monitoring) functions. These features allow real-time tracking of parameters such as temperature, optical power, voltage, and laser bias current. Monitoring ensures timely maintenance, helps detect link degradation early, and improves overall network reliability.
❇️ Why Pick LINK-PP for Your Fiber Optic SFP Module Needs

LINK-PP is a leading global supplier of high-quality fiber optic SFP modules and network connectivity solutions. With years of manufacturing experience and strong R&D capability, LINK-PP provides reliable, cost-effective products trusted by enterprises, integrators, and telecom operators worldwide.
Broad Selection of SFP Module
LINK-PP offers a wide range of fiber optic SFP modules, including Single Mode SFP, Multimode SFP, BiDi SFP, and CWDM/DWDM SFP. Each module is engineered for wide vendor compatibility and reliable performance across diverse network devices. With extensive product coverage and flexible options, LINK-PP is your ideal partner for sourcing reliable fiber optic SFP modules.
Comprehensive Compatibility Testing
Each fiber optic SFP module undergoes strict compatibility testing across major network equipment brands such as Cisco, Arista, Juniper, Dell and Brocade. This ensures seamless integration and stable communication in real-world environments. LINK-PP’s multi-vendor validation minimizes deployment risks and guarantees plug-and-play operation without configuration issues.
Superior Material & Component
LINK-PP fiber optic SFP modules stand out through the use of imported optical components and high-performance chips that ensure exceptional transmission accuracy and speed. Each module features a ceramic ferrule for superior alignment and low insertion loss, while thickened gold fingers enhance conductivity and durability. These premium materials not only extend product lifespan but also deliver stable, high-quality data transmission even in demanding network environments.
Rigorous Quality Assurance
LINK-PP maintains a robust quality assurance process covering all production stages — from component selection to final inspection. Each product passes performance, durability, and environmental tests to meet international standards. This rigorous control ensures consistent optical power, low error rates, and long-term stability for critical applications.
Reliable After-sales Support
We are committed to providing responsive and reliable after-sales service. Customers benefit from professional technical support, quick replacement options, and continuous product updates. With global logistics and dedicated service teams, LINK-PP ensures smooth operation and long-term confidence in every network solution.
❇️ FAQs Related to The Fiber Optic SFP Module

Here are some of the most common questions users ask when deploying the fiber optic SFP module. These answers will help you better understand compatibility, performance, and safety considerations before integrating the SFP optical module into your network.
Can I use different brands of fiber optic SFP module in my network?
Yes, you can use different brands of small form pluggable SFP modules if they comply with MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) standards. However, some network equipment vendors may lock their devices to specific brands. Always check device compatibility or use SFP modules verified through multi-vendor testing to ensure stable operation.
What is the maximum transmission distance of a fiber optic SFP module?
The maximum transmission distance of a fiber optic SFP module depends on several factors, including the fiber type and operating wavelength. Generally, the SFP multimode module can reach distances up to 550m at 850nm, while the single mode fiber SFP module operating at longer wavelengths, such as 1310nm or 1550nm, can support 10km, 20km, 40km, or even 80km.
Longer wavelengths experience lower optical attenuation, allowing signals to travel farther with less loss. Therefore, choosing the right fiber optic SFP module type and wavelength is essential for achieving optimal transmission performance.
Do BiDi fiber optic SFP modules support compatibility with standard fiber optic SFP modules?
No, BiDi SFP modules are not compatible with standard duplex SFP modules. Unlike standard modules that use two separate fibers — one for transmitting and one for receiving — BiDi modules transmit and receive data over a single fiber. They achieve bidirectional communication by using two different wavelengths, such as 1310nm for transmission (TX) and 1550nm for reception (RX), or vice versa.
Therefore, BiDi SFP modules must always be deployed in complementary pairs — each designed to match the opposite TX/RX wavelengths — to function correctly and ensure reliable data exchange.
Is it safe to use third-party fiber optic SFP modules?
Yes, it’s safe to use high-quality third-party fiber optic SFP modules as long as they meet MSA standards and pass compatibility testing. Trusted suppliers like LINK-PP conduct rigorous optical and electrical tests to ensure reliability. Using certified third-party SFP often provides excellent performance at a more competitive cost.
❇️ Summary: Are You Ready to Buy Fiber Optic SFP Module?
Throughout this article, we’ve explored what a fiber optic SFP module is, how it transmits data, and the key factors to consider when selecting the right one for your network. From understanding important performance parameters like wavelength, transmission speed, and distance, to recognizing the differences among Single Mode SFP Module, Multimode SFP Module, BiDi SFP Module, and CWDM / DWDM SFP module, you now have a clearer view of a fiber optic SFP module.
When it comes to sourcing a reliable fiber optic SFP module, LINK-PP stands out for providing high-quality, cost-effective, and fully compatible SFP module solutions designed for diverse applications. LINK-PP SFP modules offer the following key advantages:
- Hot-swappable Design: SFP modules can be replaced or upgraded without shutting down devices, minimizing downtime and simplifying maintenance.
- Flexibility: Available in various transmission speeds (100Mbps, 1Gbps, 2.5Gbps, and 4Gbps), they adapt easily to different network requirements and application scenarios.
- Compact Size: Its small form factor allows more efficient use of rack space, making it ideal for high-density or space-constrained environments.
If you’re ready to upgrade your fiber infrastructure, check out LINK-PP Official Store for reliable and standards-compliant fiber optic SFP modules that deliver seamless integration and sustained network stability.